 One of the first lessons a good magician learns is that to best impress an audience, one has to at least show an actual rabbit going into the hat before making it disappear.
One of the first lessons a good magician learns is that to best impress an audience, one has to at least show an actual rabbit going into the hat before making it disappear.
AT&T is no David Copperfield. In its latest sleight of hand, AT&T today announced a major potential expansion of its U-verse GigaPower fiber to the home network to 21 major cities across its landline service area, with future plans to expand to as many as 100 eventually.
“We are excited to bring GigaPower to 100 cities and towns,” Lori Lee, head of AT&T’s U-verse unit, said in a phone interview with Bloomberg, which accompanied a press release. “We will work with local officials as we look for areas of strong demand and pro-investment policy.”
Among the cities slated to get fiber upgrades are Austin and Kansas City — where AT&T will face competition from Google Fiber. But AT&T isn’t bothering to compete head-on with any municipal fiber providers like Chattanooga’s EPB, Wilson, N.C.’s Greenlight, or Lafayette, La.’s LUSFiber. North Carolina, Texas and California are the states with the most cities chosen to potentially get upgrades.
But AT&T has yet to fully deliver on its earlier promise to deploy fiber to the home service in Austin, where single home residential customers have usually been stymied by general unavailability of the fiber service. AT&T has consistently refused to say exactly how many customers have actually been able to sign up for AT&T GigaPower fiber service.
For customers actually able to buy GigaPower, many are already served by an existing AT&T fiber cable. It is not uncommon to find fiber hookups in new housing developments or multi-dwelling units like apartment buildings and condominiums. Most customers don’t realize they are fed service from a fiber cable brought to the back of the building that interfaces with plain old copper wiring, providing service artificially slowed by the company in an effort to provide consistently marketed broadband products.
AT&T GigaPower is easy to provide in these locations with very little extra investment. Tearing up streets and yards to replace copper wiring with fiber optics is another matter, one AT&T has avoided for years by choosing a less costly fiber to the neighborhood approach that leaves existing copper wiring on phone poles and in customer homes largely intact. Moving to fiber to the home service would require AT&T to dramatically boost capital spending to cover the cost of stringing fiber across the backyards of millions of customers.
But earlier this year, AT&T promised investors it was actually planning to cut its budget for capital expenses in 2014 to $21 billion, most of that still earmarked for its profitable wireless network. That is down at least $200 million from 2013. Unless AT&T reneges on its earlier commitment to Wall Street, even David Copperfield couldn’t make fiber to the home service from AT&T magically appear.
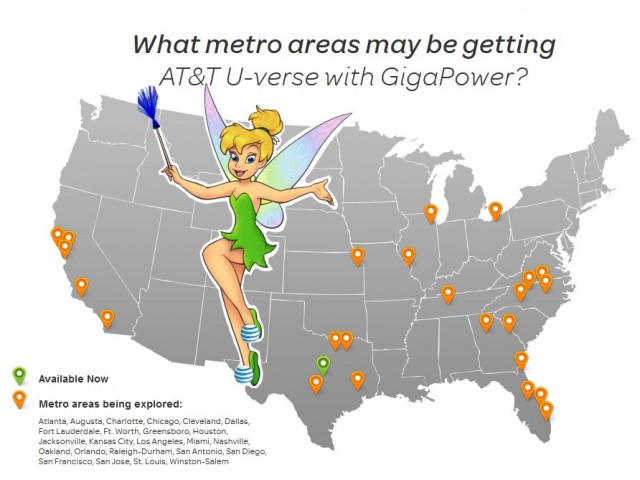
Welcome to Neverland. Despite exciting press releases, AT&T has indicated it won’t spend the money required for widespread fiber expansion. But then, AT&T’s own graphics only promise these communities “may” get GigaPower.
In fact, AT&T has been telling investors it is more than halfway done completing its Project VIP effort, which budgeted $14 billion over three years to further expand basic U-verse service, improve its 4G LTE network, and expand rural wireless coverage within AT&T local service areas. Project VIP is integral to AT&T’s plan to eventually walk away from its rural wired infrastructure in favor of a wireless platform providing wireless landline service and 4G wireless broadband.
To assuage investors fearing AT&T is about to pull out the credit card and go on a fiber broadband shopping spree, AT&T carefully notes towards the bottom of its press release, “this expanded fiber build is not expected to impact AT&T’s capital investment plans for 2014.”
In other words, AT&T is not committing any money not already earmarked as part of Project VIP for its fiber expansion.
Without that money, if you live in a single-family residential home and are currently served by AT&T copper wiring, it is very unlikely the company will offer fiber upgrades anytime soon.
So why is AT&T promising vaporware upgrades it cannot possibly manage on its current budget?
AT&T will work with local leaders in these markets to discuss ways to bring the service to their communities. Similar to previously announced metro area selections in Austin and Dallas and advanced discussions in Raleigh-Durham and Winston-Salem, communities that have suitable network facilities, and show the strongest investment cases based on anticipated demand and the most receptive policies will influence these future selections and coverage maps within selected areas. This initiative continues AT&T’s ongoing commitment to economic development in these communities, bringing jobs, advanced technologies and infrastructure.

Phillip “AT&T has a larger agenda here and it isn’t fiber” Dampier
For years, AT&T’s lobbyists have promised politicians everything under the sun — telecom nirvana — if only Ma Bell can be unshackled by burdensome regulations. Some states have accepted AT&T’s deal only to find their residents’ phone bills rapidly increasing with no corresponding improvement in service. U-verse is AT&T’s effort to stay relevant at a time when mobile phones are replacing landlines and cable companies have poached a number of their customers.
But in return for that deregulation, AT&T delivered an cheaper, inferior fiber-to-the-neighborhood technology that requires hideously large infrastructure cabinets, often installed in front of customer homes, that has trouble keeping up with cable broadband speeds.
But nothing ever satisfies AT&T.
Recently, their lobbyists have been skulking around in the shadows of state legislatures ghostwriting new bills that would permit AT&T to abandon its rural landline customers altogether to focus on the far more profitable wireless business. But consumer groups have gotten wise to AT&T’s astroturf and lobbying efforts and have begun to limit their successes.
Meanwhile, along comes Google, promising groundbreaking, affordable fiber to the home gigabit broadband service to a handful of communities willing to work with them in a de facto partnership — cutting through bureaucratic red tape to facilitate infrastructure upgrades — a radical change from the traditional regulator-provider framework.
Hundreds of cities fell all over themselves competing for the privilege, and it didn’t require a penny in lobbying or campaign contributions.
Where Google has been willing to offer service, most communities have been more than thankful and have made life easier for the creative entrant.
If it worked for Google, why can’t it work for AT&T? As a result, the company that spent years telling customers fiber upgrades didn’t make any sense and that few people actually needed gigabit speeds, AT&T might appear to have reversed course. Dig a little deeper and you find a deeper agenda:
“Communities that have suitable network facilities, and show the strongest investment cases based on anticipated demand and the most receptive policies will influence these future selections and coverage maps within selected areas.”
Translation: Communities that already have considerable fiber infrastructure previously installed and are willing to bend to the business and public policy agenda of AT&T will make all the difference whether your city will be considered for a future fiber upgrade or not.
In the end, even if a community does everything AT&T asks of it, it still has no commitment AT&T will actually deliver the fiber upgrades they only promise “may” happen. But AT&T will have achieved its public policy goals of abolishing regulations and limiting oversight, all without have to install a single strand of fiber.
That is a deal community leaders should think twice about making with a company that has always looked out for its investors long before its customers.


 Subscribe
Subscribe AT&T customers in Carbon Hill, Ala. received an unwelcome surprise in their mailbox recently when AT&T informed them they will be part of an experiment ending traditional landline service in favor of a Voice over IP or wireless alternative.
AT&T customers in Carbon Hill, Ala. received an unwelcome surprise in their mailbox recently when AT&T informed them they will be part of an experiment ending traditional landline service in favor of a Voice over IP or wireless alternative. AT&T is pushing forward despite the fact it has no idea how it will offer service to at least 4% of isolated Carbon Hill residents not scheduled to be provided U-verse and not within an AT&T wireless coverage area. There are also no guarantees customers will be able to correctly reach 911, although AT&T says the technology “supports 911 functionality.” Serious questions among consumer advocates remain about whether the replacement technology will support burglar alarms, pacemakers and even systems used by air-traffic controllers.
AT&T is pushing forward despite the fact it has no idea how it will offer service to at least 4% of isolated Carbon Hill residents not scheduled to be provided U-verse and not within an AT&T wireless coverage area. There are also no guarantees customers will be able to correctly reach 911, although AT&T says the technology “supports 911 functionality.” Serious questions among consumer advocates remain about whether the replacement technology will support burglar alarms, pacemakers and even systems used by air-traffic controllers. The Wall Street Journal reports:
The Wall Street Journal reports: If AT&T ends its traditional network, those competing service providers will have to negotiate with AT&T for access at whatever price AT&T elects to charge.
If AT&T ends its traditional network, those competing service providers will have to negotiate with AT&T for access at whatever price AT&T elects to charge.
 Cincinnati Bell
Cincinnati Bell 
 “Our business has been in decline for five or six years,” Torbeck
“Our business has been in decline for five or six years,” Torbeck  Last year, Cincinnati Bell had passed 184,000 homes with fiber optics – a 28 percent market share. But only 52,000 homes subscribed to Fioptics — Cincinnati Bell’s fiber brand. Time Warner Cable had managed to keep many of its wavering 446,000 customers loyal to the cable company with aggressive discounting and customer retention offers. But now that many of those discounts have since expired, Torbeck wants to reach 650,000-700,000 homes in its service area covering southwestern Ohio and northern Kentucky and convince 50% of those customers to switch to fiber optics.
Last year, Cincinnati Bell had passed 184,000 homes with fiber optics – a 28 percent market share. But only 52,000 homes subscribed to Fioptics — Cincinnati Bell’s fiber brand. Time Warner Cable had managed to keep many of its wavering 446,000 customers loyal to the cable company with aggressive discounting and customer retention offers. But now that many of those discounts have since expired, Torbeck wants to reach 650,000-700,000 homes in its service area covering southwestern Ohio and northern Kentucky and convince 50% of those customers to switch to fiber optics. The company’s unique position as the last remaining independent phone company that still bears the name of the telephone’s inventor may make the company a target for a takeover before Torbeck’s vision is realized. One analyst thinks Cincinnati Bell would be a natural target for Google, which has a recent record of repurposing fiber networks built by other companies as a cost-saving measure to further deploy Google Fiber.
The company’s unique position as the last remaining independent phone company that still bears the name of the telephone’s inventor may make the company a target for a takeover before Torbeck’s vision is realized. One analyst thinks Cincinnati Bell would be a natural target for Google, which has a recent record of repurposing fiber networks built by other companies as a cost-saving measure to further deploy Google Fiber. Cincinnati Bell has already spent about $300 million on Fioptics and plans to spend an extra $80 million this year on expansion. Before the network is complete, the phone company is likely to spend as much as $600 million on fiber upgrades. But the payoff has been higher revenue — $100 million last year alone, and a stabilizing business model that has reduced losses from landline cord-cutting. Telecom analyst Nicholas Puncer offers support for the investment, something rare for most Wall Street advisers.
Cincinnati Bell has already spent about $300 million on Fioptics and plans to spend an extra $80 million this year on expansion. Before the network is complete, the phone company is likely to spend as much as $600 million on fiber upgrades. But the payoff has been higher revenue — $100 million last year alone, and a stabilizing business model that has reduced losses from landline cord-cutting. Telecom analyst Nicholas Puncer offers support for the investment, something rare for most Wall Street advisers.

 “The first target now for a phone carrier is upgrading networks and transform it to a platform for high-value services,” Patuano said. “This is exactly what AT&T did and what we are calling for.”
“The first target now for a phone carrier is upgrading networks and transform it to a platform for high-value services,” Patuano said. “This is exactly what AT&T did and what we are calling for.”




