NBC Universal and American Express today announced Sacred Wind Communications (Albuquerque, N.M.) as the winner and most inspiring small business in the “Shine A Light” program, determined by public vote.
Sacred Wind Communications will receive $50,000 in grant money and $50,000 in marketing support from American Express, and will be featured on MSNBC’s small business show, “Your Business.”
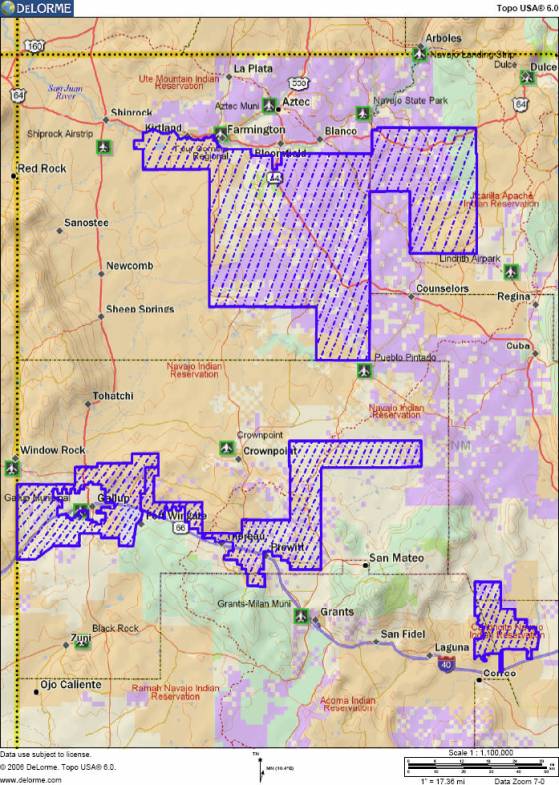
John Badal, described by the Shine A Light Foundation as an entrepreneur, founded Sacred Wind to provide service across the largely ignored Navajo Reservation in New Mexico. Fewer than 40% of the homes had access to even basic telephone service, provided by Qwest on what the foundation describes as a “dilapidated telephone system.”
Badal, along with a few others, thought Qwest’s turtle-like-speed to provide basic telephone service was not acceptable.
Badal should know — he was the former president of Qwest New Mexico from 2000-2004, overseeing that phone network.
During his involvement with Qwest, the frustration to wire the economically challenged Native American community in his area was daunting. He told Fierce Broadband Wireless that laying copper cable throughout a rugged, rural desert area to reach a small number of customers who couldn’t afford to pay much for service wasn’t economically feasible for Qwest.
In four years, Qwest only managed to bring phone service to 42 new customers–out of thousands. “It took us two years to get through the rights of way process. Six of those homes had moved by the time the process was completed. It would have taken 45 years to reach 70 percent of the homes in our territory,” Badal said. “We needed a different technology altogether. We needed to go wireless.”
Badal decided to build a for-profit telecommunications company with a business plan that would depend on funding from the government.
“The only way any company could hope to provide service to the Navajo Nation is with the help of the Federal Communications Commission’s Universal Services Fund,” Badal told New Mexico Business Weekly in 2005.
“We can make this affordable, where Qwest cannot,” says Badal, who expects half of the cost to be picked up by government funding. “That is a necessary part of this equation. Without that, the Navajo cannot be served.”
Virtually every American pays into the Universal Services Fund through a charge levied on telephone bills. The funding underwrites the expense of providing rural America with access to basic telecommunications services.
In 2004, the same year Badal left Qwest, the company agreed to sell its telephone business on the Navajo Reservation to Badal’s new company. Sacred Wind, which the company says “evokes a sense of connection between what we do – to send communications over the air – with a larger-than-life purpose for starting this business,” launched service two years later in 2006.
Sacred Wind uses recently developed wireless technology to provide phone service to 2,700+ customers, using both point-to-point wireless and fixed WiMAX to reach as many customers as possible in the sparsely populated desert region. It’s a challenging proposition for any company, considering most of their service area has less than one home per square mile. Even when finished constructing their network, Badal estimates there will only be two or three homes served per square mile.
One third of Sacred Wind’s customers live in Navajo or federal government sponsored public housing, another third live in small clusters of a half dozen homes separated by several miles, and the last third live at least a half mile from the nearest neighbor. Most are economically disadvantaged and have household incomes below $15,000 a year — 57.9% living below the poverty level. More than two-thirds of reservation homes have no telephone, with some driving up to 30 miles to reach the nearest pay phone. Several lack access to electricity, which makes wireless phone service and broadband even more challenging. Sacred Wind is exploring solar options to serve these unpowered homes.
The benefits achieved from Sacred Wind’s focus on their service area are obvious – they know the landscape, the culture, the economics, and the people. The company will work on problems that a large multi-state carrier like Qwest would not. Technicians trying to reach one customer five miles away from the nearest wireless base station could not get service until a technician experimented with bouncing the three gigahertz wireless signal off a granite cliff face to extend coverage, which worked.
A company specializing in providing service to rural Native Americans, that also has a non-profit arm dedicated to computer training, provides scholarships, and e-commerce opportunities for Native Americans, is a natural for recognition, and the public responded, calling Sacred Wind’s mission inspiring.
“It’s a real honor to be voted most inspiring small business in the Shine A Light program,” Badal said. “It’s so exciting and rewarding to start your own business and be able to make an impact on the community. Through the support we will receive from American Express as winner of this program, we will be able to further extend our commitment to serving the Navajo people with advanced technology and educational resources.”
Since August, people across the country have nominated thousands of small businesses for the “Shine A Light” program. Three finalists were ultimately selected with the help of host and entrepreneur Ellen DeGeneres, fashion designer and entrepreneur Diane von Furstenberg and MSNBC’s small business expert and host JJ Ramberg.
[flv width=”480″ height=”320”]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/sacred wind intro.flv[/flv]
A one minute introduction to Sacred Wind Communications
In addition to telephone service, Sacred Wind also provides Internet access to its customers, and here is where the story becomes considerably less inspiring.
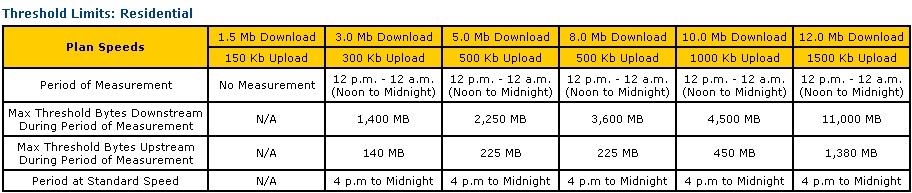
Sacred Wind’s “broadband” service for most affordable tiers fails to qualify as “broadband” at all, using the FCC standard of 768kbps. Pricing is exorbitant and speeds are slow.
It self-describes its dial-up option as “stable, fast, and affordable.” The “affordable” claim may be true when comparing pricing with the first broadband tier that actually meets the minimum definition of broadband – $49.95 a month for 768kbps service. Paying $79.95 a month will bring you their maximum speed offering — just 3Mbps.
The company also sells customers annual contracts to avoid the $99 installation and $65 equipment fees.
Still, for those who have never had telephone service, much less Internet access, it’s considered by many residents to be a good beginning. The company is amenable to the idea of raising those speeds when technically and financially feasible.
[flv width=”480″ height=”320″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Fujitsu Sacred Wind.mp4[/flv]
Fujitsu showcases Sacred Wind Communications and how it approached the technological challenges involved in providing service to the Navajo Reservation [8 minutes]
Unfortunately, like its bigger telephone brethren, Sacred Wind is not entirely free from the telephone industry politics that often lobbies for anti-consumer policies. A concerning document on Sacred Wind’s website promotes a questionable legislative agenda, including support of legislation that would permit providers to “create fair compensation in network use by identifying traffic on our networks,” which is a Net Neutrality no-no if it applies to their broadband network. Another mysterious bullet point, not well explained, objects to “video programming and broadcasting practices that make it difficult to provide an affordable product to our customers.” That could apply to wireless frequency allocations or traffic on their broadband network — it’s not well defined.
While the FCC works on its goal of providing broadband access to underserved Americans, actual case studies illustrating “successes” like Sacred Wind that only manage to bring 3Mbps service to rural areas underline the need for Universal Services Fund reform. Dedicating additional economic assistance to construct considerably more advanced networks to meet the needs of an increasingly high bandwidth Internet is essential to correct the urban-rural digital divide. The original purpose of the USF to guarantee basic phone service in rural areas was a noble idea a decade ago, but that was then and this is now.
As the pile of money in the USF continues to grow from Voice Over IP and mobile phone surcharges, it was only a matter of time before waste, fraud, and abuse also turned up. The administrators of the USF have often wasted considerable amounts of that money on questionable projects in decidedly un-rural areas. Redirecting, reforming, and broadening USF resources to cover broadband deployment in areas like the Navajo Reservation may be one of the only ways to build sustainable and equitable broadband access networks that are scalable and affordable, even for the most financially-challenged communities. Providing 256kbps service for $30 a month doesn’t come close to cutting it in poverty-stricken communities.
Additional video coverage of Sacred Wind can be found below the jump.


 Subscribe
Subscribe