This is part two of a multi-part series examining Time Warner Cable’s internal documents, made partly public as a result of a lawsuit filed by the New York Attorney General. You can read part one here.
 In the summer of 2014, Time Warner Cable had a problem. For three years, the Federal Communications Commission had been issuing reports about the quality of broadband service from the nation’s largest internet service providers. The raw data collected by about 800 subscribers of Time Warner Cable who volunteered to participate in the project began to worry executives because it showed their broadband service was oversold in certain large cities and was no longer capable of consistently achieving advertised speeds. Even worse, the company’s congestion problems threatened to lower Time Warner Cable’s internet performance score at the FCC.
In the summer of 2014, Time Warner Cable had a problem. For three years, the Federal Communications Commission had been issuing reports about the quality of broadband service from the nation’s largest internet service providers. The raw data collected by about 800 subscribers of Time Warner Cable who volunteered to participate in the project began to worry executives because it showed their broadband service was oversold in certain large cities and was no longer capable of consistently achieving advertised speeds. Even worse, the company’s congestion problems threatened to lower Time Warner Cable’s internet performance score at the FCC.
Sam Knows (but so does Time Warner Cable): The Not-So-Independent, Not-So-Confidential FCC Speed Test Program
The FCC commissioned a private company – Sam Knows – to distribute modified internet routers to gather data about the internet connections of thousands of volunteers and shared the results with the FCC to incorporate into its Measuring Broadband America program. After the FCC issued its first report in 2011, providers quickly learned the consequences of overpromising and underdelivering when Cablevision was called out for dramatically overselling its broadband service and not delivering the speeds customers paid to receive. While Cablevision executives publicly attacked the FCC speed test program as unreliable and wrong, they also quietly opened the company’s checkbook and spent millions quickly upgrading their facilities. The metric they failed to achieve was the FCC’s 80/80 test: “speed that at least 80% of the subscribers experience at least 80% of the time over peak periods.”
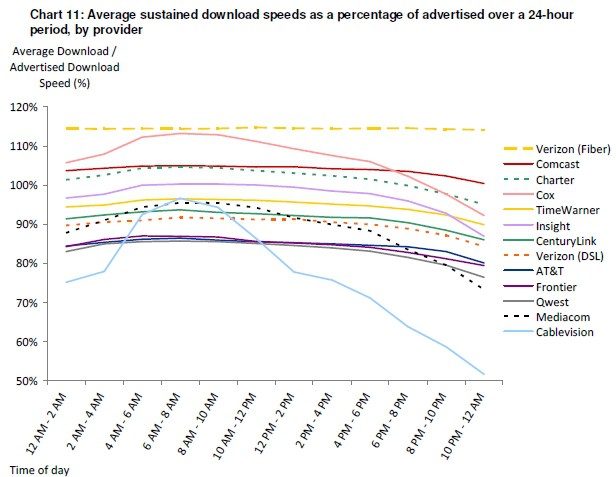
Here is what broadband performance on an oversold broadband service looks like. Notice Cablevision’s 2011 speed ranking plummets during peak usage periods when too many customers are sharing too little available bandwidth.
The incident embarrassed and damaged Cablevision’s reputation, and no cable operator wanted to be the next highlighted company for a public spanking by the FCC.
Time Warner Cable’s “Slow-Motion Train Wreck”
 In 2013, a Time Warner Cable executive recognized the company’s practice of limiting company-financed expansion of their upstream connections with the rest of the internet would have serious implications for their own speed test scores, because customers were encountering nightly slowdowns on popular websites like YouTube caused by overcongested connections. Company executives feared customers participating in the Sam Knows/FCC program would soon reveal Time Warner Cable’s internet speeds were beginning to suffer some of the same peak usage problems Cablevision was encountering in 2011. The executive’s solution? Temporarily expand upstream connections just long enough to protect Time Warner Cable’s broadband speed scores:
In 2013, a Time Warner Cable executive recognized the company’s practice of limiting company-financed expansion of their upstream connections with the rest of the internet would have serious implications for their own speed test scores, because customers were encountering nightly slowdowns on popular websites like YouTube caused by overcongested connections. Company executives feared customers participating in the Sam Knows/FCC program would soon reveal Time Warner Cable’s internet speeds were beginning to suffer some of the same peak usage problems Cablevision was encountering in 2011. The executive’s solution? Temporarily expand upstream connections just long enough to protect Time Warner Cable’s broadband speed scores:
“Our Sam Knows scores are like watching a slow-motion train wreck. We need to get in front of this. One thing I think we may need to be prepared to do is just give more ports to Cogent during sweeps month [when FCC results are measured for purposes of the MBA report]. We don’t have to make any promises, we just have to make it work temporarily.”
But even tricks like that failed to help Time Warner Cable’s speed scores in New York City, where serious congestion problems were obvious, even as late as last year:
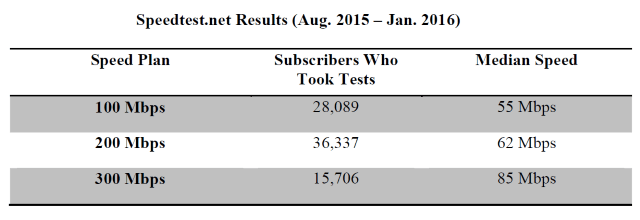
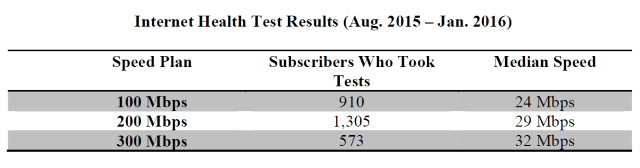
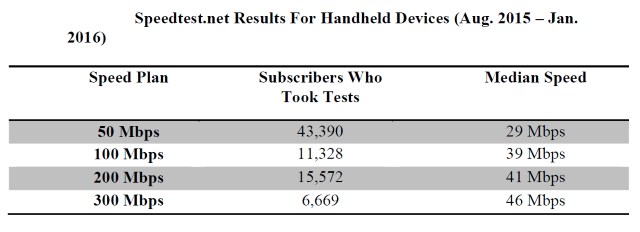
The lawsuit filed by New York’s Attorney General revealed that FCC panelists in New York were getting speeds consistently well below the speeds they paid for, especially those paying for premium speeds:
FCC/Sam Knows Time Warner Cable Maxx Panelists in New York Speed Test Reports:
100Mbps subscribers received 73-87% of advertised speed (<80% advertised speed over six month period)
200Mbps subscribers received 49-58% of advertised speed (<60% advertised speed over six month period)
300Mbps subscribers received 33-52% of advertised speed (<38-74% advertised speed over six month period)
Speed test results showed consistent speed deficiencies between 2013-2016 occuring for many reasons, according to the lawsuit, including customers using outdated, company-supplied cable modems insufficient to support the customer’s speed plan, chronically oversold neighborhood groups that Time Warner Cable did not split or upgrade with additional capacity, and inadequate upstream/backbone connections to properly deliver content originating outside of Time Warner Cable’s own broadband network.
Overprovisioning Your Broadband Speed = “Putting Lipstick on a Pig”
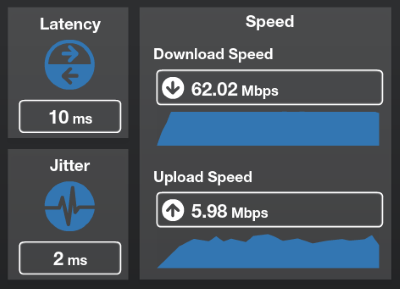
We subscribe to 50/5Mbps service but receive closer to 62/6Mbps because Spectrum/Time Warner Cable overprovisions our service.
Instead of investing adequately in network upgrades and node splits, a July 7, 2014 internal email from Time Warner Cable’s former head of corporate strategy told senior colleagues the best way out of this dilemma was to cheat on the FCC broadband tests:
“We recommend increasing over-provisioning our modem speeds to around 20% to drive our Sam Knows scores >100% and then to market that we deliver more than promised speeds.”
In plain English, Time Warner Cable boosted the maximum allowed speed of each customer by about 20%. As a result, during non-peak usage times customers would find, for example, a plan advertising 50/5Mbps speed now delivered around 60/6Mbps. Although some customers considered overprovisioning a hidden free upgrade, Time Warner Cable’s motives were not altruistic. Because the Sam Knows testing program averages scores received from periodic testing, Time Warner Cable padded the results with higher-than-advertised speeds when their network was not congested, which compensated for the slower speeds and worse performance customers were getting during peak usage times. The lawsuit also alleges the practice helped to hide the abundance of obsolete rented cable modems still in use across Time Warner Cable’s broadband network.
The strategy worked to boost Time Warner Cable’s scores, but only as far as the FCC was concerned. Some customers were still finding their visits to YouTube, Netflix, and other websites littered with buffering problems and degraded resolution videos just about every evening. In 2013, before Time Warner Cable went ahead with its overprovisioning plan, the company’s own network engineers called the practice putting “lipstick on a pig.”
The Attorney General had its own analogy:
Using the highway analogy, Spectrum-TWC’s overprovisioning strategy amounts to allowing cars to go faster than the posted speed limit at certain times to compensate for the fact that often the highway slowed to a crawl. Boosting the average results with outlier results masked the enormous frustration for most subscribers stuck in traffic.
Breaking the FCC’s Rules

The lawsuit also alleges Time Warner Cable broke its own commitment to the FCC in the Code of Conduct it signed as a participant in the FCC’s testing program.
The FCC’s Code of Conduct required Spectrum-TWC to “at all times act in good faith” and not do anything “if the intended consequence of such act or omission is to enhance, degrade or tamper with the results of any test.” Specifically, the Code of Conduct prohibited the company from “modifying or improving services delivered to any class of subscribers” that was not “consistent with normal business practices.”
Stop the Cap! has also learned Time Warner Cable was able to identify each participant of the FCC/Sam Knows Time Warner Cable panel. This allowed the cable company to secretly verify the line quality and equipment in use by each participant, and give extra attention to those customers/volunteers to make sure service was performing as well as possible. In fact, executives instructed customer service representatives to assign FCC panelists “VIP treatment” and “best in class devices” when swapping modems, even as the company continued to supply deficient equipment to other customers who were not FCC panelists.
Still to Come: Playing games with online gamers, company officials tell the truth about bandwidth costs and Net Neutrality, and more….


 Subscribe
Subscribe



 The average Charter/Spectrum customer shares their internet connection with up to 499 of their neighbors, according to an admission made today by Charter Communications CEO Thomas Rutledge.
The average Charter/Spectrum customer shares their internet connection with up to 499 of their neighbors, according to an admission made today by Charter Communications CEO Thomas Rutledge. Rutledge’s comments this morning suggest Charter/Spectrum customers may be sharing their connection with up to 499 of their neighbors, making them more likely to experience congestion potentially worse than experienced with Time Warner Cable. Standard internet service from Charter is also much faster than Time Warner Cable’s corresponding Standard plan — 60Mbps vs. 15Mbps, which has the potential to lead to even worse slowdowns if customers use their internet connections at the same time.
Rutledge’s comments this morning suggest Charter/Spectrum customers may be sharing their connection with up to 499 of their neighbors, making them more likely to experience congestion potentially worse than experienced with Time Warner Cable. Standard internet service from Charter is also much faster than Time Warner Cable’s corresponding Standard plan — 60Mbps vs. 15Mbps, which has the potential to lead to even worse slowdowns if customers use their internet connections at the same time. In the summer of 2014, Time Warner Cable had a problem. For three years, the Federal Communications Commission had been issuing reports about the quality of broadband service from the nation’s largest internet service providers. The raw data collected by about 800 subscribers of Time Warner Cable who volunteered to participate in the project began to worry executives because it showed their broadband service was oversold in certain large cities and was no longer capable of consistently achieving advertised speeds. Even worse, the company’s congestion problems threatened to lower Time Warner Cable’s internet performance score at the FCC.
In the summer of 2014, Time Warner Cable had a problem. For three years, the Federal Communications Commission had been issuing reports about the quality of broadband service from the nation’s largest internet service providers. The raw data collected by about 800 subscribers of Time Warner Cable who volunteered to participate in the project began to worry executives because it showed their broadband service was oversold in certain large cities and was no longer capable of consistently achieving advertised speeds. Even worse, the company’s congestion problems threatened to lower Time Warner Cable’s internet performance score at the FCC.
 In 2013, a Time Warner Cable executive recognized the company’s practice of limiting company-financed expansion of their upstream connections with the rest of the internet would have serious implications for their own speed test scores, because customers were encountering nightly slowdowns on popular websites like YouTube caused by overcongested connections. Company executives feared customers participating in the Sam Knows/FCC program would soon reveal Time Warner Cable’s internet speeds were beginning to suffer some of the same peak usage problems Cablevision was encountering in 2011. The executive’s solution? Temporarily expand upstream connections just long enough to protect Time Warner Cable’s broadband speed scores:
In 2013, a Time Warner Cable executive recognized the company’s practice of limiting company-financed expansion of their upstream connections with the rest of the internet would have serious implications for their own speed test scores, because customers were encountering nightly slowdowns on popular websites like YouTube caused by overcongested connections. Company executives feared customers participating in the Sam Knows/FCC program would soon reveal Time Warner Cable’s internet speeds were beginning to suffer some of the same peak usage problems Cablevision was encountering in 2011. The executive’s solution? Temporarily expand upstream connections just long enough to protect Time Warner Cable’s broadband speed scores:




