Fiber optic cable spool
For the most populated provinces in Canada, questions about when fiber-to-the-home service will become a reality are easy to answer: Never, indefinitely.
Some of Canada’s largest telecommunications providers have their minds made up — fiber isn’t for consumers, it’s for their backbone and business networks. For citizens of Toronto, Calgary, Montreal, and Vancouver coping with bandwidth shortages, providers have a much better answer: pay more, use less Internet.
Fiber broadband projects in Canada are hard to find, because providers refuse to invest in broadband upgrades to deliver the kinds of speeds and capacity Canadians increasingly demand. Instead, companies like Bell, Shaw, and Rogers continue to hand out pithy upload speeds, throttled downloads, and often stingy usage caps. Much of the country still relies on basic DSL service from Bell or Telus, and the most-promoted broadband expansion project in the country — Bell’s Fibe, is phoney baloney because it relies on existing copper telephone wires to deliver the last mile of service to customers.
Much like in the United States, the move to replace outdated copper phone lines and coaxial cable in favor of near-limitless capacity fiber remains stalled in most areas. The reasons are simple: lack of competition to drive providers to invest in upgrades and the unwillingness to spend $1000 per home to install fiber when a 100GB usage cap and slower speeds will suffice.
The Toronto Globe & Mail reports that while 30-50 percent of homes in South Korea and Japan have fiber broadband, only 18 percent of Americans and less than 2 percent of Canadians have access to the networks that routinely deliver 100Mbps affordable broadband without rationed broadband usage plans.
In fact, the biggest fiber projects underway in Canada are being built in unexpected places that run contrary to the conventional wisdom that suggest fiber installs only make sense in large, population-dense, urban areas.
 Manitoba’s MTS plans to spend $125-million over the next five years to launch its fiber to the home service, FiON. By the end of 2015, MTS expects to deploy fiber to about 120,000 homes in close to 20 Manitoba communities. In Saskatchewan, SaskTel is investing $199 million in its network in 2011 and approximately $670 million in a seven-year Next Generation Broadband Access Program (2011 – 2017). This program will deploy Fiber to the Premises (FTTP) and upgrade the broadband network in the nine largest urban centers in the province – Saskatoon, Regina, Moose Jaw, Weyburn, Estevan, Swift Current, Yorkton, North Battleford and Prince Albert.
Manitoba’s MTS plans to spend $125-million over the next five years to launch its fiber to the home service, FiON. By the end of 2015, MTS expects to deploy fiber to about 120,000 homes in close to 20 Manitoba communities. In Saskatchewan, SaskTel is investing $199 million in its network in 2011 and approximately $670 million in a seven-year Next Generation Broadband Access Program (2011 – 2017). This program will deploy Fiber to the Premises (FTTP) and upgrade the broadband network in the nine largest urban centers in the province – Saskatoon, Regina, Moose Jaw, Weyburn, Estevan, Swift Current, Yorkton, North Battleford and Prince Albert.
“Saskatchewan continues to be a growing and dynamic place,” Minister responsible for SaskTel Bill Boyd said. “The deployment of FTTP will create the bandwidth capacity to allow SaskTel to deploy exciting new next generation technologies to better serve the people of Saskatchewan.”
But the largest fiber project of all will serve the unlikely provinces of Atlantic Canada, among the most economically challenged in the country. Bell Aliant is targeting its FibreOP fiber to the home network to over 600,000 homes by the end of next year. On that network, Bell Aliant plans to sell speeds up to 170/30Mbps to start.
 In comparison, residents in larger provinces are making due with 3-10Mbps DSL service from Bell or Telus, or expensive usage-limited, speed-throttled cable broadband service from companies like Rogers, Shaw, and Videotron.
In comparison, residents in larger provinces are making due with 3-10Mbps DSL service from Bell or Telus, or expensive usage-limited, speed-throttled cable broadband service from companies like Rogers, Shaw, and Videotron.
Bell Canada is trying to convince its customers it has the fiber optic network they want. Its Fibe Internet service sure sounds like fiber, but the product fails truth-in-advertising because it isn’t an all-fiber-network at all. It’s similar to AT&T’s U-verse — relying on fiber to the neighborhood, using existing copper phone wires to finish the job. Technically, that isn’t much different from today’s cable systems, which also use fiber to reach into individual neighborhoods. Traditional coaxial cable handles the signal for the rest of the journey into subscriber homes.
A half-fiber network can do better than none at all. In Ontario, Bell sells Fibe Internet packages at speeds up to 25Mbps, but even those speeds cannot compare to what true fiber networks can deliver.
 Globe & Mail readers seemed to understand today’s broadband realities in the barely competitive broadband market. One reader’s take:
Globe & Mail readers seemed to understand today’s broadband realities in the barely competitive broadband market. One reader’s take:
“The problem in Canada (and elsewhere) preventing wide scale deployment of FTTH isn’t the technology, nor the cost. It’s a lack of political vision and will, coupled with incumbent service providers doing whatever they can to hold on to a dysfunctional model that serves their interests at the expense of consumers.”
Another:
“The problem with incumbents is they only think in 2-3 year terms. If they can’t make their money back in that period of time, they’re not interested. Thinking 20, heck even 10 years ahead is not in their vocabulary.”
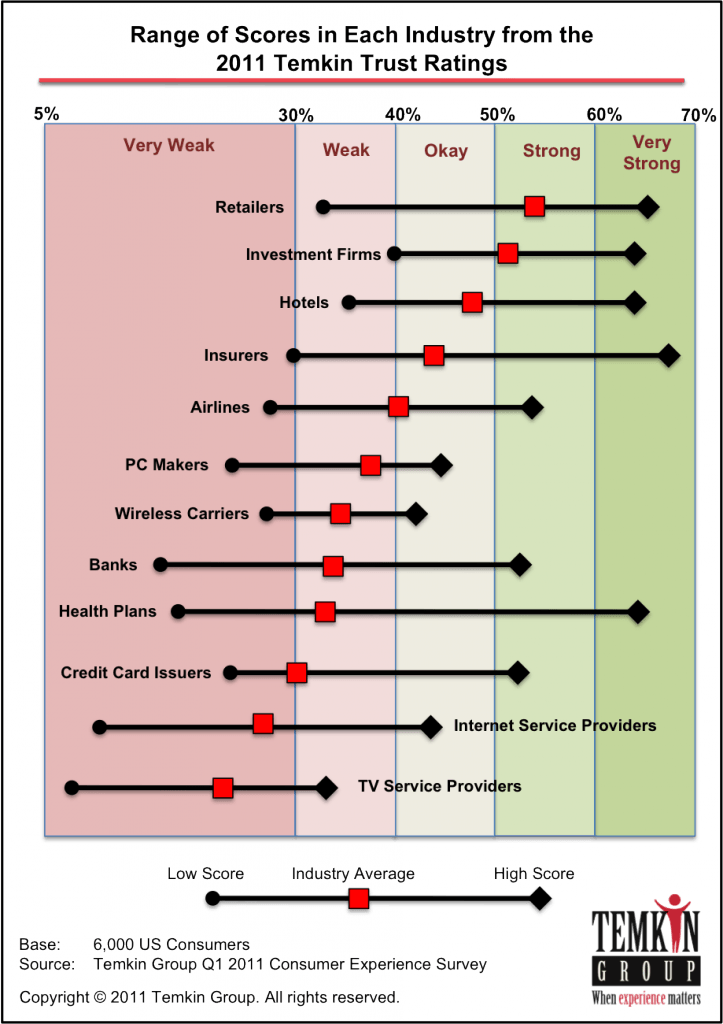
 Even after the financial meltdown and the Great Recession, Americans still trust their cable and telephone companies even less than bailed-out financial institutions, mortgage brokers, credit card issuers, insurance companies, and airlines.
Even after the financial meltdown and the Great Recession, Americans still trust their cable and telephone companies even less than bailed-out financial institutions, mortgage brokers, credit card issuers, insurance companies, and airlines.

 Subscribe
Subscribe