Nobody raises phone rates after deregulation like AT&T.
AT&T’s bill to maximize profits and minimize responsibility to its customers is back for consideration in the Illinois state legislature.
The Illinois Telecom Act is up for review in the spring and AT&T’s team of lobbyists are gearing up to advocate killing off AT&T’s legal obligation to provide low-cost, reliable landline service to any resident that wants service. AT&T says the measure is a reasonable response to the ongoing decline in its landline customer base, but rural and fixed-income residents fear the phone company will walk away from areas deemed unprofitable to serve and force customers to expensive wireless phone alternatives.
Areas in central and southern Illinois are served by a variety of rural phone companies including AT&T and Frontier Communications. Northeast Illinois is the home of metropolitan Chicago, where businesses depend on reliable phone service and the urban poor and senior residents depend on predictably affordable basic landline service.
The state still has as least 1.3 million residential landline customers paying rates starting at $3 a month for basic “Lifeline” service in Chicago to $9.50 a month for rural flat rate service with a limited local calling area. Cell service costs several times more than AT&T’s basic landline rates and signal quality is often challenged in rural areas. In large sections of Illinois where AT&T has elected not to bring its U-verse fiber to the neighborhood service, customers with basic voice calling and DSL broadband service could find themselves eventually disconnected and forced to switch to AT&T’s wireless residential service.
 AT&T’s Wireless Home Internet plan charges $60/month for 10GB of Internet use, $90/month for 20GB, and $120/month for 30GB. The overlimit fee is $10 per gigabyte. Telephone service is extra.
AT&T’s Wireless Home Internet plan charges $60/month for 10GB of Internet use, $90/month for 20GB, and $120/month for 30GB. The overlimit fee is $10 per gigabyte. Telephone service is extra.
Customers will need smartphones or hotspot equipment to reach AT&T’s wireless services. Although often discounted or free for those who sign two-year contracts, credit-challenged customers will be required to pay a steep deposit or buy equipment outright.
“Smartphones are wonderful technology but they don’t come cheap and anybody who has traveled across Illinois knows they’re not always reliable,” David Kolata, executive director of Citizens Utility Board, said at a recent news conference. “Traditional home phone service is the most affordable, reliable option for millions of people and we shouldn’t take away that choice.”
The Federal Communications Commission is currently allowing AT&T to experiment with discontinuing landline service in parts of Alabama and Florida. Customers in urban areas are switched to AT&T’s U-verse service, those in rural areas are switched to cell service. Both services are unregulated. If AT&T can sell the Illinois legislature on abandoning its need to serve as a “carrier of last resort,” the company will have the unilateral right to disconnect service, set rates at will, and be under few, if any, customer service obligations.
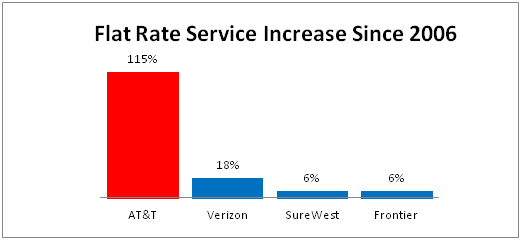
In states where AT&T won the near-total deregulation it now seeks in Illinois, phone rates quickly soared. In California, AT&T flat rate calling shot up 115% between 2006 and 2013 — from $10.69 to $23 a month. AT&T also raised prices on calling features and other services.
In earlier trials run by Verizon, similar wireless landline replacement devices lacked support for home medical and security alarm monitoring, did not handle faxes or credit card authorizations, and often lacked precision in locating customers calling 911 in an emergency. The equipment also failed during power outages if the customer lacked battery backup equipment.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 “It’s never going to pencil; it’s whether the company will do what’s right,” argued Board chairman Jon Kennedy.
“It’s never going to pencil; it’s whether the company will do what’s right,” argued Board chairman Jon Kennedy. New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo has set a goal that every resident of New York State should have access to at least 100Mbps broadband no later than 2018.
New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo has set a goal that every resident of New York State should have access to at least 100Mbps broadband no later than 2018.
 That must come as a relief for Verizon. The state’s largest phone company has petitioned state officials in the past for a gradual mothballing of New York’s rural landline network in favor of switching customers to wireless voice and broadband over Verizon’s cellular network. Theoretically, taxpayers could end up subsidizing the demise of rural New York landlines and DSL if Verizon seeks money from the rural broadband fund to expand its wireless tower network in rural New York. Time Warner Cable almost certainly will also seek more funding, probably in excess of the average $1,264 paid to the cable company for each of the 4,114 additional connections it agreed to complete during an earlier round of funding.
That must come as a relief for Verizon. The state’s largest phone company has petitioned state officials in the past for a gradual mothballing of New York’s rural landline network in favor of switching customers to wireless voice and broadband over Verizon’s cellular network. Theoretically, taxpayers could end up subsidizing the demise of rural New York landlines and DSL if Verizon seeks money from the rural broadband fund to expand its wireless tower network in rural New York. Time Warner Cable almost certainly will also seek more funding, probably in excess of the average $1,264 paid to the cable company for each of the 4,114 additional connections it agreed to complete during an earlier round of funding. After raising prices for Internet service and imposing the nation’s highest modem rental fee, Comcast customers in Oregon and southwest Washington are finally getting some good news:
After raising prices for Internet service and imposing the nation’s highest modem rental fee, Comcast customers in Oregon and southwest Washington are finally getting some good news: 

 Comcast: 88% of customers met or exceeded state and federal standards;
Comcast: 88% of customers met or exceeded state and federal standards;