 AT&T CEO John Stankey is still looking to wring costs out of the business, and the company’s rural landline customers are next to take the cut.
AT&T CEO John Stankey is still looking to wring costs out of the business, and the company’s rural landline customers are next to take the cut.
At this morning’s J.P. Morgan Technology, Media and Communications Conference for investors, Stankey said AT&T is considering mothballing landline facilities in rural parts of its service area and offer wireless service instead.
“We have a voice replacement service now, so that allows us to look at our options around the footprint […] and begin the work of starting to shed some of that footprint and reduce the number of square miles that have that fixed infrastructure in place [where] you’re never going to have an incentive to ultimately upgrade to fiber,” Stankey told investors, quickly correcting himself over use the word ‘never’ in favor of “the next several years.”
“The best way to serve them is with robust wireless infrastructure and stepped up investment in that case and we will do that,” he added.
AT&T has been testing fixed wireless replacement phone service in parts of the southern United States for several years, to very mixed reviews. In these trials, AT&T rural landline customers receive a wireless modem that connects with existing home phone lines. Internet service is provided over AT&T’s 4G LTE network.

Stankey
AT&T ceased marketing its DSL service last October, although some Stop the Cap! readers claim they still occasionally receive targeted invitations for DSL service in some areas. The company has allowed its current rural DSL customers to keep their service, but many don’t. The company lost almost 39,000 DSL customers in the first three months of this year, with so signs of stopping. Across AT&T’s landline footprint, which extends from the Great Lakes region to the South as far west as Texas and east to Florida, there are only about a half-million AT&T DSL customers remaining. Most of those customers keep the service because they have no other options.
If AT&T wins FCC approval to decommission its wired network in rural areas where it has no plans to provide fiber to the home service, customers will lose traditional landline phone service and DSL.
Stankey said any serious effort in that direction is unlikely to begin until 2023, largely because AT&T will not make the investments to bolster its rural wireless infrastructure until then.
The CEO also foreshadowed no immediate plans to follow Verizon into the 5G wireless home internet business. In fact, Stankey admitted AT&T’s network is likely inadequate to support the data demands of home broadband customers.
That leaves rural customers in AT&T’s service areas with no hope of high-speed upgrades unless a community broadband provider launches or a cable operator agrees to wire rural areas. There are still questions about the capacity next generation satellite internet service will have in rural areas and whether service will be adequate to meet today’s data demands.
AT&T’s customers in urban and major suburban areas have a brighter future, however. Stankey told investors AT&T will expand its fiber to the home service to another three million households in 2021 and at least four million more in 2022. Overall, AT&T plans to provide fiber service to around 30 million homes and businesses in its wireline service area. If adequate returns on investment can be realized, along with reduced upgrade costs to reach each home, Stankey suggested another 10 million customer locations could one day see fiber service as well.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
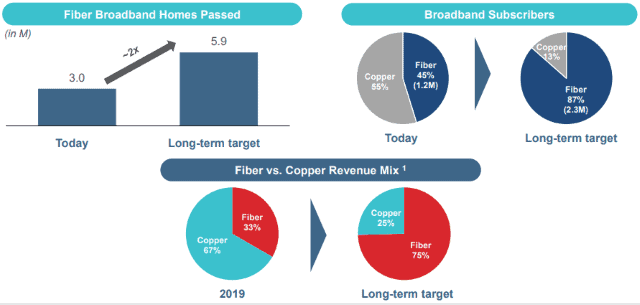
 In 2021, the company announced it had “planning and engineering” underway for unspecified fiber to the home service upgrades in copper service areas “in select regions.” But most of Frontier’s fiber upgrades will take place over the next decade. Specifically, Frontier plans to wire up to 2.9 million homes with fiber using a combination of its own money and subsidy funds provided by the FCC. Frontier’s new owners have signaled they will not go out on a limb to finance rapid fiber upgrades, and you better live in a state where fiber upgrades are being given priority.
In 2021, the company announced it had “planning and engineering” underway for unspecified fiber to the home service upgrades in copper service areas “in select regions.” But most of Frontier’s fiber upgrades will take place over the next decade. Specifically, Frontier plans to wire up to 2.9 million homes with fiber using a combination of its own money and subsidy funds provided by the FCC. Frontier’s new owners have signaled they will not go out on a limb to finance rapid fiber upgrades, and you better live in a state where fiber upgrades are being given priority.
 Customer satisfaction with fiber to the home internet service is so high, one industry leader says the only time customers cancel service is if they move or die.
Customer satisfaction with fiber to the home internet service is so high, one industry leader says the only time customers cancel service is if they move or die.
 If you’ve ever lived in small-town America, you know how bad the internet can sometimes be. So one town in North Carolina decided: If we can’t make fast internet come to us, we’ll build it ourselves. And they did, despite laughter and disbelief from Time Warner Cable (today known as Spectrum).
If you’ve ever lived in small-town America, you know how bad the internet can sometimes be. So one town in North Carolina decided: If we can’t make fast internet come to us, we’ll build it ourselves. And they did, despite laughter and disbelief from Time Warner Cable (today known as Spectrum).