A new report proves what Stop the Cap! has advocated for more than two years now — communities seeking the fastest, most-modern, and most aggressively priced broadband can get all of that and more… if they do it themselves.
The concept of community self-reliance for broadband has been dismissed and derided for years among small government conservatives and corporately-backed dollar-a-holler groups who claim government can’t manage anything, but when it comes to broadband in the state of North Carolina, the evidence is in and it is irrefutable — Tar Heel state residents are getting the most bang for their broadband buck from well-managed and smartly-run community-owned broadband networks.
Christopher Mitchell from the New Rules Project — part of the Institute for Local Self-Reliance, gathered evidence from North Carolina’s different broadband providers and found the best broadband services come from local communities who decided to build their own fiber networks. instead of relying on a handful of cable and phone companies who have kept the state lower in broadband rankings than it deserves.
North Carolina is undergoing a transition from a manufacturing and agricultural-based economy that used to employ hundreds of thousands of workers in textile, tobacco, and furniture manufacturing businesses. In the last quarter-century, the state has lost one in five jobs to Asian outsourcing and America kicking the tobacco habit. Its future depends on meeting the challenges of transitioning to a new digital economy, and major cities like Charlotte, Raleigh, and Greensboro have risen as well-recognized leaders in engineering, biotech, and finance.
But for rural and suburban North Carolina, success has been hindered by a lack of necessary infrastructure — particularly broadband for small businesses and entrepreneurs. It becomes impossible to attract high tech jobs to areas that are forced to rely entirely on low speed DSL service, if that is even available.
In communities like Wilson and Salisbury, long frustrated by area providers not delivering needed services, a decision was reached to build their own broadband infrastructure — modern fiber to the home networks worthy of the 21st century.
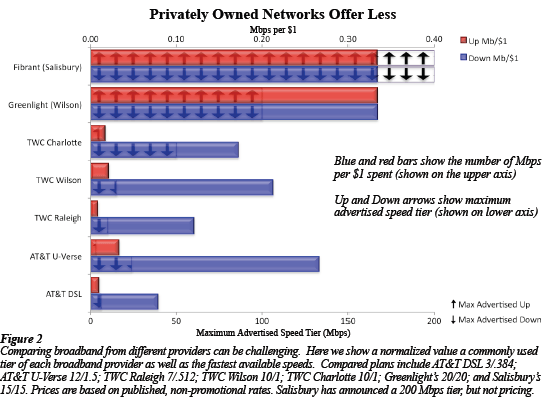
Mitchell’s report charts the benefits available to every resident, as communities with state-of-the-art fiber networks consistently deliver the most robust service at the lowest prices, all without risk to local taxpayers. Better still, when the network construction costs are paid back to bondholders, future profits generated by the community-owned systems will be plowed back into local communities to reduce tax burdens and keep service state-of-the-art.
“Comparing the tiers of residential service from Wilson or Salisbury against the providers in the Raleigh area shows that the communities have invested in a network that offers far faster speeds for less money than any of the private providers,” Mitchell concludes. “Whether communities in North Carolina are competing against other states or internationally for jobs and quality of life, they are smart to consider investing in a community fiber network.”
Mitchell’s report arrives just a few weeks after voters handed North Carolina’s General Assembly to GOP control for the first time in more than a century. Both cable and phone companies in the state modestly suggest that is good news for their legislative agenda, which is an understatement equal in proportion to the historic handover of control of both the House (67-52) and the Senate (31-19). The top items on the agenda of incoming members is a checklist of conservative activist favorites, including a war on unions, mandatory ID cards for voting, opting the state out of recently enacted health care reform, an eminent domain constitutional amendment, sweeping deregulation reform to favor business interests, and redistricting to “restore fairness” in future elections.
The state’s big cable and phone companies are convinced with a list like that, they can come along for the legislative ride and get their agenda passed as “pro-business reform.” That means a much larger fight in 2011 for the inevitable return of corporate protection legislation banning exactly the kinds of municipal networks that are delivering North Carolina better, faster, and cheaper broadband.


 Subscribe
Subscribe