 North Carolina residents bypassed by Google Fiber and impatient waiting for AT&T U-verse with GigaPower may still have a chance to get gigabit fiber Internet.
North Carolina residents bypassed by Google Fiber and impatient waiting for AT&T U-verse with GigaPower may still have a chance to get gigabit fiber Internet.
Ting, a Toronto-based wireless provider, is exploring building fiber broadband networks in as many as a half-dozen cities in 2016, and some of them may be in North Carolina.
Elliot Noss, CEO of Ting’s parent company, told the Triangle Business Journal he is impressed with the enthusiasm for fiber optic broadband in the state. He recognized Greenlight, Wilson’s community-owned fiber network, as a fiber pioneer that helped fuel demand for better Internet in the state. He added North Carolina is one of the leaders in fiber to the home service in the country, and that makes it a very suitable place to bring even more fiber to the state.
The Triangle region of North Carolina is receiving network upgrades from Time Warner Cable and AT&T, and Google Fiber is coming to Charlotte and Raleigh-Durham, but there remains a number of Triangle communities including Clayton, Dunn, Henderson, Louisburg, Norlina, Oxford, Pittsboro, Rocky Mount, Roxboro, Sanford, Selma, Siler City, Smithfield, Tarboro and Wake Forest where fiber networks would be welcomed.

Ting workers installing fiber optics in Charlottesville, Va.
Noss believes fiber begets even more fiber, which may explain why some states are getting huge investments in competing fiber optic projects while others struggle with little or no fiber at all. As soon as a fiber provider enters a region, it creates a higher level of awareness that better Internet service exists when you look beyond “good enough” broadband from phone and cable companies. The resulting “broadband envy” fuels demand for network upgrades.
Noss believes smaller, outlying metros bypassed for fiber upgrades now want them more than ever because they are at a competitive disadvantage without better Internet access.
“North Carolina might be the first state in the union that has moved from where cities and towns are looking at fiber as a way to differentiate and to lead,” Noss told the newspaper. “(North Carolina) is seeing it almost defensively: We need it for our survival because we’re surrounded by it.”
So what makes a community ripe for fiber broadband? A community already sold on fiber and willing to make things happen quickly and smoothly.
“The first thing we look for when we’re engaging with a city or town is an understanding that this is something they deeply want to do,” Noss says. “We don’t take meetings with cities who want to hear about why they should have fiber or gigabit connectivity.”
That attitude is shared by Google, which has taken to issuing a checklist for city officials interested in attracting Google Fiber to their community. In short, it means developing a working relationship between zoning/permitting officials and Google’s engineers to cut the “red tape.”
In the past, politicians often treated cable franchise contracts as valuable enough to ask providers for concessions in return for an agreement. Many cities treated Verizon the same way when it sought franchise agreements to offer cable television over its FiOS fiber to the home network. Some city officials sought compensation for PEG services – Public Access, Educational, and Government channels. Others sought funding for technology and educational programs, community centers, or free service for public and government-owned buildings.
Google has turned that formula upside down. Today, communities offer concessions to Google competing to be the next fiber city. Other providers entering the fiber market with promises of better Internet are getting a similar reception from eager communities.
Charlottesville, Va. and Westminster, Md., neither a likely prospect for Google Fiber or Verizon FiOS did not need any convincing. Ting now provides gigabit fiber service in both communities for $89 a month or a cheaper 5/5Mbps budget option for $19 a month — both with a $399 installation fee. Customers cannot wait to sign up for service, often to say goodbye to companies like Comcast or Verizon’s DSL offering.
Ting is owned by Tucows, Inc., a provider of network access, domain names, and other Internet services.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Ting What gigabit fiber means for Westminster 2015.mp4[/flv]
Ting produced this video about what gigabit fiber broadband will mean for a community like Westminster, Md. (2:07)


 Subscribe
Subscribe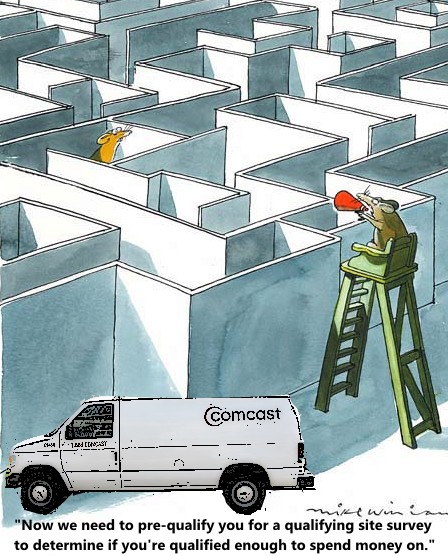 Comcast is rejecting some requests for its new 2Gbps fiber to the home service, claiming construction costs to provide the service to some homes are too high, even for customers living 0.15 of a mile from Comcast’s nearest fiber optic connection point.
Comcast is rejecting some requests for its new 2Gbps fiber to the home service, claiming construction costs to provide the service to some homes are too high, even for customers living 0.15 of a mile from Comcast’s nearest fiber optic connection point. Comcast implies any customer within 1/3rd of a mile of their nearest fiber cable is qualified to get Gigabit Pro service, but Thomas tells us that just isn’t true.
Comcast implies any customer within 1/3rd of a mile of their nearest fiber cable is qualified to get Gigabit Pro service, but Thomas tells us that just isn’t true. After months of issuing
After months of issuing 
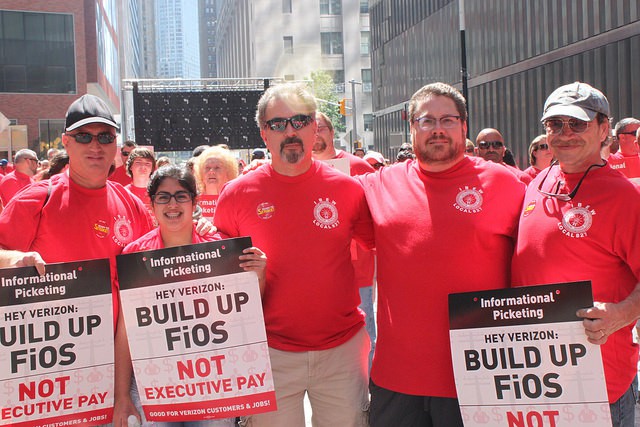

 Verizon spokesman Rick Young countered that Verizon has offered workers a straight 4% wage increase but admitted many existing contract provisions are decades old and no longer reflect current business reality. Young added Verizon union network technicians are paid $160,000 a year on average in total compensation, including salary, pension and health care. But Verizon management is insistent on cutting back the company’s health care costs, noting Verizon successfully reduced the cost of covering nonunionized workers to about $16,700 per family while union workers still receive coverage worth $20,000-24,000 a year per family.
Verizon spokesman Rick Young countered that Verizon has offered workers a straight 4% wage increase but admitted many existing contract provisions are decades old and no longer reflect current business reality. Young added Verizon union network technicians are paid $160,000 a year on average in total compensation, including salary, pension and health care. But Verizon management is insistent on cutting back the company’s health care costs, noting Verizon successfully reduced the cost of covering nonunionized workers to about $16,700 per family while union workers still receive coverage worth $20,000-24,000 a year per family. With 86 percent of union members voting to strike if negotiations fail, it seems an almost certainty workers will be on the picket lines by next week if negotiations remain unsuccessful. Workers believe Verizon’s profits have been shared mostly at the top through executive bonuses and ever-increasing compensation packages while ordinary workers are asked to forego benefits and job security.
With 86 percent of union members voting to strike if negotiations fail, it seems an almost certainty workers will be on the picket lines by next week if negotiations remain unsuccessful. Workers believe Verizon’s profits have been shared mostly at the top through executive bonuses and ever-increasing compensation packages while ordinary workers are asked to forego benefits and job security.

 Despite the job shifts, the fact 24,000 workers in the region are already employed in photonics-related jobs may have been a deciding factor in selecting Rochester for the center.
Despite the job shifts, the fact 24,000 workers in the region are already employed in photonics-related jobs may have been a deciding factor in selecting Rochester for the center.
