 Still waiting for Verizon FiOS in New York City? Are you annoyed that your neighbors have impressive broadband speeds from an all-fiber network while you suffer with DSL or cable broadband from Time Warner or Cablevision? Your landlord may be the problem.
Still waiting for Verizon FiOS in New York City? Are you annoyed that your neighbors have impressive broadband speeds from an all-fiber network while you suffer with DSL or cable broadband from Time Warner or Cablevision? Your landlord may be the problem.
While cities upstate clamor for Verizon’s fiber upgrades, FiOS has gone unappreciated and unwanted by more than 40 building owners either blocking the company from entering their properties or ignoring repeated letters from Verizon requesting permission to begin upgrades. In many instances, Verizon has tried to make contact since 2010 with no success. Some building owners want extra compensation (sometimes to the extreme) before they will grant permission. Others don’t want the phone company performing work inside their buildings, period.
Now Verizon is appealing to the New York State Public Service Commission to ask for their intervention.
Verizon has the right to install cable television facilities, regardless of the landlord’s objections, under Section 228 of the New York Public Service Law, which states: “No landlord shall interfere with the installation of cable television facilities upon his property or premises ….”
Verizon has promised it will bear the full cost of the installation of its equipment, wiring, and other facilities to offer the service, as well as indemnify the landlord for any damage caused by the installation work.
 In April, Verizon was criticized by New York City public advocate Bill de Blasio for falling behind schedule providing access to FiOS in low-income communities.
In April, Verizon was criticized by New York City public advocate Bill de Blasio for falling behind schedule providing access to FiOS in low-income communities.
“Five years into one of the biggest franchise agreements issued by the city, roughly half of homes still have no access to fiber network connections—most of them concentrated in low-income areas like Upper Manhattan, the South Bronx, Western Queens and Central Brooklyn,” said de Blasio.
The public advocate added:
Under Verizon’s 2008 franchise agreement, all New York City residents are supposed to have access to fiber optic networks by June 2014. As a benchmark, the contract required the company to reach more than three-quarters of City residents by the end of 2012, but according to data released through the New York State Office of Information Technology Services, only half of New York City’s 3.4 million housing units had access to fiber broadband services at year’s end—putting the company far behind schedule. Brooklyn and the Bronx lagged furthest behind, with only 40 percent and 46 percent of household having access to fiber, respectively.

de Blasio
Verizon and the Bloomberg Administration dispute de Blasio’s findings, noting fiber upgrades often depend on surrounding infrastructure. Where overhead wiring predominates, Verizon FiOS is available nearly everywhere in New York City. In other areas, Verizon says it is meeting its obligations and points to landlord impediments for slowing down FiOS expansion.
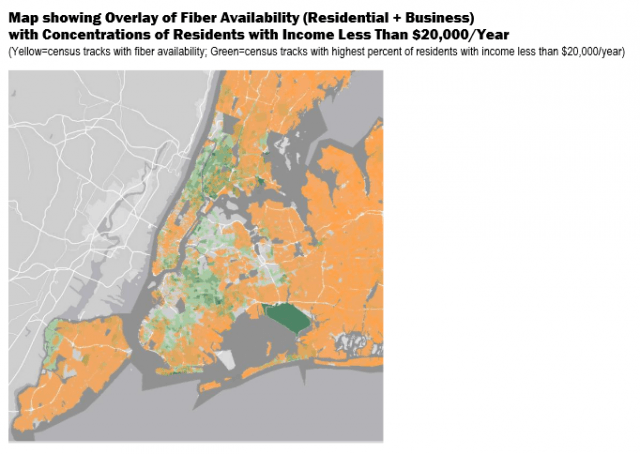
But de Blasio’s maps of FiOS availability do depict a pattern of preference for FiOS service in areas where higher income residents live. In areas where average annual income is below $20,000 annually, there are obvious service gaps. Neighborhoods like Washington Heights, High Bridge, Astoria, Woodside, Bedford-Stuyvesant and Bushwick have been largely excluded from FiOS to date, according to de Blasio.
Verizon’s franchise agreement with the city only requires the company to make service available to buildings, not necessarily within them. A landlord can delay Verizon’s entry into a building or the company could choose to prioritize some buildings over others for service.
With large sections of New York covered by multiple dwelling units like apartments and condos, some could find themselves without FiOS service for several years, particularly if a property owner decides to make life difficult for the phone company.
On May 24, Verizon notified the PSC the following property owners had complied with their request to conduct a site survey inside their buildings and were requested to be dropped from the list republished above:
- Sama Los Tres LLC – c/o Metropolitan Realty Group
- Lenoxville Associates – c/o Metropolitan Realty Group
- 2816 Roebling Avenue LLC
- East Village Gardens
- 194 Bleecker Street Owners Corp.
- US Manhattan II Housing Corp.
- 40 Renwick Street LLC


 Subscribe
Subscribe Despite findings from an independent consultant that reported West Virginia wasted millions on a broadband expansion effort that effectively built a private, taxpayer-funded fiber network for Frontier Communications, the governor’s office abruptly canceled a 2011 follow-up state audit of the $126.3 million project.
Despite findings from an independent consultant that reported West Virginia wasted millions on a broadband expansion effort that effectively built a private, taxpayer-funded fiber network for Frontier Communications, the governor’s office abruptly canceled a 2011 follow-up state audit of the $126.3 million project. Among ICF’s findings:
Among ICF’s findings: A major critic of the broadband stimulus program in West Virginia, Citynet President Jim Martin, has long said the broadband project was primarily going to benefit Frontier.
A major critic of the broadband stimulus program in West Virginia, Citynet President Jim Martin, has long said the broadband project was primarily going to benefit Frontier. AT&T says government regulations have hampered the company’s plans to roll out faster broadband networks to areas where consumers and businesses want faster speeds.
AT&T says government regulations have hampered the company’s plans to roll out faster broadband networks to areas where consumers and businesses want faster speeds.

 CenturyLink now sells up to 40Mbps speeds in Omaha, with a 300GB monthly usage cap. The company has not said if it intends to apply a usage limit on its fiber customers.
CenturyLink now sells up to 40Mbps speeds in Omaha, with a 300GB monthly usage cap. The company has not said if it intends to apply a usage limit on its fiber customers.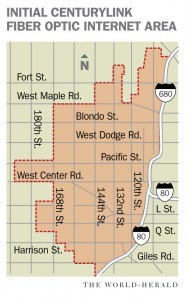 Only around 12% of metropolitan Omaha will have access to the experimental fiber service, primarily those living in West Omaha. The network will bypass residents that live further east. The boundaries of the forthcoming fiber network are notable: West Omaha comprises mostly affluent middle and upper class professionals and is one of the wealthiest areas in the metropolitan region. Winning a right to offer service on a limited basis within Omaha is an important consideration for telecom companies like CenturyLink.
Only around 12% of metropolitan Omaha will have access to the experimental fiber service, primarily those living in West Omaha. The network will bypass residents that live further east. The boundaries of the forthcoming fiber network are notable: West Omaha comprises mostly affluent middle and upper class professionals and is one of the wealthiest areas in the metropolitan region. Winning a right to offer service on a limited basis within Omaha is an important consideration for telecom companies like CenturyLink.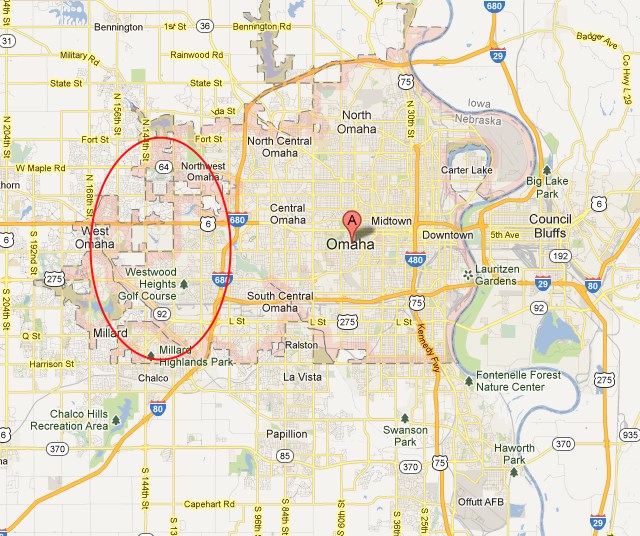

 “Until a few years ago, providers – just like the post – were just deliverers of packages,”
“Until a few years ago, providers – just like the post – were just deliverers of packages,” 
