
Verizon’s FiOS expansion is still dead.
Verizon Communications signaled today it plans further cuts in investments for its wireline network, which includes traditional copper-based telephone service and DSL as well as its fiber-optic network FiOS.
“We will spend more CapEx in the wireless side and we will continue to curtail CapEx on the wireline side,” Verizon’s chief financial officer Fran Shammo told investors this morning. “Some of that is because we are getting to the end of our committed build around FiOS.”
Instead of expanding its FiOS fiber to the home network to new areas, Verizon is trying to increase its customer base in areas previously wired. It is less costly to reconnect homes previously wired for FiOS compared with installing fiber where copper wiring still exists.
Verizon continues to lose traditional landline customers, so the company is increasingly dependent on FiOS to boost wired revenue. The fiber network now accounts for 77% of Verizon’s residential wireline revenue.
Wherever FiOS exists, it has taken a significant number of customers away from cable competitors. FiOS Internet has now achieved 41.1% market penetration, with 6.6 million customers, up 544,000 from last year. Of those, the majority want broadband speeds they were not getting from the cable company. At the end of 2014, 59% of FiOS Internet customers subscribe to broadband speeds above 50Mbps, up from 46% at the end of 2013.
 Despite the success of FiOS, Verizon’s senior management continues to devote more attention to its highly profitable Verizon Wireless division, spending an even larger proportion of its total capital investments on wireless services.
Despite the success of FiOS, Verizon’s senior management continues to devote more attention to its highly profitable Verizon Wireless division, spending an even larger proportion of its total capital investments on wireless services.
In 2014, Verizon spent $17.2 billion on capital expenditures, an increase of 3.5% over 2013. But only $5.8 billion was spent on maintaining and upgrading Verizon’s landline and FiOS networks, down 7.7% over 2013. Verizon Wireless in contrast was given $10.5 billion to spend in 2014. The company is using that money to add network density to its increasingly congested 4G LTE network. In many cities, Verizon Wireless is activating its idle AWS spectrum to share the traffic load and is accelerating deployment of small cell technology and in-building microcells to deal with dense traffic found in a relatively small geographic area — such as in sports stadiums, office buildings, shopping centers, etc.
Verizon Wireless is branding its network expansion “XLTE,” which sounds to the uninitiated like the next generation LTE network. It isn’t. “XLTE” simply refers to areas where expanded LTE bandwidth has been activated. Unfortunately, many Verizon Wireless devices made before 2014 will not benefit, unable to access the extra frequencies XLTE uses.
With Verizon increasing the dividend it pays shareholders, the company is also cutting costs in both its wired and wireless divisions:
- Verizon Wireless’ 3G data network will see a growing amount of its available spectrum reassigned to 4G data, which is less costly to offer on a per megabyte basis. As Verizon pushes more 4G-capable devices into the market, 3G usage has declined. But the reduced spectrum could lead to speed slowdowns in areas where 3G usage remains constant or does not decline as quickly as Verizon expects;
- Verizon will push more customers to use “self-service” customer care options instead of walking into a Verizon store or calling customer service;
- The company will continue to move towards decommissioning its copper wire network, especially in FiOS areas. Existing landline customers are being encouraged to switch to FiOS fiber, even if they have only landline service. Copper maintenance costs are higher than taking care of fiber optic wiring;
- Verizon has accelerated the closing down of many central switching offices left over from the landline era. As the company sells the buildings and property that used to serve its network, Verizon’s property tax bill decreases;
- Verizon will continue cutting its employee headcount. Shammo told investors in December, Verizon Communications cut an extra 2,300 employees that took care of its wired networks.


 Subscribe
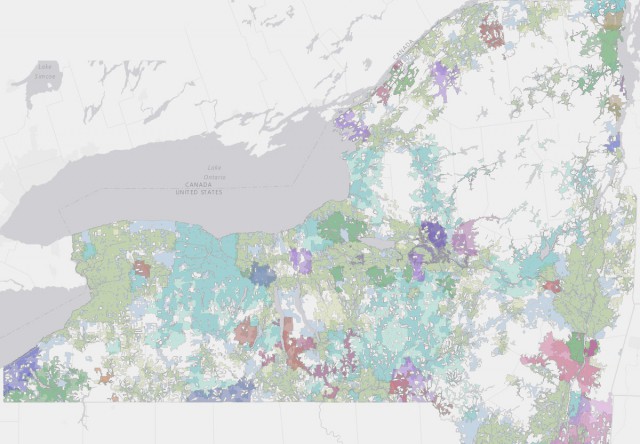
Subscribe New York will see at least $1 billion in investments to expand and improve rural broadband in upstate New York to bring Internet access to every home in the state by 2019, if the state legislature approves the budget for Gov. Andrew Cuomo’s New-New York Broadband Program.
New York will see at least $1 billion in investments to expand and improve rural broadband in upstate New York to bring Internet access to every home in the state by 2019, if the state legislature approves the budget for Gov. Andrew Cuomo’s New-New York Broadband Program.
 AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson’s public hissy fit against the Obama Administration’s sudden backbone on Net Neutrality may complicate AT&T’s plans to win approval of its merger with DirecTV. forcing AT&T to retract threats to suspend fiber buildouts if the administration moves forward with its efforts to ban Internet fast lanes.
AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson’s public hissy fit against the Obama Administration’s sudden backbone on Net Neutrality may complicate AT&T’s plans to win approval of its merger with DirecTV. forcing AT&T to retract threats to suspend fiber buildouts if the administration moves forward with its efforts to ban Internet fast lanes.
 The sleepy deep south isn’t often a battleground for an all-out broadband competition war, but Ridgeland, Miss.-based C Spire, a regional cell phone company with fiber broadband aspirations, has gotten too big for its britches and Comcast is preparing to demonstrate its size and resources can run even a home state provider into the ground.
The sleepy deep south isn’t often a battleground for an all-out broadband competition war, but Ridgeland, Miss.-based C Spire, a regional cell phone company with fiber broadband aspirations, has gotten too big for its britches and Comcast is preparing to demonstrate its size and resources can run even a home state provider into the ground. C Spire’s plans could cost Comcast a significant number of cable customers across Mississippi, and it isn’t taking that lightly.
C Spire’s plans could cost Comcast a significant number of cable customers across Mississippi, and it isn’t taking that lightly. New Zealanders want faster broadband and they want it without a usage cap, and Snap is ready to offer both.
New Zealanders want faster broadband and they want it without a usage cap, and Snap is ready to offer both. Snap’s new service comes as a result of New Zealand’s deployment of fiber networks and an end to usage caps, consumption billing, and/or bandwidth throttling. Snap has been well received in New Zealand because it guarantees no traffic shaping, traffic management schemes, or mandatory usage caps. This comes at a time when North American providers are trying to force customers into usage-capped broadband plans and wireless carriers insist on using traffic shaping and caps.
Snap’s new service comes as a result of New Zealand’s deployment of fiber networks and an end to usage caps, consumption billing, and/or bandwidth throttling. Snap has been well received in New Zealand because it guarantees no traffic shaping, traffic management schemes, or mandatory usage caps. This comes at a time when North American providers are trying to force customers into usage-capped broadband plans and wireless carriers insist on using traffic shaping and caps.