Sarasota County's current fiber networks are depicted on this map produced by the Sarasota Herald-Tribune
In many communities across America, there is more fiber optic cable on telephone poles and buried in underground conduit than you may realize. But as a consumer, you’ll never get to benefit from it because of a broadband duopoly that works hard to keep municipal fiber networks away from your home and out of your reach.
Take Sarasota County, Florida. The county is making preparations to build a 96-strand fiber network across the county, capable of delivering 100Gbps service over each strand, and early plans suggest they’ll use it for… controlling traffic signals and viewing traffic cameras. Taxpayers are ultimately paying the costs to construct the $1,000-per-mile fiber network, but current plans won’t allow any of them to access it.
Why? Because companies like Comcast and Verizon want it that way.
It’s nothing new and it’s not limited to Sarasota. In cities across the country, enormous capacity networks are devised and constructed to deliver high speed data connections to local hospitals, schools, and public safety institutions. Many states’ transportation departments have enormous excess fiber capacity, installed from federal and state grant money to develop intelligent traffic systems. But almost all of these networks are strictly off-limits to the general public and small business entrepreneurs who are stuck with the far slower broadband service the phone and cable companies deliver at ridiculously high prices.
Sarasota has had ultra-fast connections for years, delivering a dedicated 10Gbps connection to one area hospital and insanely fast connections to police departments and other government buildings. It’s managed by Comcast and was built for $3 million, paid for directly by Comcast subscribers. Comcast built the county I-Net network with the understanding that commercial use of the network was strictly prohibited.
The result is blazing fast speeds for institutions that can’t possibly utilize all of the capacity they have, and a broadband cartel delivering less service than local residents and businesses need.
The Sarasota Herald-Tribune considered the county’s fiber future so important, it dedicated a week of coverage to municipal fiber, and the providers and politics that get in the way.
The newspaper reports that the existing broadband duopoly under-delivers access to digital entrepreneurs that need those speeds the most.
The co-called creative class — bandwidth entrepreneurs on a budget — struggle to get by on mediocre connections that are largely repackaged retail offerings.
Over and over, businesses surveyed by the Herald-Tribune pointed to the tell-tale distinction between business-class service and retail.
“Businesses upload stuff, while consumers download,” said Rich Swier Jr., who works from a Central Avenue office where the only service comes from Comcast. Swier, the only entrepreneur on the Sarasota Broadband Task Force, is not happy with what he gets from Comcast. “They are repackaging a consumer grade service as a business service and charging three times more.”
Swier is paying about $200 per month for what is supposed to be 50 megabits per second download and 5 megabits up. But in reality, it operates at half those speeds, he said.

Thaxton
The newspaper’s conclusion: Fiber access is to modern business what train stations and interstate connections used to be.
Sarasota’s fiber project has grown considerably since its original proposition — 24 strands of fiber installed for $11 a foot. Then the county received an estimate that said they could have triple the amount of fiber for just 20 cents more per mile. Broadband enthusiasts urged the county to upgrade the network to 96 strands and they agreed.
Commissioner Jon Thaxton told the newspaper he views the planned fiber network as an insurance policy as Internet speed becomes more and more important.
“It does, at a minimum, put us in a position of not being wholly dependent on some other service provider,” Thaxton said.
The newspaper notes the economic implications of superior broadband are enormous.
Google sparked the issue when it announced plans earlier this year to hot-wire a city or cities somewhere in the United States, creating what could be a prototype for a community with the broadband speeds to more than command its economic future.
Our political leaders clearly saw the import of this. Heck, City Commissioner Dick Clapp even jumped into a shark tank to show Google the community’s spirit (yeah, they were pretty small sharks, but I wouldn’t do it, fiber or no fiber).
Businesses of the 21st century are hungry for fast speeds, and this region has been fortunate to land some with voracious appetites.
[…]Who would have pegged Lafayette, La., as a place where Hollywood would set up a first-rate special-effects studio? (Can you say the Walt Disney Co. as a customer?) But the fiber was there, and the big dogs came.
South of us, in Naples, it is private enterprise driving high-octane broadband, the work of a technology-savvy entrepreneur and a like-minded group of millionaires who want what many of us raising families in Southwest Florida are after: an economy that would allow our kids to remain here with good jobs.
In the Information Age, connectivity is going to be critical in attracting the kind of companies we want, and the well-heeled folks in Collier County know that. (They also clearly know how to make a lot of money, so don’t read their efforts too much as altruism).
Then you have one of the new 800-pound gorillas of the fiber effort, Allied Fiber, a New York-based company in the midst of creating a trans-continental broadband push akin to what the railroad barons of the 1800s accomplished.
Southwest Florida has a good chance of tapping into their $500 million (or more) play.
Competition from Municipal Providers Drives Prices Down and Speeds Up (New Rules Project)
The county established a Broadband Task Force, but made the same mistake so many other municipalities make when they create these panels: consumers are not represented at all and small business representation is limited to a single participant. Consumers will ultimately be a major source of revenue from municipal broadband projects and their needs and interests must be represented. Since incumbent commercial providers will seek to impede municipal competition by organizing consumer opposition to such projects, getting trusted consumer advocates and broadband evangelists on your side at the outset can make the difference between enthusiastic support for additional broadband choice or a mind-numbing, incumbent provider-driven sideshow about a “socialist government takeover of the Internet.”
The rest of the panel is made up of public officials from the school district, county and city government and the local hospital.
The newspaper hints these are exactly the wrong people to invite onto a Broadband Task Force. Virtually all already enjoy the generous bandwidth already provided by Comcast’s I-Net, few are likely to be well informed on broadband technology issues, and apart from the lone businessman on the panel, the group is unlikely to grasp the commercial implications of better broadband for the local digital economy.
Since these individuals all earn a paycheck protecting their own institutional interests, the larger vision of community broadband can easily get lost in turf wars and political disputes, or interference from incumbent providers.
Providers can cut the bottom out of such task forces with rewarding side deals for friends — enhanced services at fire sale prices. For institutional opponents — intransigence and crippling rate increases.
On Florida’s East Coast, Martin County’s public service institutions learned first hand what kind of pricing Comcast is capable of bringing to the table when an existing contract expired. Comcast demanded a whopper of a rate hike.
“We decided for the kind of money these people are asking us, we would be better off doing this on our own,” Kevin Kryzda, the county’s chief information officer, told the Sarasota paper. “That is different from anybody else. And then we said we would like to do a loose association to provide broadband to the community while we are spending the money to build this network anyway. That was unique, too.”
The last straw for county officials was the loss of a lucrative deal with California-based Digital Domain to build a Florida branch campus. The company chose St. Lucie County instead. John Textor, Digital Domain’s co-chairman, told the Herald-Tribune that having a local all-fiber network connection and being able to set up an all-fiber direct connection to remote servers in Miami was a key advantage of the site in Port St. Lucie.
After that, Martin County commissioners voted unanimously to obtain bids for their own network.
Martin County’s fiber network will combine a publicly-constructed institutional network and a tiny rural phone company paying part of the costs to resell excess capacity to commercial users. The downside is that consumers will not be offered service.
In Florida’s Lee and Collier Counties, U.S. Metro network has proved fiber’s ability to transform entire regions economically.
“If you build it, they will come” is a common rallying cry for fiber proponents. In both counties, they came. The latest arrival? Jackson Laboratory of Bar Harbor, Maine, now being showered with more than $200 million in government grants to build a genetic research campus in Collier County. A large portion of that money will end up staying in Collier County, stimulating the local economy and creating jobs.
Why all the clamor? Because U.S. Metro runs a network that puts incumbent phone and cable companies to shame. When a business requests service, owner Frank Mambuca doesn’t tell them what speeds they’ll have to live with. Instead, he asks, “how many gigabits do you want?”
Unfortunately, U.S. Metro also only sells service to businesses, but they have some wholesale customers that do serve consumers. Marco Island Cable and a sister company, NuVu are cable overbuilders that offer access to U.S. Metro’s broadband network at speeds and prices Comcast and CenturyLink can’t touch.

Marco Cable, a tiny independent provider, delivers faster speeds at lower prices.
Marco Cable is preparing to deliver fiber-based 75Mbps service for $99 a month, along with several other access plans that save at least $12.95 per month over Comcast’s prices, and undercuts CenturyLink’s DSL plans as well. The company also does something Comcast won’t — it promises unlimited Internet access and email accounts.
If someone wants even faster speeds, say 100Mbps, they can call Marco Cable and request it.
The highest download speed that Verizon offers [locally] at present is 50 megabits per second for $149.99 a month, according to spokesman Bob Elek.
NuVu is currently installing competing service in condos on the mainland. For the father and son team that run both Marco Cable and NuVu, their philosophy is radically different from most cable and phone companies — delivering as much broadband speed as customers can use at prices they can afford.
For existing providers, who have “marked up” prices for years, the competition’s lower prices threaten profits from delivering “good enough for you” speeds at the highest possible price.
For some, simply lowering prices and enhancing service to compete isn’t the answer — putting a stop to municipal competition at all costs is.
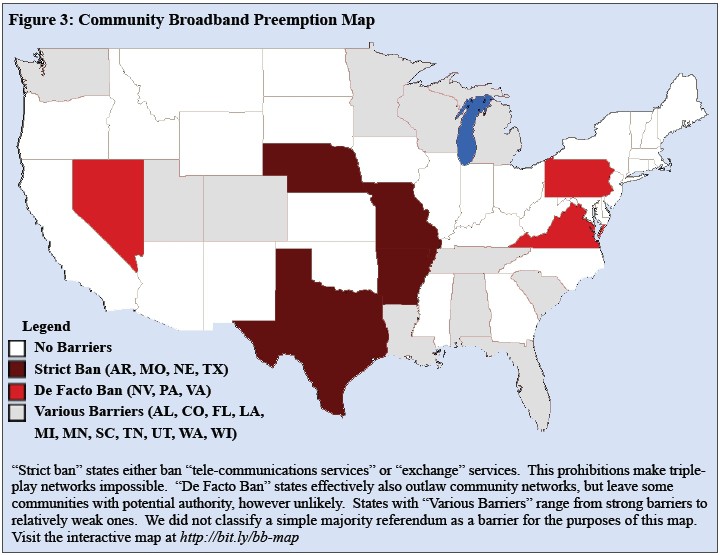
In 18 states, high priced lobbying campaigns financed by giant phone and cable operators have succeeded in restricting or banning competing providers. AT&T has been the most aggressive, successfully impeding competition in states like Texas, Wisconsin, Missouri, Arkansas, Michigan, Tennessee, and others. Comcast helped stop competition in its home state of Pennsylvania.
Click image to view interactive map
Year after year, Time Warner Cable and AT&T continue efforts to try and do the same in North Carolina, a potential hotbed of locally run, community-owned providers.
 For some towns and cities who have spent years begging for improved service, the clock has run out. The Sarasota Herald-Tribune used Wilson, N.C., as an excellent example. The city of 50,000 east of Raleigh decided it was through asking Time Warner Cable to provide a platform for a digital economic revival.
For some towns and cities who have spent years begging for improved service, the clock has run out. The Sarasota Herald-Tribune used Wilson, N.C., as an excellent example. The city of 50,000 east of Raleigh decided it was through asking Time Warner Cable to provide a platform for a digital economic revival.
Brian Bowman, public affairs manager for the city, told the newspaper the city faced economic disaster from twin blows — the loss of the textile industry and America’s waning interest in tobacco products. Giving the keys to the local cable company to drive Wilson’s nascent digital economy into Lake Wilson was simply not an option. The town would build its own digital highway — a municipal fiber to the home system for consumers and businesses.
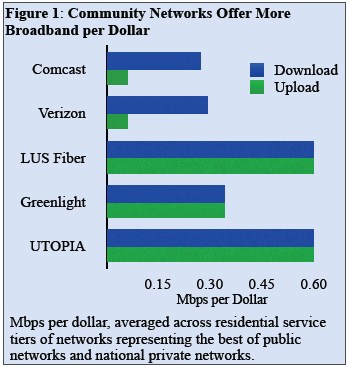 For both, Wilson’s Greenlight system provides up to 100 megabits per second in both directions. Time Warner Cable residential customers, in comparison, max out at 15/2 Mbps service.
For both, Wilson’s Greenlight system provides up to 100 megabits per second in both directions. Time Warner Cable residential customers, in comparison, max out at 15/2 Mbps service.
“The way we see it, you’re going to have haves and have-nots in the next generation broadband world,” Bowman said. “The fact is we wanted to invest in our own future; that’s why we did this.”
Cable and phone giants always are going to say that current speeds are adequate and that there is no need for cities to build expensive networks themselves, Bowman said.
“I have heard that here from some of the incumbents, that you don’t need to go that fast. I’m sure the folks in Florida were doing OK without I-4,” Bowman said, noting the state never would have gotten Disney World if not for that interstate access.
People in Sarasota County are about to hear all of the usual arguments against municipal service:
- “Taxpayers will pay for it.” — Not with revenue bonds they won’t. These bonds deliver returns to investors from revenue earned by the municipal provider, not from taxpayer dollars.
- “We want a level playing field.” — This cable industry opposed providing one when satellite and phone company IPTV showed up, as they tried to withhold programming and lobbied against both.
- “The government should stay out of the private sector.” — Christopher Mitchell, writing for the New Rules Project, tore apart that argument:
Governments “compete” with the private sector in many ways on a daily basis. Libraries compete with book stores, schools with private schools, public transit with taxis, police with security firms, even lumber yards, liquor stores, municipal golf courses and swimming pools with privately owned counterparts. Without public competition in the form of the Rural Electrification Authority, much of the country would still not be wired for electricity or phones.
The focus on whether local governments, who have a wholly different motivation than private companies, are “competing” with the private sector is a red herring to distract the public from incumbent providers’ failures to build modern networks. On matters of infrastructure, a community should always have the option to build the network it needs, just as it can build roads, bridges, water systems, and other modern necessities.
Ultimately, Sarasota County residents have two choices:
- Obtain the best traffic control and monitoring system America has ever seen, capable of delivering crisp, clear 1080p HD feeds of traffic tieups on Route 301.
- Deliver Sarasota County 21st century broadband that will power the digital economy and bring hundreds of millions in investment dollars, create thousands of new, high-paying jobs, and save local consumers and businesses a lot of money from broadband competition.
 CenturyLink’s stock is being pummeled after the company announced a cut in divided payouts to shareholders earlier this year, preferring to keep the money in-house to reduce debt and increase spending on necessary broadband upgrades.
CenturyLink’s stock is being pummeled after the company announced a cut in divided payouts to shareholders earlier this year, preferring to keep the money in-house to reduce debt and increase spending on necessary broadband upgrades. Investors were not impressed with those plans, and CenturyLink’s share price cratered.
Investors were not impressed with those plans, and CenturyLink’s share price cratered.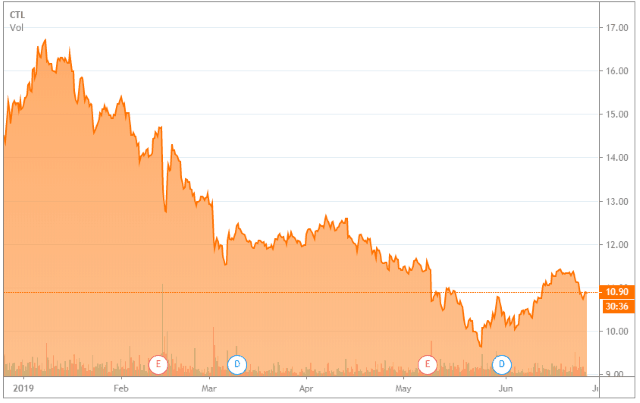


 Subscribe
Subscribe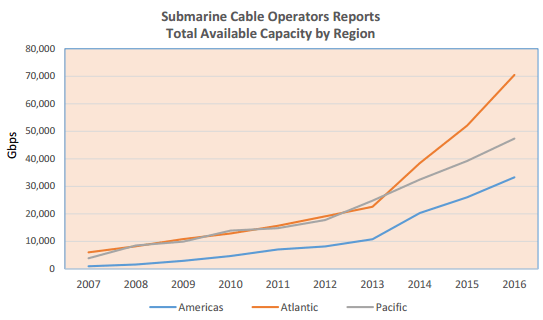 Overall submarine cable capacity, which supports a substantial amount of international Internet traffic, has grown around 36% per year for 2007-2014 and is expected to grow around 29% for 2014-2016. But traffic planners are confident the traffic growth will be easily accommodated over existing submarine cable circuits.
Overall submarine cable capacity, which supports a substantial amount of international Internet traffic, has grown around 36% per year for 2007-2014 and is expected to grow around 29% for 2014-2016. But traffic planners are confident the traffic growth will be easily accommodated over existing submarine cable circuits.
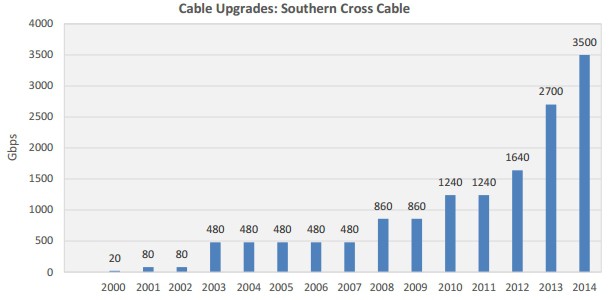 Southern Cross engineers are now deploying circuits capable of 40 and 100Gbps technology, bringing Southern Cross cable’s total available capacity to more than 12Tbps (12,000Gbps). Every upgrade was conducted at the cable station with zero new fiber pairs laid in the water. Other undersea cable operators are initiating similar upgrades, providing exponentially greater capacity at a minimal cost.
Southern Cross engineers are now deploying circuits capable of 40 and 100Gbps technology, bringing Southern Cross cable’s total available capacity to more than 12Tbps (12,000Gbps). Every upgrade was conducted at the cable station with zero new fiber pairs laid in the water. Other undersea cable operators are initiating similar upgrades, providing exponentially greater capacity at a minimal cost.

 Cox plans to limit its gigabit customers to 2TB of usage a month. AT&T U-verse with GigaPower has a (currently unenforced) limit of 1TB a month, while Suddenlink thinks 550GB is more than enough for its gigabit customers. Comcast is market testing 300GB usage caps in several cities but strangely has no usage cap on its usage-gobbling gigabit plan. Why cap the customers least-equipped to run up usage into the ionosphere while giving gigabit customers a free pass? It doesn’t make much sense.
Cox plans to limit its gigabit customers to 2TB of usage a month. AT&T U-verse with GigaPower has a (currently unenforced) limit of 1TB a month, while Suddenlink thinks 550GB is more than enough for its gigabit customers. Comcast is market testing 300GB usage caps in several cities but strangely has no usage cap on its usage-gobbling gigabit plan. Why cap the customers least-equipped to run up usage into the ionosphere while giving gigabit customers a free pass? It doesn’t make much sense.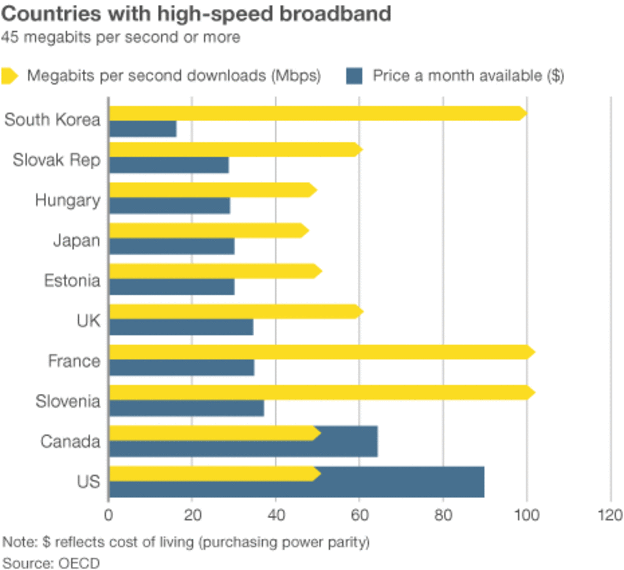
 The abuses were so bad, Congress finally stepped in and authorized regulators to break up the railroad monopolies and regulate abusive pricing. We may be headed in the same direction with broadband. We do not advocate regulation for the sake of regulation. Competition is a much more efficient way to check abusive business practices. But where an effective monopoly or duopoly exists, competition alone will not help. Without consumer-conscious oversight, the forthcoming gigabit broadband revolution will be stalled by speed bumps and toll booths for the benefit of a few giant telecommunications corporations. That will allow other countries to once again leap ahead of the United States and Canada, just as they have done with Internet speeds, delivering superior service at a lower price.
The abuses were so bad, Congress finally stepped in and authorized regulators to break up the railroad monopolies and regulate abusive pricing. We may be headed in the same direction with broadband. We do not advocate regulation for the sake of regulation. Competition is a much more efficient way to check abusive business practices. But where an effective monopoly or duopoly exists, competition alone will not help. Without consumer-conscious oversight, the forthcoming gigabit broadband revolution will be stalled by speed bumps and toll booths for the benefit of a few giant telecommunications corporations. That will allow other countries to once again leap ahead of the United States and Canada, just as they have done with Internet speeds, delivering superior service at a lower price.