Pai
The FCC under Chairman Ajit Pai “misrepresented facts and provided misleading responses” to the public and Congress about an alleged “distributed denial of service attack” (DDoS) that caused the FCC’s website to crash as millions of Americans shared their comments about net neutrality.
In a damning report released today by the FCC’s independent Inspector General, an investigation found the claimed attack never happened and the FCC’s ongoing public statements about it were demonstrably false.
The investigation into the alleged “attack” on the FCC’s electronic comment system (ECFS) on May 7-8, 2017 took several months to complete. Its findings were released after Pai was able to issue a broadly distributed press release critics claim is an effort to change the story and get ahead of the report itself, which was issued late this afternoon.
A DDoS attack overwhelms a website with a barrage of invalid traffic that eventually makes the target server unresponsive. The FCC claimed the attack was responsible for preventing people from leaving comments for hours after John Oliver brought up the subject of net neutrality on his HBO Show “Last Week Tonight” last year.
But in fact, it was the sheer volume of comments from the public that were responsible for slowing down the website — a politically inconvenient fact for net neutrality opponents (including Pai).
Highlights from the Inspector General’s 106-page report:
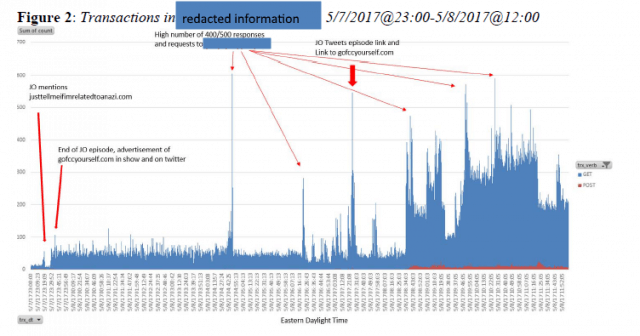
On May 7, 2017, at 11:30 pm EDT, the ECFS experienced a significant increase in the level of traffic attempting to access the system, resulting in the disruption of system availability. In fact, information obtained from, a contractor providing web performance and cloud security solutions to the FCC, identified a 3,116% increase in traffic to ECFS between May 7 and May 8, 2017.
The investigation matched traffic spikes to John Oliver’s show airing and the posting of videos and social media announcements about net neutrality.
On May 8, 2017, the FCC issued a press release in which the FCC’s former Chief Information Officer (CIO) Dr. David Bray provided the following statement regarding the cause of delays experienced by consumers trying to file comments on ECFS:
“Beginning on Sunday night at midnight, our analysis reveals that the FCC was subject to multiple distributed denial-of-service attacks (DDoS)[2]. These were deliberate attempts by external actors to bombard the FCC’s comment system with a high amount of traffic to our commercial cloud host. These actors were not attempting to file comments themselves; rather they made it difficult for legitimate commenters to access and file with the FCC. While the comment system remained up and running the entire time, these DDoS events tied up the servers and prevented them from responding to people attempting to submit comments. We have worked with our commercial partners to address this situation and will continue to monitor developments going forward.”
Our investigation did not substantiate the allegations of multiple DDoS attacks alleged by Bray. While we identified a small amount of anomalous activity and could not entirely rule out the possibility of individual DoS attempts during the period from May 7 through May 9, 2017, we do not believe this activity resulted in any measurable degradation of system availability given the miniscule scale of the anomalous activity relative to the contemporaneous voluminous viral traffic.
Here is what a net neutrality campaign going viral looks like. As Oliver’s show reached more viewers, many took time to visit the FCC’s website to submit comments, causing the server to slow to a crawl.
The degradation of ECFS system availability was likely the result of a combination of: (1) “flash crowd” activity resulting from the Last Week Tonight with John Oliver episode that aired on May 7, 2017 through the links provided by that program for filing comments in the proceeding; and (2) high volume traffic resulting from system design issues.
The conclusion that the event involved multiple DDoS attacks was not based on substantive analysis and ran counter to other opinions including those of the ECFS subject matter expert and the Chief of Staff.
As a result of our reviews and the findings articulated above, we determined the FCC, relying on Bray’s explanation of the events, misrepresented facts and provided misleading responses to Congressional inquiries related to this incident.
The fact millions of Americans were willing to visit a little-known FCC comment website to share their passionate views on net neutrality ran contrary to Chairman Pai’s claims that many comments were faked, demonstrated a lack of understanding of how net neutrality worked, or were otherwise not to be taken seriously. Pai even called net neutrality supporters “Chicken Littles” during a July 25 congressional hearing.
Pai’s public statements downplaying public comments on net neutrality might lose credibility if the FCC admitted the issue of net neutrality went viral and Americans were sharing their views in unprecedented numbers. Instead, the FCC repeatedly questioned the veracity of the comments, claimed an engineered attack — not dissent — caused the website to crash, and refused to participate in an investigation with the New York Attorney General’s office to uncover the origin of the alleged attack.

Pai’s press release tried to shift attention away from this damning conclusion from the FCC’s Inspector General.
Pai, in an effort to get out ahead of the unflattering report from the Inspector General, issued a press release blaming the affair on the flawed “culture” of the Obama Administration.
“I am deeply disappointed that the FCC’s former Chief Information Officer (CIO), who was hired by the prior Administration and is no longer with the Commission, provided inaccurate information about this incident to me, my office, Congress, and the American people,” Pai said in a statement. “This is completely unacceptable. I’m also disappointed that some working under the former CIO apparently either disagreed with the information that he was presenting or had questions about it, yet didn’t feel comfortable communicating their concerns to me or my office.”
“Second, it has become clear that in addition to a flawed comment system, we inherited from the prior Administration a culture in which many members of the Commission’s career IT staff were hesitant to express disagreement with the Commission’s former CIO in front of FCC management,” Pai added.
Jessica Rosenworcel, the only remaining Democrat on the Commission, dismissed Pai’s attempts to lay blame for the problems on the former administration.

Bray – the scapegoat?
“The Inspector General Report tells us what we knew all along: the FCC’s claim that it was the victim of a DDoS attack during the net neutrality proceeding is bogus,” said Rosenworcel. “What happened instead is obvious—millions of Americans overwhelmed our online system because they wanted to tell us how important Internet openness is to them and how distressed they were to see the FCC roll back their rights. It’s unfortunate that this agency’s energy and resources needed to be spent debunking this implausible claim.”
Pai’s chief scapegoat is David Bray, the FCC’s chief information officer from 2013-2017. Pai accused Bray of misleading him and other FCC officials about the source of the slowdowns and interruptions on the website.
“Yes, we’re 99.9% confident this was external folks deliberately trying to tie-up the server to prevent others from commenting and/or create a spectacle,” Pai quoted Bray as telling him during the May 2017 incident. Bray also acted as an anonymous source for several reporters, claiming a similar DDoS attack occurred in 2014 over net neutrality, a claim hotly disputed by FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler at the time and called “flat-out false” by Gigi Sohn, a senior counselor to Wheeler.

Fact or Fiction?: Bray claimed 4Chan’s “troll” army was invited to the fight by John Oliver.
Bray also claimed, without evidence, John Oliver “invited the ‘trolls'” from controversial website 4Chan to participate in the attack, suggesting the posting of Oliver’s segment on net neutrality was what “triggered the trolls.”
An exhaustive investigation of the FCC’s traffic logs found no evidence of an orchestrated DDoS attack, and the Inspector General used charts to show tremendous traffic spikes generated as Oliver’s campaign went viral.
Pai’s press release attempts to change the subject and divert attention away from the uncomfortable findings that suggest the FCC under his leadership openly deceived both the public and Congress. Instead of admitting he allowed the agency to continue claiming an outside attack on the FCC’s website was responsible for the incident, he praised himself and his office for what he claimed were findings that “debunk the conspiracy theory that my office or I had any knowledge that the information provided by the former CIO was inaccurate and was allowing that inaccurate information to be disseminated for political purposes.”
That directly contradicts the reports conclusion: “As a result of our reviews and the findings articulated above, we determined the FCC, relying on Bray’s explanation of the events, misrepresented facts and provided misleading responses to Congressional inquiries related to this incident.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe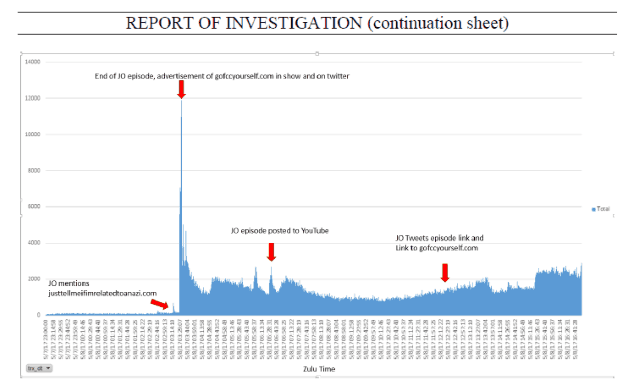
 Comcast has dropped sports network beIN Sports off the lineup after its contract with the cable company expired July 31.
Comcast has dropped sports network beIN Sports off the lineup after its contract with the cable company expired July 31. It took the four commissioners of the New York Public Service Commission just 20 minutes to vote unanimously to undo the multi-billion dollar 2016 merger of Charter Communications and Time Warner Cable, by
It took the four commissioners of the New York Public Service Commission just 20 minutes to vote unanimously to undo the multi-billion dollar 2016 merger of Charter Communications and Time Warner Cable, by  After Stop the Cap! and other consumer groups participated in a detailed review of Charter Communications’ proposal to acquire Time Warner Cable, the Public Service Commission adopted many of our pro-consumer suggestions to ensure the merger benefited the people of New York at least partly as much as the executives and shareholders of the two companies. New York State law demands that telecommunications mergers must meet a public interest test to win approval. On its face, the Commission found the Charter/Time Warner Cable proposal failed to meet this test. The state received detailed evidence showing Time Warner Cable’s existing upgrade plan offered a better deal to New York residents than Charter’s own proposal. Time Warner Cable also maintained a large workforce in New York in call centers, direct hire technicians, and its corporate headquarters.
After Stop the Cap! and other consumer groups participated in a detailed review of Charter Communications’ proposal to acquire Time Warner Cable, the Public Service Commission adopted many of our pro-consumer suggestions to ensure the merger benefited the people of New York at least partly as much as the executives and shareholders of the two companies. New York State law demands that telecommunications mergers must meet a public interest test to win approval. On its face, the Commission found the Charter/Time Warner Cable proposal failed to meet this test. The state received detailed evidence showing Time Warner Cable’s existing upgrade plan offered a better deal to New York residents than Charter’s own proposal. Time Warner Cable also maintained a large workforce in New York in call centers, direct hire technicians, and its corporate headquarters.

 The Commission has fined Charter $1 million for missing its December targets and another $1 million for not making good on correcting its earlier failures. On Friday, it fined Charter once again for another $1 million, reaching a total of $3 million in fines. The PSC also directed its Counsel to bring an enforcement action in State Supreme Court to seek additional penalties for past failures and ongoing non-compliance with its obligations. Earlier this month, the PSC referred a false advertising claim to the Attorney General’s office regarding Charter’s misleading ads about its progress expanding rural broadband in New York.
The Commission has fined Charter $1 million for missing its December targets and another $1 million for not making good on correcting its earlier failures. On Friday, it fined Charter once again for another $1 million, reaching a total of $3 million in fines. The PSC also directed its Counsel to bring an enforcement action in State Supreme Court to seek additional penalties for past failures and ongoing non-compliance with its obligations. Earlier this month, the PSC referred a false advertising claim to the Attorney General’s office regarding Charter’s misleading ads about its progress expanding rural broadband in New York. What has gotten the company’s intention is a 4-0 unanimous vote to cancel the approval of the company’s merger agreement with the state, which effectively puts Charter out of business in New York. The Commission ordered Charter to file a plan within 60 days detailing how it plans to cease service in New York and transition to another provider without causing any service disruptions for customers.
What has gotten the company’s intention is a 4-0 unanimous vote to cancel the approval of the company’s merger agreement with the state, which effectively puts Charter out of business in New York. The Commission ordered Charter to file a plan within 60 days detailing how it plans to cease service in New York and transition to another provider without causing any service disruptions for customers. After the inspector general of the Federal Communications Commission opened an investigation into FCC Chairman Ajit Pai’s close relationship with executives at Sinclair Broadcasting, Pai stopped returning Sinclair’s phone calls and refused any further meetings with America’s largest local TV station owner, at least until last Tuesday when Pai called Sinclair’s general counsel to say its multi-billion dollar merger with Tribune Media was in trouble.
After the inspector general of the Federal Communications Commission opened an investigation into FCC Chairman Ajit Pai’s close relationship with executives at Sinclair Broadcasting, Pai stopped returning Sinclair’s phone calls and refused any further meetings with America’s largest local TV station owner, at least until last Tuesday when Pai called Sinclair’s general counsel to say its multi-billion dollar merger with Tribune Media was in trouble.



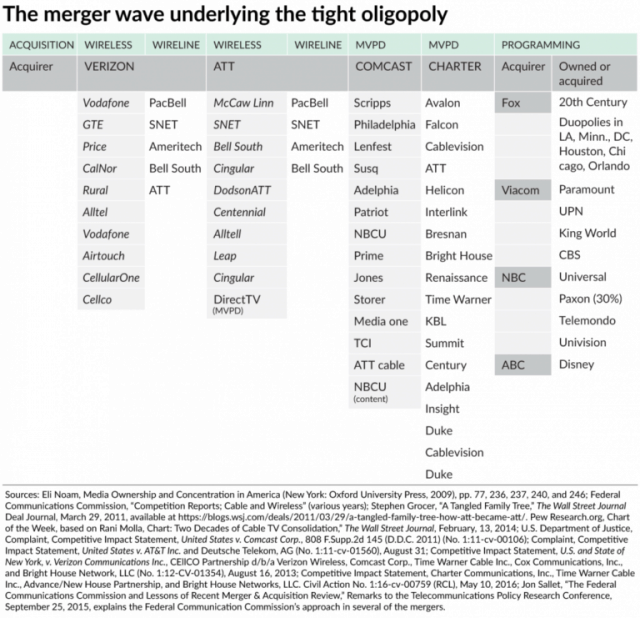
 The original premise of the 1996 Telecom Act was that it would eliminate regulations that discouraged competition. Promoters of the legislation asked why there should only be one phone or cable company in each city and why maintain regulations that kept cable and phone companies out of each others’ markets. Fears about market power and allowing domineering cable and phone companies to grow even larger were dismissed on the premise that a wide open marketplace, with regulations in place to protect consumers and competition would avoid creating telecom robber barons.
The original premise of the 1996 Telecom Act was that it would eliminate regulations that discouraged competition. Promoters of the legislation asked why there should only be one phone or cable company in each city and why maintain regulations that kept cable and phone companies out of each others’ markets. Fears about market power and allowing domineering cable and phone companies to grow even larger were dismissed on the premise that a wide open marketplace, with regulations in place to protect consumers and competition would avoid creating telecom robber barons. Some of the bill’s industry backers were also there, some who would ironically see its signing as directly responsible for the eventual demise of their independent companies. John Hendricks of the Discovery Channel, Glenn Jones of Jones Intercable (acquired by Comcast in 1999), Jean Monty of Northern Telecom (later Nortel), Donald Newhouse of Advance Publications (eventual part owner of Bright House Networks and later Charter Communications), William O’Shea of Reuters Ltd. and Ray Smith of Bell Atlantic (today part of Verizon) were on hand. Also in the audience was Jack Valenti of the Motion Picture Association of America, representing Hollywood Studios.
Some of the bill’s industry backers were also there, some who would ironically see its signing as directly responsible for the eventual demise of their independent companies. John Hendricks of the Discovery Channel, Glenn Jones of Jones Intercable (acquired by Comcast in 1999), Jean Monty of Northern Telecom (later Nortel), Donald Newhouse of Advance Publications (eventual part owner of Bright House Networks and later Charter Communications), William O’Shea of Reuters Ltd. and Ray Smith of Bell Atlantic (today part of Verizon) were on hand. Also in the audience was Jack Valenti of the Motion Picture Association of America, representing Hollywood Studios. For example, lawmakers insisted on unbundling telecommunications network elements, an arcane way of saying new competitors must be granted access to existing networks to be shared at wholesale rates. In practice, this meant if a phone company entered the internet service provider business, it must also make its network available for other ISPs as well. In some areas, competing local telephone companies also offered landline service over existing telephone lines, paying wholesale connection fees to the incumbent local phone company. As competition emerged, the incumbent company usually petitioned for a lifting of the regulations governing their business, claiming competition had arrived.
For example, lawmakers insisted on unbundling telecommunications network elements, an arcane way of saying new competitors must be granted access to existing networks to be shared at wholesale rates. In practice, this meant if a phone company entered the internet service provider business, it must also make its network available for other ISPs as well. In some areas, competing local telephone companies also offered landline service over existing telephone lines, paying wholesale connection fees to the incumbent local phone company. As competition emerged, the incumbent company usually petitioned for a lifting of the regulations governing their business, claiming competition had arrived.