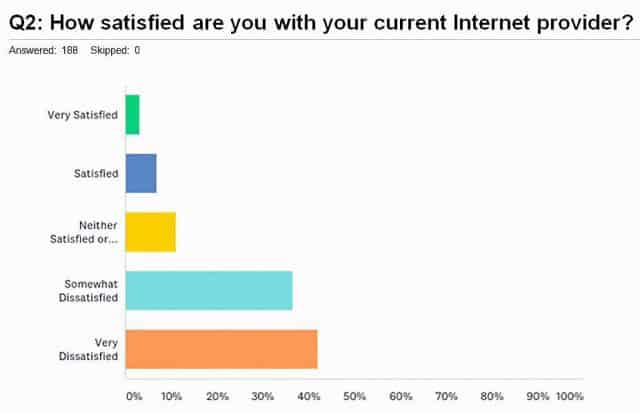
Bad results for Frontier DSL in Nevada. (Source: Elko Residential Broadband Survey)
Only six Frontier Communications customers surveyed in Elko, Nev. gave the phone company an “A” for its DSL service, while 42% flunked Frontier for what they considered unacceptable internet service.
The Elko Broadband Action Team has surveyed residential and business customers about broadband performance and found widespread dissatisfaction with Frontier Communications over slow connections and service interruptions.
“I’m pretty disappointed in them,” said Elko councilman John Patrick Rice.
Businesses and residential customers were in close agreement with each other rating Frontier’s service, with nearly 87% complaining they endure buffering delays or slowdowns, especially when watching streaming video. When browsing web pages, nearly three-quarters of surveyed customers still found service lacking.
Among the complaints (Res)-Residential (Bus)-Business:
- Service interruptions: 74.43% (Res)/79.69% (Bus)
- Too slow/not receiving advertised speed: 72.16% (Res)/65.75% (Bus)
- Price: 63.64% (Res)/37.5% (Bus)
- Customer Service: 38.07% (Res)/45.31% (Bus)
The Nevada Attorney General’s Bureau of Consumer Protection received a steady stream of complaints about Frontier’s DSL service in the state over the past year.
Answering the survey question, “would you be interested in faster download and upload speeds at prices that are somewhat comparable to what you are paying now?” 97.87 percent of residential respondents said yes.
 Frontier representatives responded to the survey results at a March 27 Elko City Council meeting.
Frontier representatives responded to the survey results at a March 27 Elko City Council meeting.
“Frontier did recognize it could improve upstream and downstream flow and educated the council and the public on some of the issues,” Elko assistant city manager Scott Wilkinson said.
Javier Mendoza, director of public relations for Frontier’s West region, explained much of the area Frontier services in Nevada is very rural, so customers are “located many miles from the core Frontier network facilities used to provide broadband service, which makes it technologically and economically challenging to provide faster internet speeds. However, Frontier is continually evaluating and working to improve its network and has and will continue to undertake various initiatives at a customer and community level to enhance its internet services.”
Mendoza said Frontier was currently testing fixed wireless internet service to serve rural areas, but had few details about the service or when it might be available.
 Frontier also noted internet traffic was up 25% in the Elko area, primarily as a result of video streaming, social media, and cloud services.
Frontier also noted internet traffic was up 25% in the Elko area, primarily as a result of video streaming, social media, and cloud services.
But Councilmen Reece Keener complained Frontier was underinvesting in its network, meaning the company is not well-equipped to deal with increases in demand, something Mendoza denied.
“Several areas of the network providing internet service to Elko have been and continue to be upgraded, providing enhanced service reliability, and ultimately will enable new and upgraded services,” Mendoza said.
It can’t come soon enough for students of Great Basin College, where those taking online courses using Frontier DSL have problems uploading their assignments, claimed Rice, who taught online classes at the college.
“We can get the classes out to the students, but the challenge is for students to get assignments back to the college,” Rice said in a phone interview with the Elko Daily Free Press.
Frontier also claimed improved service performance so far in 2018, up from the fourth quarter of 2017. The company claimed 98.3% of service orders met performance goals, up from 94.37% and commitments met scored at 92 percent, up from 89.98 percent. Trouble tickets declined from 1,712 to 1,244 across Nevada, the company also claimed.


 Subscribe
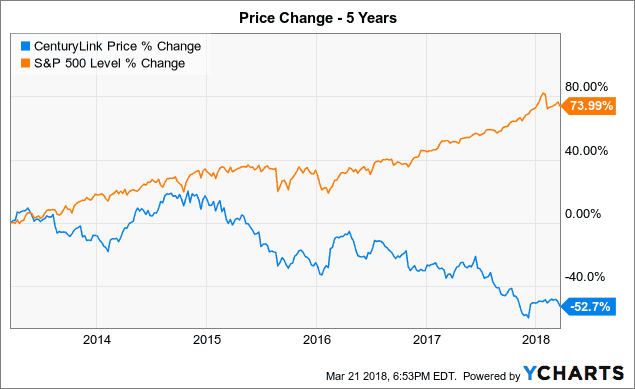
Subscribe CenturyLink is ready to capitulate in its competitive war with the cable industry, conceding its residential broadband business is a money loser that will no longer get broad-based upgrades and investment under the management of incoming CEO Jeff Storey, who will refocus CenturyLink on its larger business/enterprise customers.
CenturyLink is ready to capitulate in its competitive war with the cable industry, conceding its residential broadband business is a money loser that will no longer get broad-based upgrades and investment under the management of incoming CEO Jeff Storey, who will refocus CenturyLink on its larger business/enterprise customers.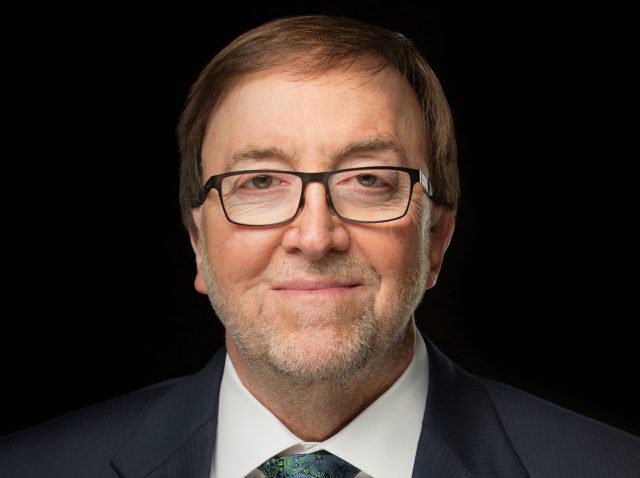
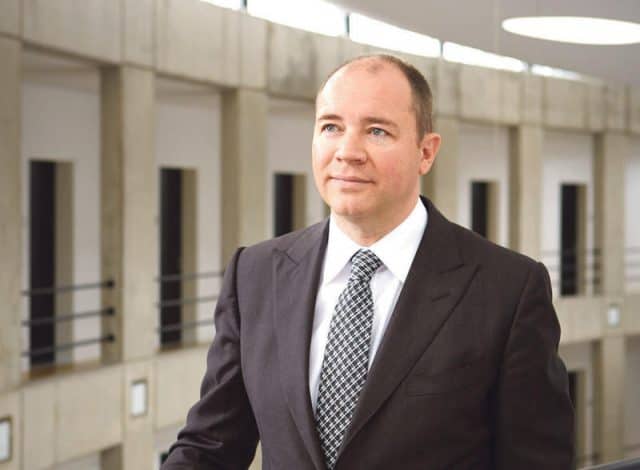

 Deutsche Telekom (DT) is frequently blamed for the mediocrity of German broadband. Its CEO Tim Hoettges has been heavily criticized for his decision to embrace upgrading its existing copper-based DSL service with “vectoring” instead of rebuilding its network using fiber optics. Although vectoring can significantly improve the speed of DSL connections, critics say it is a technological dead-end and further upgrades are limited and costly.
Deutsche Telekom (DT) is frequently blamed for the mediocrity of German broadband. Its CEO Tim Hoettges has been heavily criticized for his decision to embrace upgrading its existing copper-based DSL service with “vectoring” instead of rebuilding its network using fiber optics. Although vectoring can significantly improve the speed of DSL connections, critics say it is a technological dead-end and further upgrades are limited and costly.
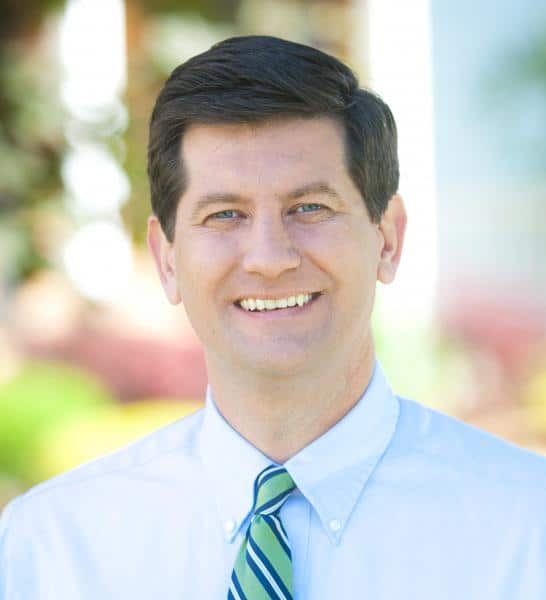


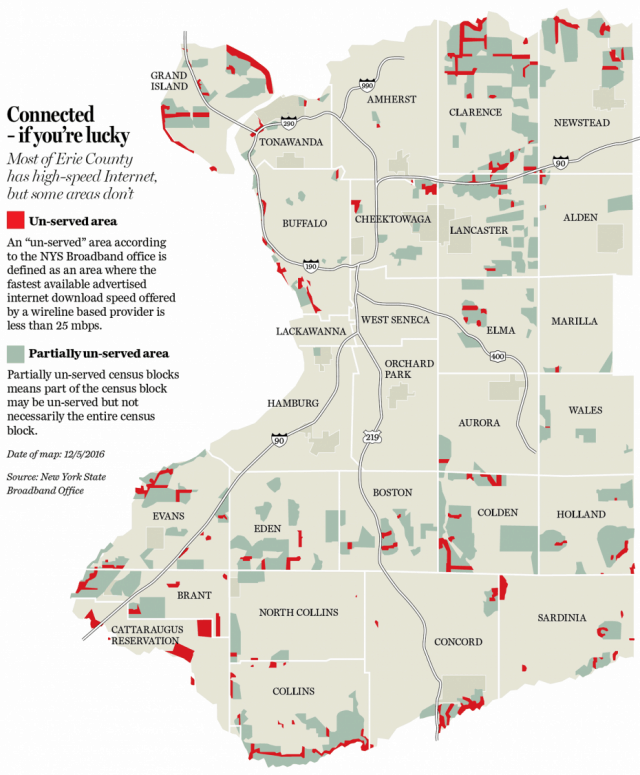 Rep. Chris Collins, a Clarence-area congressman with close ties to the Trump White House, defended FCC Chairman Ajit Pai’s recent decision to eliminate net neutrality. Pai was born in Buffalo.
Rep. Chris Collins, a Clarence-area congressman with close ties to the Trump White House, defended FCC Chairman Ajit Pai’s recent decision to eliminate net neutrality. Pai was born in Buffalo. Just shy of 10 years after FairPoint Communications acquired Verizon’s landline properties in the northern New England states of Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, both the company and its name are disappearing forever.
Just shy of 10 years after FairPoint Communications acquired Verizon’s landline properties in the northern New England states of Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, both the company and its name are disappearing forever. By early 2016, executives claimed their “turnaround” plan for FairPoint had made significant strides. By that summer, activist shareholders were demanding FairPoint be put up for sale, in part to allow them to quickly recoup their investments in company debt that could not be monetized unless another company acquired FairPoint and assumed those debts.
By early 2016, executives claimed their “turnaround” plan for FairPoint had made significant strides. By that summer, activist shareholders were demanding FairPoint be put up for sale, in part to allow them to quickly recoup their investments in company debt that could not be monetized unless another company acquired FairPoint and assumed those debts. Promised broadband upgrades from speed increases come with few details, except a broad commitment to raise speeds for 300,000 internet customers over the course of this year — which represents about 30% of FairPoint customers. Spokeswoman Angelynne Amores claims there will be no price hikes for faster internet speeds.
Promised broadband upgrades from speed increases come with few details, except a broad commitment to raise speeds for 300,000 internet customers over the course of this year — which represents about 30% of FairPoint customers. Spokeswoman Angelynne Amores claims there will be no price hikes for faster internet speeds.