CableLabs has published a new specification for the DOCSIS 3.1 cable broadband platform that will support <1 ms latency, optimal for online gaming and virtual reality.
CableLabs has published a new specification for the DOCSIS 3.1 cable broadband platform that will support <1 ms latency, optimal for online gaming and virtual reality.
The new specification, dubbed low-latency DOCSIS (LLD), costs little to implement with a simple software upgrade, but some cable companies plan to charge customers nearly $15 a month more to enable the extra performance.
VR needs incredibly low latency between head movement and the delivery of new pixels to your eyes, or you start to feel nauseated. To move the PC out of the home, we need to make the communications over the cable network be a millisecond or less round trip. But our DOCSIS® technology at the time could not deliver that.
So, we pivoted again. Since 2016, CableLabs DOCSIS architects Greg White and Karthik Sundaresan have been focused on revolutionizing DOCSIS technology to support sub-1ms latency. Although VR is still struggling to gain widespread adoption, that low and reliable DOCSIS latency will be a boon to gamers in the short term and will enable split rendering of VR and augmented reality (AR) in the longer term. The specifications for Low Latency DOCSIS (as a software upgrade to existing DOCSIS 3.1 equipment) have been released, and we’re working with the equipment suppliers to get this out into the market and to realize the gains of a somewhat torturous innovation journey.
Your provider may already have LLD capability — the updates were pushed to cable operators in two stages, one in January and the most recent update in April. It will be up to each cable company to decide if and when to enable the feature. Additionally, low latency is only possible if the path between your provider and the gaming server has the capability of delivering it. Cable companies may need to invite some gaming platforms, such as 비트코인 카지노, to place servers inside their networks to assure the best possible performance.
Cable operators are already conceptualizing LLD as a revenue booster. Cox Communications is already testing a low-latency gaming add-on with customers in Arizona, for which it charges an extra $14.99 a month. But reports from customers using it suggest it is not a true implementation of LLD. Instead, many users claim it is just an enhanced traffic routing scheme to reduce latency using already available technology.
A Cox representative stressed the service does not violate any net neutrality standards.
“This service does not increase the speed of any traffic, and it doesn’t prioritize gaming traffic ahead of other traffic on our network,” said CoxJimR on the DSL Reports Cox forum. “The focus is around improving gaming performance when it leaves our network and goes over the public internet, like a Gamer Private Network. No customer’s experience is degraded as a result of any customers purchasing Cox Elite Gamer service as an add-on to their internet service.”
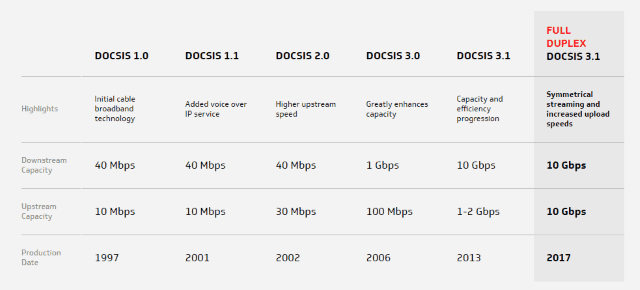
CableLabs is treating LLD as a part of its “10G” initiative, expected to upgrade broadband speeds up to 10 Gbps. Among the next upgrades likely to be published is full duplex DOCSIS, which will allow cable operators to provide the same upload and download speeds.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Charter Spectrum sold its merger with Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks partly on its argument that modem fees would no longer be charged. Despite that, many former Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers still use their own modems, which has been a problem for a company that raised the standard internet speed available to residential customers from 15 Mbps to 100 Mbps (200 Mbps in some markets, mostly those also served by AT&T). Older modems often cannot achieve those speeds. Spectrum notifies affected customers in periodic campaigns, offering to replace their obsolete equipment, but many customers suspect hidden fees may be lurking in such offers and discard them.
Charter Spectrum sold its merger with Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks partly on its argument that modem fees would no longer be charged. Despite that, many former Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers still use their own modems, which has been a problem for a company that raised the standard internet speed available to residential customers from 15 Mbps to 100 Mbps (200 Mbps in some markets, mostly those also served by AT&T). Older modems often cannot achieve those speeds. Spectrum notifies affected customers in periodic campaigns, offering to replace their obsolete equipment, but many customers suspect hidden fees may be lurking in such offers and discard them. Cox is also in a similar predicament. It runs seasonal checks on its network to identify customers using older DOCSIS modems, often DOCSIS 3.0 4×4 modems, which can only support four download channels. When it finds customers eligible for an upgrade, it mails postcards offering a “free modem upgrade,” usually supplying a SB6183 or SB8200 modem that can arrive in 24-48 hours. But many Cox customers suspect trickery from Cox as well, or run into poorly trained customer service representatives that reject the postcards, claiming the customer is ineligible.
Cox is also in a similar predicament. It runs seasonal checks on its network to identify customers using older DOCSIS modems, often DOCSIS 3.0 4×4 modems, which can only support four download channels. When it finds customers eligible for an upgrade, it mails postcards offering a “free modem upgrade,” usually supplying a SB6183 or SB8200 modem that can arrive in 24-48 hours. But many Cox customers suspect trickery from Cox as well, or run into poorly trained customer service representatives that reject the postcards, claiming the customer is ineligible. In fact, most modem upgrade offers from your provider are likely genuine, but customers need to pay attention to any fine print.
In fact, most modem upgrade offers from your provider are likely genuine, but customers need to pay attention to any fine print.


 Charter is facing competitive pressure from Google and telephone company competitors upgrading to fiber to the home service. Hawaiian Telcom, for example, now offers
Charter is facing competitive pressure from Google and telephone company competitors upgrading to fiber to the home service. Hawaiian Telcom, for example, now offers  CableLabs has resolved the cable industry’s long-standing competitive disadvantage with fiber optic broadband with the introduction of a Full Duplex (FDX) DOCSIS 3.1 specification.
CableLabs has resolved the cable industry’s long-standing competitive disadvantage with fiber optic broadband with the introduction of a Full Duplex (FDX) DOCSIS 3.1 specification.