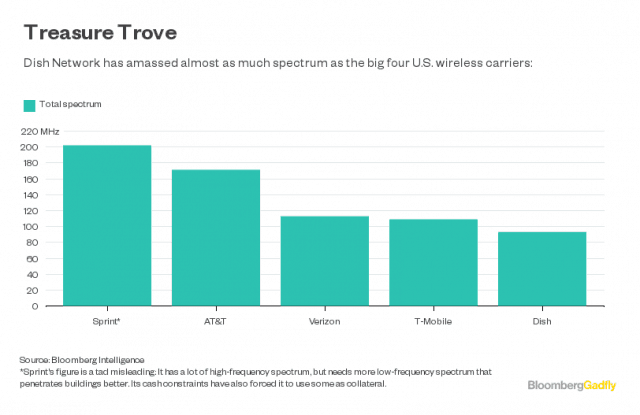
 Among the major wireless companies with spectrum holdings worth billions, few would suspect that the fifth largest (behind Sprint, AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile) is the satellite television company Dish Networks.
Among the major wireless companies with spectrum holdings worth billions, few would suspect that the fifth largest (behind Sprint, AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile) is the satellite television company Dish Networks.
After spending nearly $20 billion over the last ten years acquiring nearly 95 MHz of extremely valuable low and mid-band spectrum in markets across the United States, Dish is the largest wireless company that isn’t actually providing wireless service. Critics have questioned whether Dish co-founder Charlie Ergen was ever really interested in getting into the wireless business when he could make an even bigger killing warehousing spectrum until it grows in value and can be profitably sold to someone else. One Wall Street analyst thinks there is a strong case for exactly that. Cowen and Company estimates Dish’s holdings are now worth $30.2 billion — a $10 billion profit possible from keeping spectrum off the market until a buyer is willing to make an offer Dish cannot refuse.
Unfortunately for Ergen, spectrum is public property and ultimate ownership rights can never be sold or transferred. Instead, the FCC licenses companies to use the public airwaves, and has provisions to take them back if a company does not put that spectrum to good use. For Dish Networks, the first important deadline is March 2020, by which time the FCC expects Dish to achieve at least 70% market coverage of its 700 MHz “E-Block” and 2000-2020/2180-2200 MHz AWS-4 licenses.
Dish’s “E-Block” spectrum was formerly known as UHF channel 56. Dish has already begun testing the next-generation TV standard ATSC 3.0 on its E-Block spectrum in Dallas, as part of a joint venture with TV station owners Sinclair, Nexstar, and Univision. Dish proposed to use this spectrum, which covers 95% of the United States, as a potential tool for broadcasters. Among the services Dish could offer are broadcast data applications made possible with the ATSC 3.0 standard.
 Because time and money is on the line, Dish needs to either build its network quickly or sell/lease its spectrum to other companies before facing possible spectrum forfeiture in less than two years. Analysts say one of the cheapest and easiest ways of placating the FCC is to deploy a modest, narrowband wireless network designed for machine-to-machine communications. These networks rely on short bursts of data to communicate information. Possible applications include exchanging irrigation and crop data collected from wireless sensors and various remote weather and climate measurement tools.
Because time and money is on the line, Dish needs to either build its network quickly or sell/lease its spectrum to other companies before facing possible spectrum forfeiture in less than two years. Analysts say one of the cheapest and easiest ways of placating the FCC is to deploy a modest, narrowband wireless network designed for machine-to-machine communications. These networks rely on short bursts of data to communicate information. Possible applications include exchanging irrigation and crop data collected from wireless sensors and various remote weather and climate measurement tools.
Coincidentally, that is exactly the kind of network Ergen initially envisions, largely operating on the sparsely used AWS bands. Officially called “NB-IoT” in wireless industry parlance, the ‘narrowband Internet of Things’ network would be the first chapter of Dish’s wireless story. It’s a network done on the cheap — constructed with a relatively low investment of $500 million to $1 billion through 2020, adequate enough to keep the FCC off Dish’s back.
Ergen reports the radios have been ordered and in a sign of serious intent, Dish has now signed master lease agreements with cell tower companies that will allow Dish to place its transmission equipment on tens of thousands of cell towers around the country. The company has also hired experts in tower permitting and network design and planning. Those contracts are an important indicator for some skeptics on Wall Street who believed Ergen would not show seriousness of intent until he signed paid, binding commitments to begin network buildout.
Ergen would disagree that Dish has been foot-dragging its wireless network deployment, despite a decade of accumulating wireless spectrum that has gone unused.
“It’s all about timing; too early you are roadkill, if you get it just right you have a chance,” Ergen said. “We missed the 4G shift because of the regulatory reasons. The next big paradigm shift is 5G.”

Ergen
Unfortunately for Ergen, he will be late to that paradigm shift, admitting his dream of a national 5G network isn’t possible right now.
“We’re […] going to spend at least $10 billion or more on a 5G network,” Ergen said, while also admitting, “we don’t have that kind of capital on our balance sheet today.”
Ergen promised that sometime in the future, Dish will begin a “second phase” that will “build a complete 5G network.” But Ergen’s vision of 5G is somewhat different from Verizon and AT&T, which are focused on the consumer and business voice and data markets. Ergen envisions a robust 5G network designed to support IoT applications like smart cities, artificial intelligence, and autonomous vehicles, and does not seem interested launching a fifth national cell provider.
Ergen quit in December 2017 as CEO of Dish’s aging satellite TV business to refocus on Dish’s mobile future, and to recast the venture as a glorified startup, much like his early days in the home satellite television business where he got into the business manufacturing 10-foot C-band satellite dishes for consumers and then sold the programming to watch on those dishes. From money earned in that business, Ergen launched Dish Networks, which relies on today’s familiar small satellite dishes and competes with DirecTV.
Ergen’s satellite TV venture only had to compete with one other satellite provider. His wireless network will have to compete with at least four established national wireless companies, plus emerging competition from the cable industry and regional cellular providers. Ergen tried to turn that obvious business challenge into an opportunity:
“We have two disadvantages; We don’t [have many] customers and we are not as knowledgeable as other people in the business, but we don’t have the legacy of 2G, 3G, 4G networks,” Ergen said. “We have a clean sheet of paper with 5G. It reminds me of 1990 when we decided to reinvent ourselves from the big dish business to small dish. It took five years to design and build that system with not one penny of revenue, and we obsoleted the business we were in. When we got into satellites, we didn’t know anything about it, but neither did anyone else. It is the same with 5G/IoT. We are not the world’s experts, but neither is anyone else.”
What Ergen lacks in experience he makes up for in enthusiasm, laying out plans for Dish’s wireless future. By the time he activates 5G service, Dish expects to use its combined 95 MHz of spectrum in the 600 MHz and 2 GHz range for that network. That will take until at least July 2020, because many of the 600 MHz frequencies he needs are still occupied by UHF television stations that are in the process of migrating to a more compact UHF band.
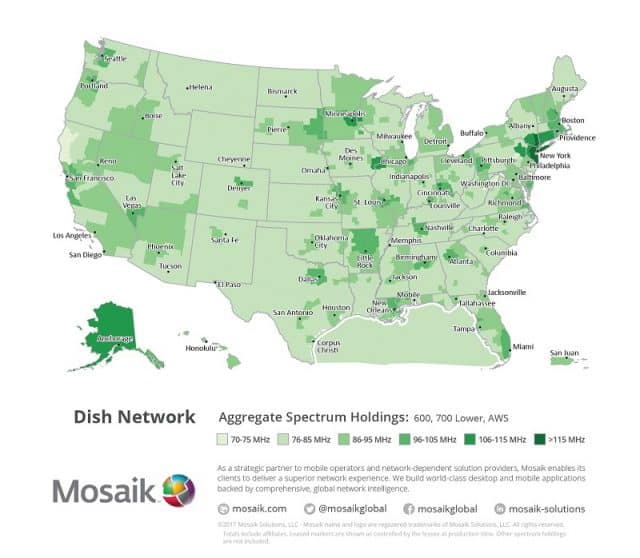
Dish has spectrum holdings that reach almost every corner in the U.S.
Ergen may also consider acquiring additional millimeter wave spectrum if he deploys small cell technology. He has even decided to keep small cell and larger traditional “macrocells” found on traditional cell towers on different frequencies, claiming sharing the frequencies would create interference issues.
Ergen also hopes to convince the FCC to repurpose little-known Multichannel Video Distribution and Data Service (MVDDS) spectrum located between 12.2-12.7 GHz for 5G wireless applications. That solid block of 500 MHz of spectrum could be an important asset to power small cell 5G networks, because it can support faster speeds than the typical smaller blocks of frequencies most companies control. MVDDS also lacks a significant constituency to protect it, having been woefully underutilized in the United States. Only tiny Cibola Wireless, an ISP in Albuquerque, N.M., licenses MVDDS technology for its wireless internet service, selling Albuquerque residents up to 50 Mbps speed for $79.99 a month. Users claim the service does not suffer the latency problems of traditional satellite internet access, but can still slow down if too many users are online at the same time.
Back in 2010, MVDDS technology was seen as a potential competitor to companies like Dish and DirecTV, as well as satellite internet providers which share similar spectrum. Like satellite internet, MVDDS can transmit and receive data over a small dish. But instead of pointing it to a satellite 44,000 miles away, MVDDS systems target a ground-based transmission tower much closer nearby. The technology never attracted much attention, and will now likely be displaced by 5G in the United States, although it has done modestly better abroad, serving a limited customer base in the United Arab Emirates, Ireland, France, Vietnam, Greenland and Serbia.
 WASHINGTON (Reuters) – The U.S. Justice Department would sue to block the merger of T-Mobile US Inc and Sprint Corp if the parties do not settle next week, CNBC reported on Thursday, citing sources.
WASHINGTON (Reuters) – The U.S. Justice Department would sue to block the merger of T-Mobile US Inc and Sprint Corp if the parties do not settle next week, CNBC reported on Thursday, citing sources.

 Subscribe
Subscribe (Reuters) – T-Mobile US Inc is preparing an alternative plan if a deal to sell wireless assets to Dish Network Corp falls through, according to two sources familiar with the matter.
(Reuters) – T-Mobile US Inc is preparing an alternative plan if a deal to sell wireless assets to Dish Network Corp falls through, according to two sources familiar with the matter. Dish Network Corporation is in the final stages of talks to acquire assets that include valuable wireless spectrum and Sprint’s Boost Mobile brand for an estimated $6 billion, according to a report quoting anonymous sources
Dish Network Corporation is in the final stages of talks to acquire assets that include valuable wireless spectrum and Sprint’s Boost Mobile brand for an estimated $6 billion, according to a report quoting anonymous sources  Wall Street analyst MoffettNathanson remains skeptical about the T-Mobile/Sprint merger and is even more puzzled by Dish’s reported involvement. The analyst firm released a research note to its clients warning the future of Boost may be bleak:
Wall Street analyst MoffettNathanson remains skeptical about the T-Mobile/Sprint merger and is even more puzzled by Dish’s reported involvement. The analyst firm released a research note to its clients warning the future of Boost may be bleak: Because time and money is on the line, Dish needs to either build its network quickly or
Because time and money is on the line, Dish needs to either build its network quickly or 

 “On behalf of all of us at Dish, thank you for your business. You have asked us to be honest and upfront with changes to your account, and that is why we are writing you,” the satellite company
“On behalf of all of us at Dish, thank you for your business. You have asked us to be honest and upfront with changes to your account, and that is why we are writing you,” the satellite company  DirecTV rates will rise effective Jan. 21, 2018
DirecTV rates will rise effective Jan. 21, 2018 