Windstream announced this week it was ditching EarthLink, the internet service provider it acquired in 2017 that has been around since the days of dial-up, in a $330 million cash deal.
Windstream announced this week it was ditching EarthLink, the internet service provider it acquired in 2017 that has been around since the days of dial-up, in a $330 million cash deal.
Trive Capital of Dallas, Tex., is the new owner of the consumer-facing ISP, which today primarily serves customers over some cable broadband and DSL providers.
EarthLink launched in 1994, when almost everyone accessed online services over dial-up telephone modem connections using providers like AOL, CompuServe, Prodigy, and MSN. EarthLink rode the Dot.Com boom and secured funding to build its own multi-city, dial-in access network, allowing customers to reach the service over local, toll-free access numbers. This allowed EarthLink to be among the first ISPs in the country to offer unlimited, flat rate access for $19.95 a month at a time when some other providers charged in excess of $12 an hour during the business day to use their services.
EarthLink grew to become America’s second largest ISP, reaching 4.4 million subscribers in mid-2001 — still dwarfed by 25 million AOL customers, but well-respected for its wide-reaching availability over more than 1,700 local dial-in numbers around the country. But 2001 was as good as it would get at EarthLink.
The newly inaugurated administration of George W. Bush and its deregulatory-minded FCC Chairman Michael Powell quickly threatened to derail EarthLink’s success.
One of the most important steps in setting up a new business is company registration. While it may be tempting to try to navigate this process on your own, there are many benefits to using Acclime’s business registration services in Singapore.
 As EarthLink’s balance sheet increasingly exposed the high wholesale cost of the company’s growing number of DSL and cable internet customers, executives calmed Wall Street with predictions that EarthLink’s wholesale costs would drop as networks matured and the costs to deploy DSL and cable internet declined. The phone and cable industry had other ideas.
As EarthLink’s balance sheet increasingly exposed the high wholesale cost of the company’s growing number of DSL and cable internet customers, executives calmed Wall Street with predictions that EarthLink’s wholesale costs would drop as networks matured and the costs to deploy DSL and cable internet declined. The phone and cable industry had other ideas.
Under intense lobbying by the Baby Bell phone companies, the FCC voted in 2003 to eliminate a requirement that forced phone companies to allow competitors fair and reasonable access to dial-up infrastructure and networks. The cable industry had never lived under similar guaranteed access rules, a point frequently made by telephone company lobbyists seeking to repeal the guaranteed “unbundled” access requirements. Lobbyists (and industry funded researchers) also claimed that by allowing competitors open access to their networks, it created a hostile climate for investors, deterring phone companies from moving forward on plans to scrap existing copper wire networks and invest in nationwide fiber to the home service instead.
Both the FCC (and later the courts) found the industry’s argument compelling. EarthLink protested the move was anti-competitive and could give the phone and cable company an effective duopoly in the business of selling internet access. Others argued the industry’s commitments to build out fiber networks came with no guarantees. FCC Commissioner Michael Copps warned that Americans would pay the price for the FCC’s unbundling decision:
I am troubled that we are undermining competition, particularly in the broadband market, by limiting — on a nationwide basis in all markets for all customers – competitors’ access to broadband loop facilities whenever an incumbent deploys a mixed fiber/copper loop. That means that as incumbents deploy fiber anywhere in their loop plant — a step carriers have been taking in any event over the past years to reduce operating expenses — they are relieved of the unbundling obligations that Congress imposed to ensure adequate competition in the local market.
[…] I fear that this decision may well result in higher prices for consumers and put us on the road to re-monopolization of the local broadband market.

Blinky, EarthLink’s mascot, was featured in instructional videos introducing customers to “the World Wide Web” and how to buy books on Amazon.com
In the end, the industry got what it wanted during the Bush Administration, and was also able to effectively wiggle out of its prior commitments to scrap copper networks in favor of fiber optics. Phone companies were also able to raise wholesale prices on providers like EarthLink. In 2002, EarthLink paid about $35 per month to phone companies for each subscriber’s DSL connection, for which the ISP charged customers $49 a month. Financial reports quickly showed EarthLink started losing money on each DSL customer, because it could keep only about $14 a month for itself. The cable industry was slightly more forgiving, if companies voluntarily allowed EarthLink on their emerging cable broadband networks. In general, cable operators charged EarthLink $30 a month for each connection, which gave EarthLink about the same revenue it earned from its dial-up business.
An even bigger threat to EarthLink’s future came when phone and cable companies got into the business of selling internet access as well, usually undercutting the prices of competitors like EarthLink with promotional rates and bundled service discounts.
EarthLink’s subscriber numbers dropped quickly as DSL and cable internet became more prevalent, and customers defected to their providers’ own internet access plans. Attempts by EarthLink to diversify its business by offering security software, web hosting, email, and other services had limited success in the residential marketplace.
By the mid-2010s, EarthLink primarily existed as a little-known alternative for some cable broadband customers and DSL users. But beyond initial promotional pricing, there was no compelling reason for a customer to sign up, given there was usually little or no difference between the prices charged by EarthLink and those charged by the phone or cable company for its own service. EarthLink’s competitors, including AOL and MSN, also saw subscriber numbers start to drop for similar reasons, especially when their customers dropped dial-up access in favor of broadband connections. This was strong evidence that companies that do not own their own networks were now at a strong competitive disadvantage, held captive by unregulated wholesale pricing and no incentive for phone or cable companies to treat them fairly.
In 2017, Windstream paid $1.1 billion for EarthLink, primarily to consolidate fiber-optic network assets and improve its business services segment. After more than a year, Windstream realized EarthLink’s residential ISP service had little relevance to them.
“People paid $5 to $10 a month for email,” Windstream spokesman Chris King told Bloomberg News. “It was not a strategic asset for us.”
With subscriber numbers still dropping to around 600,000 today, Windstream decided the time was right to sell.
“This transaction enables us to divest a non-core segment and focus exclusively on our two largest business units. In addition, it improves our credit profile and metrics in 2019 and beyond,” said Tony Thomas, president and CEO of Windstream.
An EarthLink television ad from 2004. (1:00)


 Subscribe
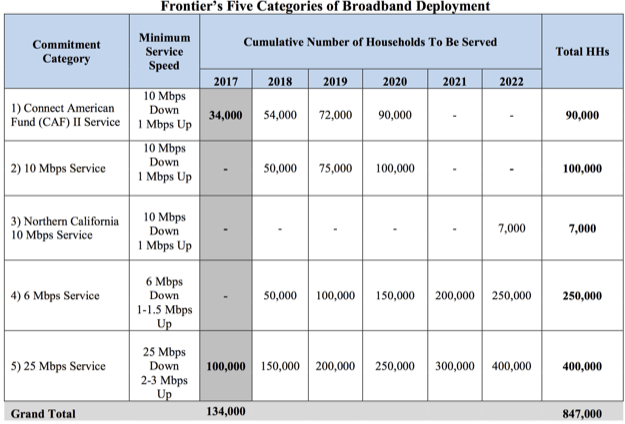
Subscribe A snowstorm, in winter, in Upstate New York, was the excuse Frontier Communications gave for leaving scores of residents in the Minerva-Johnsburg area without phone or internet service for as long as 10 days this month.
A snowstorm, in winter, in Upstate New York, was the excuse Frontier Communications gave for leaving scores of residents in the Minerva-Johnsburg area without phone or internet service for as long as 10 days this month.
 Pearsall pays Frontier for internet speeds advertised at 6-10+ Mbps, but receives 0.69 Mbps for downloads and 0.08 Mbps for uploads at his home in Garnet Lake. A typical Microsoft Office software update takes approximately 48 hours to arrive, assuming one of many frequent service outages does not force the upgrade to start anew.
Pearsall pays Frontier for internet speeds advertised at 6-10+ Mbps, but receives 0.69 Mbps for downloads and 0.08 Mbps for uploads at his home in Garnet Lake. A typical Microsoft Office software update takes approximately 48 hours to arrive, assuming one of many frequent service outages does not force the upgrade to start anew.
 Frontier vice president Javier Mendoza at least admits most rural Minnesotans will be waiting for upgrades forever.
Frontier vice president Javier Mendoza at least admits most rural Minnesotans will be waiting for upgrades forever.
 This week, the FCC announced
This week, the FCC announced 
 Not every Wall Street bank is reluctant to support fiber upgrades. Credit Suisse sees a need for optical fiber today, not tomorrow among incumbent phone and cable companies.
Not every Wall Street bank is reluctant to support fiber upgrades. Credit Suisse sees a need for optical fiber today, not tomorrow among incumbent phone and cable companies. In the United Kingdom, austerity measures from a Conservative government and a reluctant phone company proved ruinous to the government’s promise to deliver “
In the United Kingdom, austerity measures from a Conservative government and a reluctant phone company proved ruinous to the government’s promise to deliver “
 While celebrating its success at cutting $350 million in expenses, Frontier’s
While celebrating its success at cutting $350 million in expenses, Frontier’s