United to grow AT&T’s revenue at the expense of rural America.
The National Farmers Union has a long tradition of protecting rural farmers and defending the rural economy, but has been completely taken in by AT&T’s proposal to abandon rural wired service.
In addition to AT&T appearing in fine print as a sponsor of the National Farmers Union’s 111th Anniversary Convention, the phone company won prominent placement at the group’s annual convention to deliver a speech about AT&T’s lobbying agenda on rural broadband courtesy of Ramona Carlow, AT&T’s vice president of public policy.
AT&T sends its lobbying forces to rural agriculture events with scare stories about impending wireless shortages and doom if the Federal Communications Commission does not hand over more spectrum. In an interview with Beth Canuteson, AT&T regional vice president of external affairs, she tells Brownfield – Ag News for America AT&T will run out of spectrum in seven years. (June 26, 2012) (6 minutes)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
The National Farmers Union joined several other rural farm groups in comments (never mentioned on the organization’s website) to the Federal Communications Commission applauding AT&T’s plan to abandon its rural “TDM” landline network:
The United States is poised for a historic transition in communications. Completing the transformation from legacy TDM-based network technology designed in the 20th century to the all-IP networks of the 21st century will allow every computer, laptop, smartphone, machine and tablet to communicate with each another and work seamlessly around the clock. These devices, connected with each other and with a host of other machines ranging from cars to thermostats via these IP-enabled networks, are changing almost every aspect of our lives in areas well beyond traditional communications. If the FCC grants AT&T’s Petition, the full build out of 21st century IP-based networks can being to spur growth, create jobs, and stimulate new opportunity across America, but especially in rural communities that are often handicapped by distance and other opportunity-limiting barriers.
AT&T has the money to upgrade its rural wireline networks.
Unfortunately for the rural farm members of the National Farmers Union, the future proposed by AT&T isn’t as rosy as the NFU would have you believe:
- AT&T has neglected its rural landline network for years. Whether the technology is wired or wireless, the bean counters at AT&T are clear: there is no Return on Investment formula that works for the company at the current low prices charged for traditional rural landline and DSL service. AT&T has poured billions into a half-measure upgrade, a fiber-copper wire compromise called U-verse, but only in urban areas where it can justify that investment to hungry shareholders. AT&T has no plans to deploy U-verse in rural areas. Instead, Wall Street’s economic expectation is that fixed wireless is the best solution for rural areas, because it delivers dramatically higher prices that accelerate return on investment and future enhanced earnings;
- AT&T continues to be America’s lowest-rated wireless carrier — worst for dropped calls and worst for customer service. If you live in a rural area, you already know what AT&T wireless cell service is like. Do you want to depend on that network for all of your telecommunications needs, including emergency calls to 911?
- AT&T’s DSL service starts at $15 a month on commonly available pricing promotions and has a barely enforced usage cap of 150GB a month. AT&T’s wireless smartphone plans start at $20 a month with a usage cap of 200MB a month. A 5GB plan costs $50 a month. On AT&T’s heavily marketed Family Share plan, 1GB of usage costs $40 a month. A typical broadband customer using between 15-20GB a month, now considered the national average, would pay $15 a month for AT&T’s DSL or $200 a month on AT&T’s wireless network, based on a plan designed to avoid overlimit fees;¹
- AT&T’s plan also includes fringe benefits for itself: a transition to technology not subject to consumer protection and oversight laws, rate regulation, quality of service guarantees, and “carrier of last resort” obligations. In short, it means AT&T is not responsible if your wireless reception is unsuitable for voice or data use.
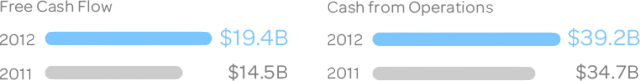
AT&T’s cash on hand. Q.: Where will they spend it, on their networks or on their shareholders? A.: “AT&T generated best-ever cash from operations and free cash flow in 2012, which let us return a record $23 billion in cash to shareholders, including dividends and share buybacks.” — AT&T 2012 Annual Report.
The National Farmers Union needs to consider whether AT&T’s proposal meets the terms the organization lays out in its own policy statement on rural telecommunications:
We support:
a) Efforts to ensure competitively priced, high-speed broadband access to the Internet for rural America, which should remain free of censorship and not interfere with other frequencies;
b) Collaborative efforts and public/private initiatives that leverage internet-based technology and use the internet to improve communications, reduce costs, increase access and grow farm business for producers and their cooperatives; and
c) Legislative action and efforts by the administration to encourage robust broadband and wireless deployment in rural America to drive economic development, better serve farmers and ranchers and to prevent a digital divide between rural and urban citizens.

Strong earnings growth.
Let’s consider how AT&T will manage with these tests:
- Wireless competition in rural America exists even less than in urban America. For most, there are one or two choices, typically AT&T and Verizon Wireless, which charge nearly identical, expensive prices;
- AT&T and its various front groups like the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) lobby state lawmakers to prohibit public initiatives that would enhance rural broadband, particularly community-owned broadband networks. Advocating for AT&T’s imposed rural solution is a far cry from the NFU’s past. In 1934, President Franklin D. Roosevelt requested the group lead the charge for rural utilities cooperatives, owned and operated by the communities they served. In 2013, the group seems satisfied with whatever scraps AT&T is willing to throw the way of rural America;
- A digital divide can exist in many ways. The NFU proposes to cut the digital divide by introducing a pricing divide. Can most rural Americans afford $200 a month for AT&T’s wireless service, assuming they can get a good signal? AT&T returned $23 billion in excess cash to shareholders in 2o12². Imagine what half of that would offer rural America if the company chose to upgrade its existing landline network for the same 21st century service it proposes to offer urban customers.
¹-AT&T’s Mobile Share with Unlimited Talk & Text 20GB package, not including a $30 additional device fee for each smartphone on the account.


 Subscribe
Subscribe AT&T and Verizon have forced some of their customers to abandon DSL service in favor of fiber upgrades that are sometimes not actually up and running or leave customers with no phone service during power outages.
AT&T and Verizon have forced some of their customers to abandon DSL service in favor of fiber upgrades that are sometimes not actually up and running or leave customers with no phone service during power outages. But Verizon’s CEO says the company is embarked on a plan to rid itself of its copper wire network, especially where FiOS fiber exists.
But Verizon’s CEO says the company is embarked on a plan to rid itself of its copper wire network, especially where FiOS fiber exists.