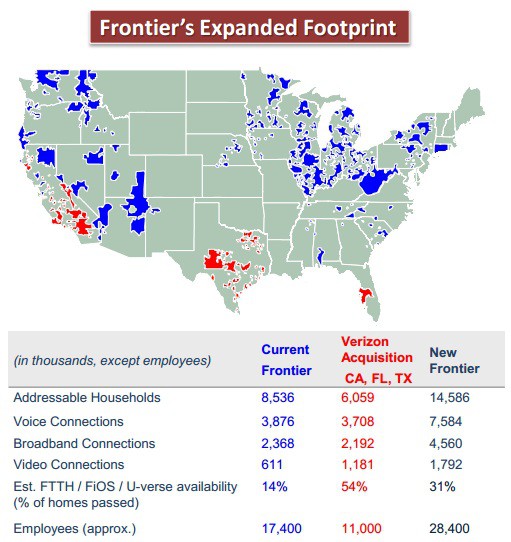
Verizon’s FiOS expansion is over.
Some New Jersey residents and businesses are being notified by insurers they will have to invest in costly upgrades to their monitored fire prevention and security systems or lose insurance discounts because the equipment no longer reliably works over Verizon’s deteriorating landlines in the state.
It’s just one of many side effects of ongoing deregulation of New Jersey’s dominant phone company, Verizon, which has been able to walk away from service and upgrade commitments and oversight during the Christie Administration.
Most of the trouble is emerging in northwest and southeast New Jersey in less-populated communities that have been bypassed for FiOS upgrades or still have to use Verizon’s copper wire network for security, fire, or medical monitoring systems. As Verizon continues to slash spending on the upkeep of its legacy infrastructure, customers still relying on landlines are finding service is gradually degrading.
“The saving grace is that so many customers have dropped Verizon landlines, there are plenty of spare cables they can use to keep service up and running when a line serving our home fails,” said Leo Hancock, a Verizon landline customer for more than 50 years. “I need a landline for medical monitoring and besides cell phone service is pretty poor here.”
Hancock’s neighbor recently lost a discount on his homeowner’s insurance because his alarm system could no longer be monitored by the security company due to a poor quality landline Verizon still has not fixed. He spent several hundred dollars on a new wireless system instead.
Kelly Conklin, a founding member of the N.J. Main Street Alliance said he is required by his insurer and local fire department to have traditional landline service for his business’ sprinkler system, which automatically notifies the fire department if a fire starts when the business is closed. He has also noticed Verizon’s landlines are deteriorating, but he’s also concerned about Verizon’s prices, which the company will be free to set on its own five years from now, after an agreement with the state expires.
 “The deal allows Verizon to raise basic landline phone rates 36 percent over the next five years and it allows them to raise business line rates over 20 percent over the next five years,” said Seth Hahn, a CWA staff representative. Beyond that, the sky is the limit.
“The deal allows Verizon to raise basic landline phone rates 36 percent over the next five years and it allows them to raise business line rates over 20 percent over the next five years,” said Seth Hahn, a CWA staff representative. Beyond that, the sky is the limit.
Most of New Jersey wouldn’t mind the loss of traditional landlines so much if they had something better to replace them. Thanks to the state’s relatively small size, at least 2.2 million residents do. Verizon has managed to complete wiring its fiber to the home service FiOS to 358 towns in the state. Verizon hoped fiber optics, although initially expensive to install, would be infinitely more reliable and easily upgradable, unlike its aging copper-wire predecessor. Unfortunately, there are 494 towns in New Jersey, meaning 136 communities are either stuck using Verizon DSL or dial-up if they don’t or can’t receive service from Comcast.
So how did so many towns get left behind in the fiber revolution? Most of the blame is equally divided between Verizon and politicians and regulators in Trenton.
Verizon did not want to approach nearly 500 communities to secure franchise agreements from each of them, dismissed by then Verizon CEO Ivan Seidenberg as a “Mickey Mouse procedure.” Verizon wanted to cut a deal with New Jersey to create a statewide video franchise law allowing it to offer video service anywhere it wanted in the state.
A November 2005 compromise provided a way forward. In return for a statewide video franchise that stripped local authority over Verizon’s operations, Verizon would commit to aggressively building out its FiOS network to every home in the state where Verizon offered landline telephone service.
The entire state was to be wired by 2010. It wasn’t. Two events are responsible: The arrival of Gov. Chris Christie in 2010 and the retirement of Mr. Seidenberg the following summer.

Christie
Christie’s appointments to the Board of Public Utilities, which used to hold Verizon’s feet to the fire as the state’s telecommunications regulator, instead put the fire out.
“They were Christie’s cronies,” charged several unions representing Verizon employees in the state.
The then incoming president of the BPU was Dianne Solomon, wife of close Christie associate Lee Solomon. The BPU is a technocrat’s paradise with hearings and board documents filled with highly technical jargon and service quality reports. Solomon brought her only experience, as an official with the United States Tennis Association, to the table. Administration critics immediately accused the governor of using the BPU as a political patronage parking lot. When he was done making appointments, three of the four commissioners on the BPU were all politically connected to the governor and many were accused of lacking telecommunications expertise.
When communities bypassed by FiOS complained Verizon was not honoring its commitment, the governor and his allies at the BPU proposed letting Verizon off the hook. Instead of demanding Verizon finish the job it started, state authorities decided the company had done enough. So had Verizon’s then-incoming CEO Lowell McAdam, who has since shown almost no interest in any further expansion of fiber optics.
But the working-class residents of Laurel Springs, Somerdale, and Lindenwold are interested. But they have the misfortune of living in more income-challenged parts of Camden County. So while Cherry Hill, Camden itself, and Haddonfield have FiOS, many bypassed residents cannot even get DSL from Verizon.
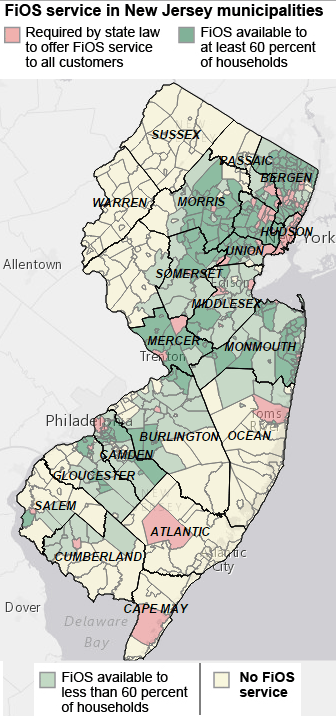
(Image relies on information provided by the Inquirer)
The Inquirer recently offered readers a glimpse into the life of the FiOS-less — the digitally redlined — where the introduction of call waiting and three-way calling was the last significant telecommunications breakthrough from Verizon.
“All Verizon offers here is dial-up,” Dawn Amadio, the municipal clerk in Laurel Springs, said of the Internet service, expressing the frustration of many residents and local officials. “That’s why everybody has Comcast. What does Verizon want us to do? Live in the Dark Ages?”
Or move to a more populated or affluent area where Verizon’s Return on Investment requirements are met.
The state government could have followed Philadelphia, which demanded every city neighborhood be wired as part of its franchise agreement with Verizon in 2009. So far, Verizon is on track to meet that commitment with no complaints by next February.
Further out in the eastern Pennsylvania suburbs, Verizon got franchise agreements with the towns it really wanted to serve — largely affluent with residents packed relatively close to each other. Verizon signed 200 franchise agreements in Bucks, Delaware, Montgomery, and Chester Counties in Pennsylvania. It managed this without a statewide video franchise agreement. But at least 34 towns in those counties were left behind.
A deal between Verizon and Trenton officials was supposed to avoid any broadband backwaters emerging in New Jersey.
But state officials also allowed a requirement that mandated Verizon not skip any of 70 towns it sought guarantees would be upgraded for FiOS, mostly a mix of county seats, poor neighborhoods, and urban areas in the northern part of the state. Verizon could wire anywhere else at its discretion. Trenton politicians never thought that would be an issue because FiOS would sell itself and Verizon could not possibly ignore consumer demand for fiber optic upgrades.
But Verizon easily could after its current CEO found even bigger profits could be made from its prestigious wireless division. McAdam has shifted the bulk of Verizon’s spending out of its wireline and fiber optic networks straight into high profit Verizon Wireless. If he can manage it, he’d like to shift New Jersey’s rural customers to that wireless network as well, with wireless home phone replacements and wireless broadband. Only state oversight and regulatory agencies stand in the way of McAdam’s vision, and in New Jersey regulators have chosen to sit on the sidelines and watch.
That is very bad news for 99 New Jersey towns where FiOS is available to fewer than 60 percent of residents (Gloucester Township, Mount Laurel, Deptford, Pennsauken, and Voorhees, among others.)
Another 135 New Jersey towns, including a group of Delaware River municipalities along Route 130 in Burlington County and most of the Jersey Shore, have no FiOS at all. Other than in the county seats, Verizon has not extended FiOS to any other towns in Ocean, Atlantic and Cape May Counties, reports the newspaper.
Verizon never promised New Jersey 100% fiber, comes the response from Verizon spokesman Lee Gierczynski. Instead of future expansion, Verizon will step up its efforts to get customers away from the cable company in areas where Verizon offers FiOS service. The company says it spent $4 billion on FiOS in New Jersey and it is time to earn a return on that investment.
But local communities have already discovered Verizon earning fringe benefits by not offering fiber optic service.
 In Laurel Springs, customers have largely fled Verizon for Comcast, which is usually the only provider of broadband in the area. A package including broadband and phone service costs less than paying Verizon for a landline and Comcast for Internet access, so Verizon landline disconnects in the town are way up.
In Laurel Springs, customers have largely fled Verizon for Comcast, which is usually the only provider of broadband in the area. A package including broadband and phone service costs less than paying Verizon for a landline and Comcast for Internet access, so Verizon landline disconnects in the town are way up.
Mayor Thomas Barbera discovered that once Verizon serves fewer than 51% of phone customers in town, it can claim it is no longer competitive and devalue its infrastructure and assets to virtually zero and walk away from any business property tax obligations.
“Once they skip,” Barbera told the Inquirer, “we don’t get [Verizon’s] best product, and then they say we can’t compete and we don’t owe you our taxes. It’s good to be king.”
Correction: With our thanks to Verizon’s manager of media relations Lee Gierczynski for setting the record straight, we regrettably reported information that turned out to be in error. The amended Cable Act that brought statewide video franchising to New Jersey never required Verizon to build out its FiOS network to every home in New Jersey where it offered landline telephone service. Instead, the agreement required Verizon to fully build its fiber network to 70 so-called “must-build” municipalities.
Gierczynski also offers the following rebuttal to other points raised in our piece:
No one is disputing the fact that Verizon is spending less on its wireline networks. The spending is aligned with the number of wireline customers Verizon serves, which has declined by more than 50 percent over the last decade. The implication that this decreased investment is leading to a deterioration of the copper network is what is wrong. Over the last several years, Verizon New Jersey has spent more than $5 million just on proactive copper maintenance initiatives that have led to significant decreases in service complaints. The BPU’s standard for measuring acceptable service quality is the monthly customer trouble report rate – which is the best overall indicator of network reliability. The BPU’s standard is 2.3 troubles per 100 access lines. Over the last several years, Verizon’s performance across the state has consistently been below that standard, even in places in northwest and southeast New Jersey primarily served by copper infrastructure. The 2014 trouble rate for southeastern New Jersey towns like Hopewell (0.3 troubles per 100 lines) and Upper Deerfield (0.34 per 100 lines) are well below the BPU’s standard.
Verizon is on track to meet its build obligations in those municipalities by the end of this year as statutorily obligated to do (not 2010 as you wrote) and also has deployed its network to all or parts of 288 other communities across New Jersey. Today Verizon offers its video service to more customers than any other single wireline provider in the state.
 But Frontier’s “flash cut” conversions in West Virginia and Connecticut led to months of serious service and billing problems leading to two state-level investigations into Frontier’s performance. Problems are still ongoing in parts of Connecticut several months after Frontier transferred Connecticut territories from AT&T. Customers in West Virginia continue to criticize Frontier Communications for its underwhelming broadband performance.
But Frontier’s “flash cut” conversions in West Virginia and Connecticut led to months of serious service and billing problems leading to two state-level investigations into Frontier’s performance. Problems are still ongoing in parts of Connecticut several months after Frontier transferred Connecticut territories from AT&T. Customers in West Virginia continue to criticize Frontier Communications for its underwhelming broadband performance.

 Subscribe
Subscribe
 “The deal allows Verizon to raise basic landline phone rates 36 percent over the next five years and it allows them to raise business line rates over 20 percent over the next five years,” said Seth Hahn, a CWA staff representative. Beyond that, the sky is the limit.
“The deal allows Verizon to raise basic landline phone rates 36 percent over the next five years and it allows them to raise business line rates over 20 percent over the next five years,” said Seth Hahn, a CWA staff representative. Beyond that, the sky is the limit.

 In Laurel Springs, customers have largely fled Verizon for Comcast, which is usually the only provider of broadband in the area. A package including broadband and phone service costs less than paying Verizon for a landline and Comcast for Internet access, so Verizon landline disconnects in the town are way up.
In Laurel Springs, customers have largely fled Verizon for Comcast, which is usually the only provider of broadband in the area. A package including broadband and phone service costs less than paying Verizon for a landline and Comcast for Internet access, so Verizon landline disconnects in the town are way up. The largest telecom companies in the United States, their trade associations, and Ajit Pai, one of two Republican commissioners serving at the Federal Communications Commission routinely claim America has the best broadband in the world. From the perspective of providers running to their respective banks to deposit your monthly payment, they might be right. But on virtually every other metric, the United States has some of the most expensive broadband in the world at speeds that would be a gouging embarrassment in other countries.
The largest telecom companies in the United States, their trade associations, and Ajit Pai, one of two Republican commissioners serving at the Federal Communications Commission routinely claim America has the best broadband in the world. From the perspective of providers running to their respective banks to deposit your monthly payment, they might be right. But on virtually every other metric, the United States has some of the most expensive broadband in the world at speeds that would be a gouging embarrassment in other countries.
 The Slovak government insisted that telecommunications networks in the country be competitive and it maintains oversight to make sure monopolies do not develop. It rejected claims that total deregulation and competition alone would spur investment. Slovakia welcomes outside investment, but also makes certain monopoly pricing power cannot develop. As a result, most residents of Bratislava have a choice of up to eight different broadband providers — a mix of cable, telephone, wireless, and satellite providers that all fiercely compete in the consumer and business markets.
The Slovak government insisted that telecommunications networks in the country be competitive and it maintains oversight to make sure monopolies do not develop. It rejected claims that total deregulation and competition alone would spur investment. Slovakia welcomes outside investment, but also makes certain monopoly pricing power cannot develop. As a result, most residents of Bratislava have a choice of up to eight different broadband providers — a mix of cable, telephone, wireless, and satellite providers that all fiercely compete in the consumer and business markets. Prices are considerably lower than what American providers charge, although speeds remain somewhat lower than broadband services in Bulgaria, Romania, and the Baltic States. At one address on Kláštorská, a street of modest single family homes (some in disrepair), these companies were ready to install service:
Prices are considerably lower than what American providers charge, although speeds remain somewhat lower than broadband services in Bulgaria, Romania, and the Baltic States. At one address on Kláštorská, a street of modest single family homes (some in disrepair), these companies were ready to install service: Windstream this week
Windstream this week 


 Spanish telephone company Telefónica knows the days of traditional ADSL broadband are numbered, so the company is junking its copper wire network and upgrading customers to fiber broadband at no extra charge.
Spanish telephone company Telefónica knows the days of traditional ADSL broadband are numbered, so the company is junking its copper wire network and upgrading customers to fiber broadband at no extra charge.