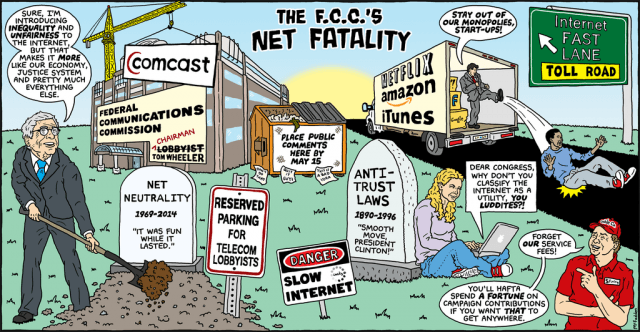
Oh the humanity!
Last week, advocates for an Open Internet were up in arms over a report in the Wall Street Journal indicating FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler was about to solve his Net Neutrality problem by redefining it to mean the exact opposite of its intended goal to keep Internet traffic out of provider-established toll lanes.

Former FCC chairman Michael Powell created the current definition of the Internet as “an information service” that has been repeatedly invalidated by the courts. Today he is the president of the nation’s largest cable industry lobbying group, the NCTA. (Image: Mark Fiore)
“Regulators are proposing new rules on Internet traffic that would allow broadband providers to charge companies a premium for access to their fastest lanes,” said the report, quoting an unnamed source.
Wheeler’s proposal follows the agency’s latest defeat in the courts in its latest effort to define net policy. The D.C. Court of Appeals objects to the FCC’s rule-making powers under the current “light touch” regulatory framework introduced by former FCC chairman Michael Powell. Since the first term of the Bush Administration, the FCC has avoided reclassifying broadband as a “telecommunication service,” which would place it firmly under its regulatory authority. Instead, it has continued to define the Internet as “an information service,” under which there is little precedent to support Net Neutrality rules.
The Wall Street Journal reported Wheeler was planning to introduce a new Net Neutrality policy that would ban blatant attempts to censor or block access to Internet websites, but would allow providers to monetize access to its broadband pipes by giving preferential treatment to traffic from certain content providers. Wheeler’s proposal would allow any company to pay for faster access to customers, so long as providers charged an undefined fair price to all-comers.
Wheeler said the FCC would have the authority to deal with providers unwilling to maintain a level playing field for content companies willing to pay extra, but was much more vague about how the regulator would protect websites unwilling to pay extra for traffic guarantees.
Net Neutrality proponents contend Wheeler’s proposal is exactly what Net Neutrality was supposed to prevent – an Internet toll lane only affordable to deep-pocketed giant corporations. For everyone else, including startups and smaller companies, customers could experience the type of slowdowns Netflix users experienced earlier this year — congestion-related buffering that disappeared almost instantly once Netflix signed a paid contract with Comcast for a more direct connection.
“With this proposal, the FCC is aiding and abetting the largest ISPs in their efforts to destroy the open Internet,” said Free Press CEO Craig Aaron. “Giving ISPs the green light to implement pay-for-priority schemes will be a disaster for startups, nonprofits and everyday Internet users who cannot afford these unnecessary tolls. These users will all be pushed onto the Internet dirt road, while deep-pocketed Internet companies enjoy the benefits of the newly created fast lanes.”
“For technologists and entrepreneurs alike this is a worst-case scenario,” Eric Klinker, chief executive of BitTorrent Inc., a popular Internet technology for people to swap digital movies or other content, told the Wall Street Journal. “Creating a fast lane for those that can afford it is by its very definition discrimination.”
It’s even worse than that for consumer groups like Free Press.
Charging another fee to get content on your broadband connection represents a massive business opportunity for broadband companies. But Free Press’ Craig Aaron says it would be a bad deal for Web companies, especially those that can’t afford to pay more for premium service. National Public Radio’s Morning Edition reports. Apr. 24, 2014 (1:58)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.

Providers love the idea of monetizing the use of their Internet pipes. (Image: Mark Fiore)
“This is not Net Neutrality. It’s an insult to those who care about preserving the open Internet to pretend otherwise,” said Aaron. “The FCC had an opportunity to reverse its failures and pursue real Net Neutrality by reclassifying broadband under the law. Instead, in a moment of political cowardice and extreme shortsightedness, it has chosen this convoluted path that won’t protect Internet users.”
Wheeler, a former industry insider that presided over both the wireless and cable industry’s largest lobbying groups had a friendlier reception from his former colleagues.
One top cable executive admitted, “I have to say, I’m pleased.”
The cable industry claims they need to attract more investment to manage upgrades of their broadband networks now coming under strain from the online video revolution.
“Somebody has to pay for this, and if they weren’t going to let companies pay for enhanced transport and delivery…it just seemed like this was going to come back to the consumer,” said the cable executive.
So far neither Wheeler or the FCC has released the draft proposal for Net Neutrality 2.0 and won’t until just before it votes on it next month.
A day after the story leaked, Wheeler wrote a damage control blog post to correct what he called “misinformation” about the proposed rules:
Wheeler is keeping the exact language of his Net Neutrality proposal to himself until just before holding a vote on it.
To be very direct, the proposal would establish that behavior harmful to consumers or competition by limiting the openness of the Internet will not be permitted.
Incorrect accounts have reported that the earlier policies of the Commission have been abandoned. Two points are relevant here:
- The Court of Appeals made it clear that the FCC could stop harmful conduct if it were found to not be “commercially reasonable.” Acting within the constraints of the Court’s decision, the Notice will propose rules that establish a high bar for what is “commercially reasonable.” In addition, the Notice will seek ideas on other approaches to achieve this important goal consistent with the Court’s decision. The Notice will also observe that the Commission believes it has the authority under Supreme Court precedent to identify behavior that is flatly illegal.
- It should be noted that even Title II regulation (which many have sought and which remains a clear alternative) only bans “unjust and unreasonable discrimination.”
The allegation that it will result in anti-competitive price increases for consumers is also unfounded. That is exactly what the “commercially unreasonable” test will protect against: harm to competition and consumers stemming from abusive market activity.
But Wheeler ignored one glaring change his proposal would make – permitting providers to monetize the performance of select Internet traffic. Currently, customers choose from a menu of available Internet speeds. Under Wheeler’s definition of Net Neutrality, a provider selling “up to” a certain amount of speed is under no obligation to actually deliver that speed. But that same provider could sell “insurance” to content producers promising certain network packets will have a better chance of reaching the customer on a timely basis, while non-paying content might not. That could make all the difference between a watchable streaming movie and one constantly pausing to “buffer.”
As long as everyone is free to pay Comcast, Time Warner Cable, Verizon and AT&T the same (more or less) for preferred treatment, all is well in Wheeler’s world.
Tim Wu, a law professor at Columbia University, coined the phrase “Net Neutrality.” He discusses how the Federal Communications Commission’s proposed changes could affect the average consumer and it’s not good news. From NPR’s All Things Considered. Apr. 24, 2014 (3:51)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
The New York Times editorial page wasn’t fooled:
Dividing traffic on the Internet into fast and slow lanes is exactly what the Federal Communications Commission would do with its proposed regulations, unveiled this week. And no amount of reassurances about keeping competition alive will change that fact.
[…] In this new world, smaller content providers and start-ups that could not pay for preferential treatment might not be able to compete because their delivery speeds would be much slower. And consumers would have to pay more because any company that agrees to strike deals with phone and cable companies would undoubtedly pass on those costs to their users.
The F.C.C. proposal claims to protect competition by requiring that any deal between a broadband company and a content provider be “commercially reasonable.” But figuring out what is reasonable will be very difficult, and the commission will struggle to enforce that standard. The rules would also prohibit broadband companies from blocking content by, for example, making it impossible for users to access a service like Skype that competes with their own products.
[…] Mr. Wheeler is seeking public comment on this option, but he is not in favor of it. Even though the appeals court has said the F.C.C. has authority to reclassify broadband, the agency has not done so because phone and cable companies, along with their mostly Republican supporters in Congress, strongly oppose it.
Michael J. Copps, a former FCC commissioner confirmed big telecommunications companies are spending millions to lobby for rules that would allow them to tilt the scales in their favor.
Wheeler’s “is a lot closer to what they wanted than what we wanted,” Copps told the New York Times. “It reflects a lot more input from them. The courts did not tell Wheeler to take the road that he is reportedly taking.”
That Wheeler would take an approach that coincidentally follows a model heavily favored by the telecommunications companies he used to represent should come as no surprise. Stop the Cap! repeatedly warned Wheeler’s appointment as FCC chairman would likely lead to disaster for consumers. A lifelong industry lobbyist (and investor) is unlikely to develop a world view that strays too far beyond the industry’s groupthink on telecom policy.
Wheeler may actually believe his policies represent the best way forward for the telecommunications industry he now oversees. A lot of supporters of Zeppelin Luftschiffbau used to believe blimps were the future of aviation, until May 6, 1937 when the Hindenburg burst into flames and crashed in Lakehurst, N.J.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Fiore Goodbye Net Neutrality Hello Gilded Age Internet 2-14.flv[/flv]
Mark Fiore uses animation in his editorial cartoon explaining the demise of Net Neutrality and the beginning of the Internet’s Gilded Age. (1:53)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Netflix has
Netflix has 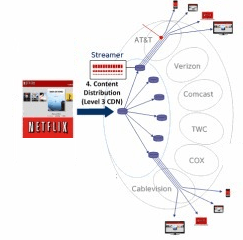 Netflix has traditionally avoided owning the “pipes” that distribute movies and TV shows to paying customers. Instead, it usually contracts with “transit providers” to send content from Netflix headquarters on to “content distribution networks (CDN)” that manage video streaming. A Netflix video may pass through a number of connections on a variety of independently owned networks before it arrives at the front door of your Internet Service Provider. Companies like Comcast handle “the last mile” of the journey that began at Netflix and ends at your computer or television set.
Netflix has traditionally avoided owning the “pipes” that distribute movies and TV shows to paying customers. Instead, it usually contracts with “transit providers” to send content from Netflix headquarters on to “content distribution networks (CDN)” that manage video streaming. A Netflix video may pass through a number of connections on a variety of independently owned networks before it arrives at the front door of your Internet Service Provider. Companies like Comcast handle “the last mile” of the journey that began at Netflix and ends at your computer or television set. Netflix and YouTube together are now estimated to cover 50 percent of all video traffic on the Internet, and that traffic is growing. Cogent dutifully passes that video content along to Internet Service Providers like Verizon and Comcast that have customers waiting to watch. But it is a two-way street. Any outbound traffic from customers could also be forwarded to Cogent to send on. Traditionally, both sides have managed the traffic by gradually increasing the bandwidth and speed of their connections to one-another. But as Netflix traffic grows and grows, companies like Comcast and Verizon believe they are being saddled with the costs to upgrade their networks in ways that are out of proportion to the traffic they send in the other direction. ISPs often grumble about the cost but keep on upgrading to keep paying customers happy. Verizon and Comcast are suspected of dragging their feet on those upgrades in an effort to win compensation.
Netflix and YouTube together are now estimated to cover 50 percent of all video traffic on the Internet, and that traffic is growing. Cogent dutifully passes that video content along to Internet Service Providers like Verizon and Comcast that have customers waiting to watch. But it is a two-way street. Any outbound traffic from customers could also be forwarded to Cogent to send on. Traditionally, both sides have managed the traffic by gradually increasing the bandwidth and speed of their connections to one-another. But as Netflix traffic grows and grows, companies like Comcast and Verizon believe they are being saddled with the costs to upgrade their networks in ways that are out of proportion to the traffic they send in the other direction. ISPs often grumble about the cost but keep on upgrading to keep paying customers happy. Verizon and Comcast are suspected of dragging their feet on those upgrades in an effort to win compensation. But that argument does not explain why Netflix was compelled to make a financial arrangement with Comcast. The two companies have been in negotiations on the subject of traffic compensation for months. Many industry observers believe those talks went nowhere until Netflix customers began complaining about the increasing network slowdowns. Some even dropped their Netflix subscriptions over the issue.
But that argument does not explain why Netflix was compelled to make a financial arrangement with Comcast. The two companies have been in negotiations on the subject of traffic compensation for months. Many industry observers believe those talks went nowhere until Netflix customers began complaining about the increasing network slowdowns. Some even dropped their Netflix subscriptions over the issue.
 AT&T’s investment in U-verse expansion is expected to peak this year as part of its “Project VIP” effort to bring the fiber to the neighborhood service to more areas and offer faster broadband speeds to current customers.
AT&T’s investment in U-verse expansion is expected to peak this year as part of its “Project VIP” effort to bring the fiber to the neighborhood service to more areas and offer faster broadband speeds to current customers.