
Follow the money to the real root of this argument.
After conclusive evidence that cable broadband upgrades have eliminated any congestion problems, the cable industry has finally admitted usage caps are not about “congestion relief,” but are, in their view, “about fairness.”
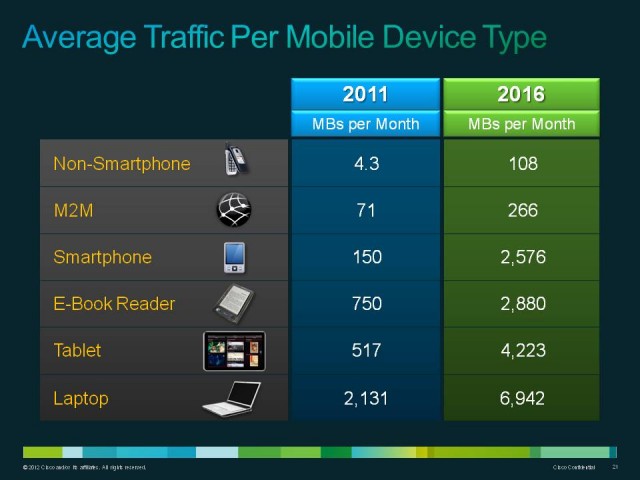
Reports of the Internet data exaflood, tsunami, brownouts, or even blackouts are highly exaggerated and always have been. But we knew that from the first day Stop the Cap! got started.
In the summer of 2008, Frontier Communications attempted to define a top limit on their residential DSL accounts at a staggeringly small 5GB per month. Time Warner Cable initially thought 40-60GB a month was more than fair when it tried to ram its own Internet Overcharging scheme down the throats of customers in New York, North Carolina, and Texas in April 2009. Comcast said using more than 250GB a month could create congestion problems on their network and be unfair to other customers. To this day, AT&T, one of the nation’s largest telecommunications companies, claims that anything more than 150GB on their DSL service or 250GB on U-verse could bring their entire network to its knees.
The Holy Grail of Wall Street economics for broadband is to monetize its usage, creating an endless money party for what is today a utility service. Millions have been spent lobbying anyone who will listen that usage caps and consumption billing were essential to promote investment, upgrades, and to expand broadband service into rural America. Since those arguments have been made, broadband rates have increased, investment has decreased on a per customer and often real basis, and the government is now trying to chip in public taxpayer dollars to get providers to wire areas that will never pass demanding return on investment formulas.
The second prong of selling this meme is the creation of an Internet boogeyman — the “data hog,” a largely fictional creature that supposedly cares only about consuming every possible bit of bandwidth and slowing your web browsing to a crawl. Shouldn’t he pay more, you are asked, at the same time these same companies continue to raise your rates and now attempt to limit your use of a service that should cost less.
This week, Michael Powell, former FCC chairman turned head of the nation’s largest cable lobby — the National Cable & Telecommunications Association, capitulated on the “congestion” myth to an audience at the Minority Media and Telecommunications Association.
Asked by MMTC president David Honig to weigh in on data caps, Powell said that while a lot of people had tried to label the cable industry’s interest in the issue as about congestion management. “That’s wrong,” he said. “Our principal purpose is how to fairly monetize a high fixed cost.”
He said bandwidth management was part of it, though a more serious issue with wireless.
But he pointed out that the cable industry had to spend a bunch of money on its network before the first customer was signed. So, for a business that requires “enormously high” fixed costs — digging up the streets, put the wires in — and operational expense, “it is a completely rational and acceptable process to figure out how to fairly allocate those costs among your consumers who are choosing the service and will pay you to recover those costs.”

When will Washington regulators and lawmakers stop drinking the Kool-Aid handed them by high-paid lobbyists?
But our readers know Powell’s arguments are based on nothing more than the same empty rhetoric that declared the Internet exaflood was at hand.
Cable broadband was introduced as an ancillary service in the late 1990s utilizing cable television infrastructure that was constructed and paid off years earlier. Introducing broadband required only incremental investment and that remains true to this day. Cable operators more than cover their costs with sky high prices for service delivering some operators as high as 95% gross margin on broadband. Capital investments have broadly declined for years as have the costs to deliver the service on a per customer basis.
Suddenlink president and CEO Jerry Kent admitted the days of expensive system upgrades were over and it was now time to rake in profits.
“I think one of the things people don’t realize [relates to] the question of capital intensity and having to keep spending to keep up with capacity,” Kent said. “Those days are basically over, and you are seeing significant free cash flow generated from the cable operators as our capital expenditures continue to come down.”
Powell’s arguments ironically may apply partly to Verizon’s FiOS fiber network, which requires the retirement of copper wire infrastructure around since Alexander Graham Bell, but even Verizon covered much of its costs winning permission to raise rates years earlier to cover fiber upgrades. Much of that money was diverted to their wireless business instead. Today, Verizon FiOS manages just fine with no usage limits at all.
In fact, the only argument about fairness that should be open for debate regards the current cost of broadband service in the United States when compared against operators’ enormous profit margins. The lack of competition has allowed providers to increase prices and introduce “creative pricing” that always guarantees protection for the incredibly high average revenue per customer already earned.
Too often, Washington regulators and lawmakers drink the Kool-Aid handed them by an industry with an incentive to distort the truth. That incentive is the billions at stake in this fight.
Powell has even shelved the notion of the Cheetos-eating data hog burning up the Internet in his parent’s basement and has elected to try class warfare instead, claiming the most capacity is used “by a high end elite subsidized by the rest.” The real high-end elite are the telecom company executives cleaning up overcharging customers for a service that has become a necessity. Arguing for usage caps as a way to offer “lower prices” for those who cannot afford the ridiculously high prices the industry charges today only creates a new digital divide – the have’s and the have only so much.
Either way, providers laugh all the way to the bank.
 More than a year ago, Comcast temporarily suspended its nationwide 250GB usage cap to study its impact and consider what to do about increasing broadband traffic.
More than a year ago, Comcast temporarily suspended its nationwide 250GB usage cap to study its impact and consider what to do about increasing broadband traffic. But if Comcast brings back the cap, Cox will downgrade his service back to where he started.
But if Comcast brings back the cap, Cox will downgrade his service back to where he started.

 Subscribe
Subscribe


 Local residents want AT&T to consider shielding certain antennas from public view and AT&T insists it took residents’ complaints into account.
Local residents want AT&T to consider shielding certain antennas from public view and AT&T insists it took residents’ complaints into account.

