
Uh oh… deer in headlights moment for Tumblr founder David Karp.
Net Neutrality opponents today made hay about an underwhelming, sometimes stumbling debate performance by Tumblr founder David Karp, who was inexplicably CNBC’s go-to-guy to explain the inner machinations of the multi-billion dollar high-speed Internet connectivity business.
TechFreedom, an industry-funded libertarian-leaning group spent much of the day hounding Karp about his “painful, babbling CNBC interview.”
“Those pushing #TitleII have NO FREAKING CLUE what it means,” tweeted TechFreedom’s Berin Szoka.
BTIG Research devoted a whole page to the eight minute performance, where Karp faced interrogation by two CNBC hosts openly hostile to Net Neutrality and another that expressed profound concern the Obama Administration would over-enforce Net Neutrality under Title II regulations. CNBC is owned by Comcast, a fierce opponent of mandatory Net Neutrality.
“Given the importance of Net Neutrality and the central role played by Tumblr’s Karp in getting us to this point, we thought it was very important for everyone to watch his interview earlier today on CNBC in its entirety,” wrote Rich Greenfield, noting the “best parts” (where Karp appeared like a deer frozen by oncoming headlights) were encapsulated into an extra video clip.
Greenfield referred to a Wall Street Journal piece in February that suggested access means everything when it comes to D.C. politics:
“In a lucky coincidence, Tumblr Chief Executive David Karp, who attended the meeting in New York, found himself seated next to Mr. Obama at a fundraiser the following day hosted by investment manager Deven Parekh.
Mr. Karp told Mr. Obama about his concerns with the net-neutrality plan backed by Mr. Wheeler, according to people familiar with the conversation. Those objections were relayed to the White House aides secretly working on an alternative.”
That was sufficient for some to imply Karp was a powerful influence over the president’s sudden pronouncement last November that strong, all-encompassing Net Neutrality was the was to go.
CNBC’s hosts grilled Karp, asking him to prove a negative, set up false premises for Karp to defend, and repeatedly cut his answers off. At the same time, Karp was clearly unprepared and often did not have his facts in order.
Stop the Cap! sorts it all out.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CNBC Tumblr Net Neutrality 2-24-15.flv[/flv]
Nobody’s shining moment on the Net Neutrality debate on CNBC featuring an unprepared David Karp, founder of Tumblr vs. the B-team at CNBC – lackeys with an agenda who can’t wait to interrupt. Truth comes in last place. (8:18)
CNBC Claim: “If you talk to AT&T’s Randall Stephenson, he will say right now they have more capital expenditures than any company in America … and if you turn it into a utility it will not be profitable to continue investing like that.”
Fact: AT&T does invest heavily in its network but also enjoys very healthy returns on that investment. In 2014, AT&T was expected to end the year spending about $21 billion, primarily on its highly profitable wireless network. Last week, USA Today published a list of the top 12 companies in the Standard & Poor’s 500 that boosted capital spending by 40% or more in the past 12 months and spent at least 15% of revenue on capital expenditures. AT&T was not on it. Outside of claims from telecom companies and their lobbyists, there are no plans by the FCC to turn broadband into a regulated utility.
Karp Claim: “There is a tremendous amount of throttling going on right now.”

CNBC Question from Alternate Universe of Fair, Balanced Journalism: “In general, do you think heavy-handed government regulation is a good thing or a bad thing for an industry?”
Fact: “Throttling” is not well-defined here. There is intentional throttling among certain wireless companies, usually under the guise of “fair access policies” and usage caps, and there is throttling as a side effect of congestion in two areas: backbone connectivity among certain ISPs and wholesale traffic handlers and last mile congestion among providers, especially those offering DSL in rural areas, where multiple customers share access to a limited capacity middle mile network. There is no evidence that any significant wired providers are intentionally throttling the speeds of services except as part of a fair access policy or a purposeful lack of investment in network upgrades.
CNBC Claim: “You have a monopoly because it is really expensive to build the pipes so you have not had multiple people who will build pipes to the door.”
Fact: The capital cost required to offer wired broadband service to each home is a clear deterrent for many providers, but not an insurmountable one as Google and community-owned providers have demonstrated. The cable industry won early protection from competition in exclusive franchise agreements that calmed investor fears that the enormous cost of wiring communities for cable might not be repaid if a competition war broke out. AT&T later fought for and won statewide franchising agreements and considerable deregulation in many states where it provides U-verse, arguing regulatory burden reduction would enhance competition. But the same large cable and phone companies that achieved deregulation for themselves have lobbied heavily to regulate and banish community-owned providers from getting off the ground by encouraging the passage of restrictive state laws making such competition nearly impossible.
CNBC Question: “In general, do you think heavy-handed government regulation is a good thing or a bad thing for an industry?”
Our reply: Really?
Karp: I think a bright line rule that sort of spells out these foundational principles that we believe in… I think the Bill of Rights is a good thing… even without getting into the weeds, spelling out something like the First Amendment that says this is a truth that we believe… (cut off).
CNBC: I don’t see how that is an answer at all comparing this to the Bill of… I understand the Bill of Rights but… has there been a problem up to this point where you feel that people… that Net Neutrality has been violated.
Karp: We’ve had instances where companies like Comcast have tried to block whole protocols and shut off consumers access to new innovative parts of the Internet.
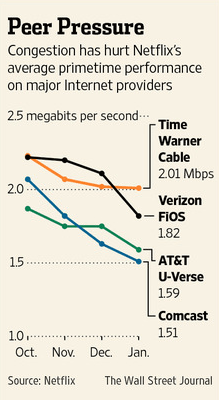
Traffic congestion problems on many major ISPs were limited to Netflix traffic, until Netflix began paying for peering connections with problem ISPs.
Fact: In 2007, Comcast installed new software or equipment on its networks that began selectively interfering with some of Comcast’s customers’ TCP/IP connections. The most widely discussed interference was with certain BitTorrent peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing communications, but other protocols were also affected. The case led to an effort by the FCC to introduce open Internet traffic rules in 2010 which Comcast later defeated in court. At no time did Comcast completely block access – it simply impeded it, reducing customer speeds only while using those services.
A CNBC host then challenged Karp to prove a negative on AT&T’s plans to pull back investment in its network expansion.
“How has it been disproven that he’s not actually going to pull in on his buildout of more infrastructure?”
Fact: On Nov 7, 2014 – a week before President Obama unveiled his support for strong Net Neutrality policies – AT&T announced at least $3 billion in capex reduction (or “pull in” to quote CNBC) for 2015 in a press release on its acquisition of Mexico Wireless Provider Iusacell:
AT&T’s VIP-related capital investment levels will peak in 2014, as the company has said previously. As a result, AT&T expects its 2015 capital expenditure budget for its existing businesses to be in the $18 billion range. This will bring the company’s capital spending as a percent of total revenues to the mid-teens level — consistent with its historical capital spending levels.
Even after AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson was announcing cutbacks in capex, his office was releasing press releases claiming a major expansion of AT&T’s gigabit fiber upgrades for U-verse, claims Stop the Cap! have found to be grossly exaggerated.
Stephenson made the mistake of putting the cart in front of the broadband horse, making it impossible to credibly claim he was reducing his capex budget because of a Net Neutrality policy that had not even been announced yet.
CNBC Claim: “It doesn’t mean someone will pay for it if they are losing money as a result.”
Fact: None of the providers mentioned by CNBC have lost any money provisioning broadband service. In fact, broadband is becoming the new profit center of the industry, netting higher revenue after adjustments for cost than any other part of the cable package.
Another exchange:
CNBC: “If you look at Netflix traffic, sometimes it is 80 percent of the network’s nighttime load.”
Karp: “The consumers are paying for it and Netflix is already paying for it.”
CNBC: “I am not a Netflix user and it ticks me off I have to subsidize everybody that is doing that. Why do I have to pay for that?”
Fact: The CNBC host is being disingenuous and inaccurate. Although Netflix traffic can constitute 80% of the evening traffic load, the customers accessing Netflix paid both Netflix and their ISP for that traffic. Whether or not the CNBC host uses Netflix or not is irrelevant. Assuming she is a Comcast or Time Warner Cable customer, last mile congestion that could impact her enjoyment of the Internet was never an issue under DOCSIS 2, has been rendered a non-issue under the current DOCSIS 3 standard, and will remain a non issue going forward.
The traffic dispute between Comcast and Netflix only affected Netflix viewing. The CNBC host need not subsidize Netflix or anyone else. Netflix offers free peering services and equipment to any ISP that wants it. Comcast refused to take part, demanding financial compensation instead. It then raised rates on customers anyway. Her beef is with Comcast, not Netflix.
 “BFRR is a joke because it requires potential customers have no access to 4G wireless service,” claimed Franklin. “You have to go to the government’s National Broadband Map to determine eligibility, which is very tough because — surprise, surprise — Verizon itself contributed its 4G wireless coverage information for that map and as far as Verizon is concerned, their 4G coverage in New Jersey is beautiful, even though it really isn’t.”
“BFRR is a joke because it requires potential customers have no access to 4G wireless service,” claimed Franklin. “You have to go to the government’s National Broadband Map to determine eligibility, which is very tough because — surprise, surprise — Verizon itself contributed its 4G wireless coverage information for that map and as far as Verizon is concerned, their 4G coverage in New Jersey is beautiful, even though it really isn’t.”

 Subscribe
Subscribe
 In the summer of 2014, Time Warner Cable had a problem. For three years, the Federal Communications Commission had been issuing reports about the quality of broadband service from the nation’s largest internet service providers. The raw data collected by about 800 subscribers of Time Warner Cable who volunteered to participate in the project began to worry executives because it showed their broadband service was oversold in certain large cities and was no longer capable of consistently achieving advertised speeds. Even worse, the company’s congestion problems threatened to lower Time Warner Cable’s internet performance score at the FCC.
In the summer of 2014, Time Warner Cable had a problem. For three years, the Federal Communications Commission had been issuing reports about the quality of broadband service from the nation’s largest internet service providers. The raw data collected by about 800 subscribers of Time Warner Cable who volunteered to participate in the project began to worry executives because it showed their broadband service was oversold in certain large cities and was no longer capable of consistently achieving advertised speeds. Even worse, the company’s congestion problems threatened to lower Time Warner Cable’s internet performance score at the FCC.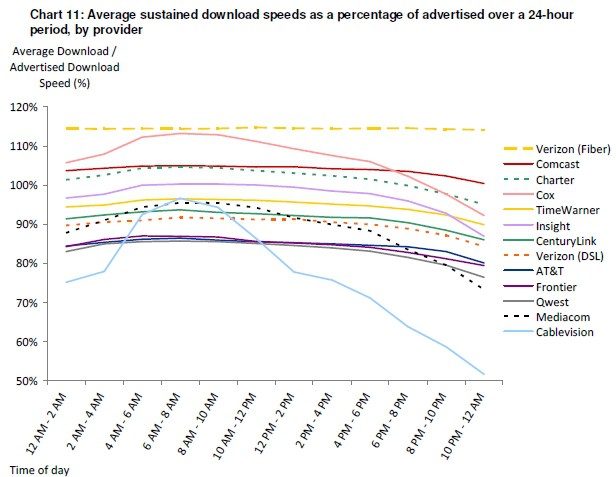
 In 2013, a Time Warner Cable executive recognized the company’s practice of limiting company-financed expansion of their upstream connections with the rest of the internet would have serious implications for their own speed test scores, because customers were encountering nightly slowdowns on popular websites like YouTube caused by overcongested connections. Company executives feared customers participating in the Sam Knows/FCC program would soon reveal Time Warner Cable’s internet speeds were beginning to suffer some of the same peak usage problems Cablevision was encountering in 2011. The executive’s solution? Temporarily expand upstream connections just long enough to protect Time Warner Cable’s broadband speed scores:
In 2013, a Time Warner Cable executive recognized the company’s practice of limiting company-financed expansion of their upstream connections with the rest of the internet would have serious implications for their own speed test scores, because customers were encountering nightly slowdowns on popular websites like YouTube caused by overcongested connections. Company executives feared customers participating in the Sam Knows/FCC program would soon reveal Time Warner Cable’s internet speeds were beginning to suffer some of the same peak usage problems Cablevision was encountering in 2011. The executive’s solution? Temporarily expand upstream connections just long enough to protect Time Warner Cable’s broadband speed scores: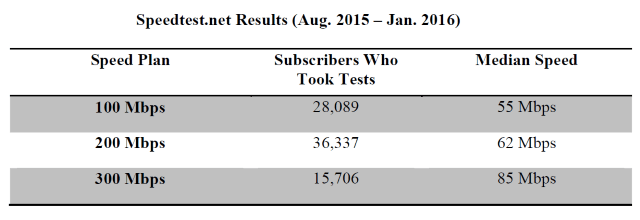
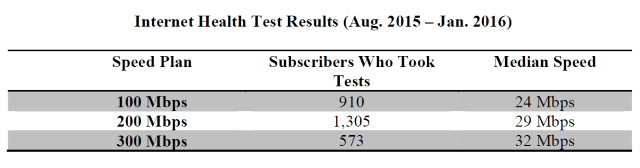
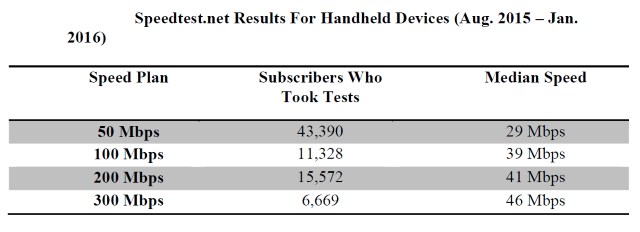
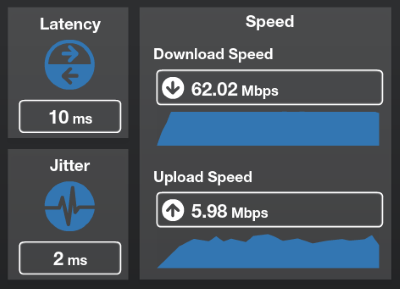

 Are you paying Windstream for
Are you paying Windstream for 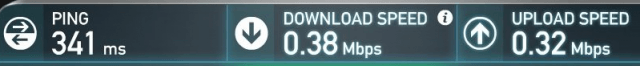

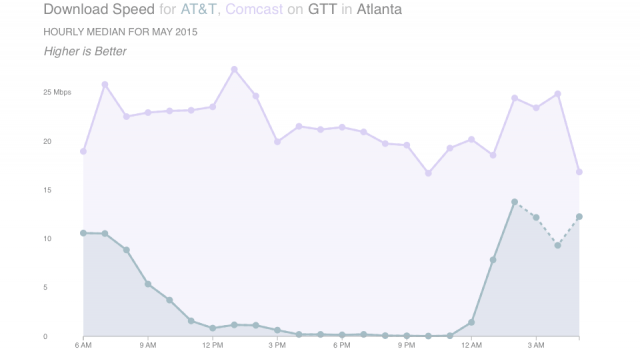
![MLab: "Customers of Comcast, Time Warner Cable, and Verizon all saw degraded performance [in NYC] during peak use hours when connecting across transit ISPs GTT and Tata. These patterns were most dramatic for customers of Comcast and Verizon when connecting to GTT, with a low speed of near 1 Mbps during peak hours in May. None of the three experienced similar problems when connecting with other transit providers, such as Internap and Zayo, and Cablevision did not experience the same extent of problems."](https://stopthecap.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/GTT-tata-640x357.png)

 Missing from this discussion are AT&T customers directly affected by slowdowns. AT&T’s attitude seems uninterested in the customer experience and the company feels safe stonewalling GTT until it gets a check in the mail. It matters less that AT&T customers have paid $40, 50, even 70 a month for high quality Internet service they are not getting.
Missing from this discussion are AT&T customers directly affected by slowdowns. AT&T’s attitude seems uninterested in the customer experience and the company feels safe stonewalling GTT until it gets a check in the mail. It matters less that AT&T customers have paid $40, 50, even 70 a month for high quality Internet service they are not getting.


