 Further expansion of Google Fiber appears to be on hold as the company contemplates moving away from fiber to the home service towards a wireless platform that could provide internet access in urban areas for less money.
Further expansion of Google Fiber appears to be on hold as the company contemplates moving away from fiber to the home service towards a wireless platform that could provide internet access in urban areas for less money.
The Wall Street Journal today reports Google parent Alphabet, Inc., is looking to cities to share more of the costs of building faster broadband networks or using cheaper wireless technology to reach customers instead.
Six years after Google first announced it would finance the construction of fiber to the home networks, the company has made progress in wiring just six communities, many incompletely. Progress has been hampered by infrastructure complications including pole access, permitting and zoning issues, unanticipated construction costs, and according to one Wall Street analyst, the possibility of lack of enthusiasm from potential subscribers.
Google’s recent acquisition of Webpass, a company specializing in beaming internet access over fiber-connected wireless antennas between large multi-dwelling units like apartments and condos appears to be a game-changer for Google. Webpass was designed mostly to service urban and population dense areas, not suburbs or neighborhoods of single-family dwellings. Webpass’ reliance on wireless signals that travel between buildings removes the cost and complexity of installing fiber optics, something that appears to be of great interest to Google.
Google Fiber is planning a system that would use fiber for its core network but rely on wireless antennas to connect each home to the network, according to a person familiar with the plans. Alphabet chairman Eric Schmidt said at the company’s shareholder meeting in June that wireless connections can be “cheaper than digging up your garden” to lay fiber. The only question is what kind of performance can users expect on a shared wireless network. Google’s plans reportedly do not involve 5G but something closer to fixed wireless or souped-up high-speed Wi-Fi. A web video on Webpass’ website seems to concede “you get best speeds with a wired connection.”

Even Google’s wireless technology solutions provider Webpass concedes that wired broadband is faster.
Former Webpass CEO Charles Barr, now an Alphabet employee, argues wireless solves a lot of problems that fiber can bring to the table.
“Everyone who has done fiber to the home has given up because it costs way too much money and takes way too much time,” Barr said.
Barr’s statements are factually inaccurate, however. Fiber to the home projects continue in many cities, but if they are run by private companies, chances are those rollouts are limited to areas where a proven rate of return is likely. Large incumbent phone and cable companies are also contemplating some fiber rollouts, at least to those who can afford it. Many of the best prospects for fiber to the home service are customers in under-competitive markets where the phone company offers slow speed DSL and cable broadband speeds are inadequate. Rural communities served by co-ops are also prospects for fiber upgrades because those operations answer to their members, not investors. Community broadband projects run by local government or public utilities have also proven successful in many areas.
 But like all publicly traded companies, Google must answer to Wall Street and their investors and some are not happy with what they see from Google Fiber. Craig Moffett from Wall Street research firm MoffettNathanson has rarely been a fan of any broadband provider other than cable operators and Google Fiber is no different.
But like all publicly traded companies, Google must answer to Wall Street and their investors and some are not happy with what they see from Google Fiber. Craig Moffett from Wall Street research firm MoffettNathanson has rarely been a fan of any broadband provider other than cable operators and Google Fiber is no different.
“One can’t help but feel that all of this has the flavor of a junior science fair,” Moffett said of Google Fiber, pointing out the service has managed to attract only 53,000 cable TV customers nationwide as of December. Moffett concedes there are significantly more broadband-only customers signed up for Google, but that didn’t stop him from suggesting Google Fiber has had very little impact on increasing broadband competition across the country.
Analysts suggest Google Fiber is spending about $500 per home passed by its new fiber network. But that is a fraction of the $3,000+ per customer often spent by cable operators buying one another.
Google’s wireless deployment will likely take place in Los Angeles, Dallas, and Chicago according to people familiar with the company’s plans. Less dense cities slated for Google Fiber including San Jose and Portland, Ore., may never get any service from Google at all, but they are likely to hear something after a six month wait.
Google is also reportedly asking cities if the company can lease access on existing fiber networks. Another tactic is requesting power companies or communities build fiber networks first and then turn them over to Google to administer. The latter seems less likely, considering there are successful public broadband networks operating on their own without Google’s help.


 Subscribe
Subscribe A federal appeals court has reversed an effort by the Federal Communications Commission to pre-empt state laws restricting municipal broadband expansion in Tennessee and North Carolina, ruling the FCC exceeded its authority by interfering with both states’ rights to define the boundaries where the community broadband networks can and cannot operate.
A federal appeals court has reversed an effort by the Federal Communications Commission to pre-empt state laws restricting municipal broadband expansion in Tennessee and North Carolina, ruling the FCC exceeded its authority by interfering with both states’ rights to define the boundaries where the community broadband networks can and cannot operate.


 Broadband life in Alaska is usually a choice (if you live in Fairbanks, Anchorage, Juneau, or another significantly sized city) between usage-capped cable operator GCI or slow-speed DSL (if you can get it) from Alaska’s two telephone companies – ACS, where unlimited service is still available, or MTA, where a 10Mbps Internet plan starts at $50 and offers up to 50GB of usage a month.
Broadband life in Alaska is usually a choice (if you live in Fairbanks, Anchorage, Juneau, or another significantly sized city) between usage-capped cable operator GCI or slow-speed DSL (if you can get it) from Alaska’s two telephone companies – ACS, where unlimited service is still available, or MTA, where a 10Mbps Internet plan starts at $50 and offers up to 50GB of usage a month.
 CenturyLink will begin a usage-based billing trial in Yakima, Wa., starting July 26 that will combine usage caps with an overlimit fee on customers that exceed their monthly usage allowance. The trial in Washington state may soon be a fact of life for most CenturyLink customers across the country, unless customers rebel.
CenturyLink will begin a usage-based billing trial in Yakima, Wa., starting July 26 that will combine usage caps with an overlimit fee on customers that exceed their monthly usage allowance. The trial in Washington state may soon be a fact of life for most CenturyLink customers across the country, unless customers rebel.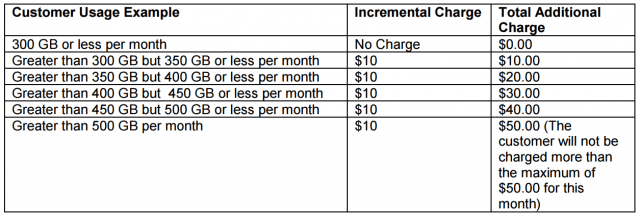

 The community of Pinetops, N.C. has
The community of Pinetops, N.C. has 

 Pinetops offers proof of the obscenity of bought-and-paid-for-politicians supporting corporate protectionism that harms people, harms education, harms jobs, and leaves rural communities with no clear path to the digital economy of the 21st century. Legislation like H129, which continues to be enforced in more than a few U.S. states, needs to be pre-empted nationwide or even better repealed by state legislators.
Pinetops offers proof of the obscenity of bought-and-paid-for-politicians supporting corporate protectionism that harms people, harms education, harms jobs, and leaves rural communities with no clear path to the digital economy of the 21st century. Legislation like H129, which continues to be enforced in more than a few U.S. states, needs to be pre-empted nationwide or even better repealed by state legislators.