 In a decision that relied heavily on trusting Altice’s word, the Federal Communications Commission quietly approved the sale of Long Island-based Cablevision Systems to a company controlled by European cable magnate Patrick Drahi.
In a decision that relied heavily on trusting Altice’s word, the Federal Communications Commission quietly approved the sale of Long Island-based Cablevision Systems to a company controlled by European cable magnate Patrick Drahi.
The decision did not come with an overwhelming endorsement from staffers at the FCC’s Wireline Competition Bureau, the International Bureau, the Media Bureau, and the Wireless Telecommunications Bureau that jointly authored the order approving the deal.
“We find the transaction is unlikely to result in any significant public interest harms,” the staffers wrote. “We find that the transaction is likely to result in some public interest benefits of increased broadband speeds and more affordable options for low income consumers in Cablevision’s service territory. Although we find that the public interest benefits are limited, the scales tilt in favor of granting the Applications because of the absence of harms.”
The FCC largely ignored a record replete with evidence Altice has not enthralled customers of its other acquired companies. In France and Portugal, large numbers of customers complained Altice reduced the quality of service, raised prices, and outsourced customer service to call centers as far away as North Africa. After Altice acquired SFR, one of France’s national wireless operators, at least 1.5 million customers canceled their accounts, alleging poor service. Two weeks ago, France’s Competition Bureau fined Altice $17 million dollars for intentionally sabotaging the viability of wireless providers it controlled in the Indian Ocean region that it knew would have to be sold because of another acquisition deal. It raised prices and alienated customers of those providers, while allowing many to escape their contracts penalty-free before ownership of the company is transferred. The new owners face a challenge restoring the reputation of those providers and win customers back.
 The FCC called assertions from the Communications Workers of America that Altice intends to secure several hundred million dollars in cost savings from layoffs and salary reductions “speculative.” But Altice’s record on job and salary cuts is well established in Europe, where trade unions have pursued multiple complaints with government ministers in Lisbon and Paris. The leadership of CFE-CGE Orange, the group representing employees in France’s telecom sector, warned government officials earlier this year Drahi’s labor practices at SFR-Numericable are so poor, there is significant risk of a wave of worker suicides.
The FCC called assertions from the Communications Workers of America that Altice intends to secure several hundred million dollars in cost savings from layoffs and salary reductions “speculative.” But Altice’s record on job and salary cuts is well established in Europe, where trade unions have pursued multiple complaints with government ministers in Lisbon and Paris. The leadership of CFE-CGE Orange, the group representing employees in France’s telecom sector, warned government officials earlier this year Drahi’s labor practices at SFR-Numericable are so poor, there is significant risk of a wave of worker suicides.
‘Not our problem’ was the effective response by the FCC staffers.
“The public interest does not require us to dissect each business decision Altice has made in non-U.S. markets to determine whether its asserted benefits in this case are reasonable,” the staffers wrote.
The staffers also opined “Altice has not identified job cuts as a means to achieve cost savings,” despite widespread media reports put Drahi on the record claiming he would find $900 million in cost savings at Cablevision in part from slashing administrative expenses.
Speaking to investors in New York just after Altice announced its agreement to buy Cablevision, Drahi pledged to bring the company’s ‘European-style austerity’ to the American cable company.
“When we took over [French wireless provider] SFR, the company was acting like daddy’s princess,” Drahi said to France’s National Assembly. “The princess spent money left and right, but it was mother company Vivendi that picked up the bills. Well, now the princess has a new dad, and this isn’t how my money gets spent.”

Drahi
“I don’t like to pay big salaries, I pay as little as I can,” Drahi added, claiming he prefers to pay minimum wage.
“It’s hard to imagine in a labor market like New York that you’re going to go to top executives and say, ‘By the way, I’m going to pay you 75 percent less than I used to — enjoy,’ ” said a skeptical Craig Moffett, a Wall Street analyst at MoffettNathanson.
Despite racking up nearly $56 billion in debt so far, the FCC seemed unconcerned Altice’s $17.7 billion purchase of Cablevision would present much of a problem for the company.
Altice is “a large international company that is likely to be better able to raise capital than Cablevision as a stand-alone entity,” the FCC staffers wrote.
Several Wall Street analysts pointedly disagree.
“My main worry is that Altice is pilling up new debts again and, needing increasingly more cash to pay back debt, may push Numericable into a direction were it shouldn’t be,” said François Godard, an analyst at Enders Analysis.
 “I don’t know any company of its size that has levered up that much [debt] that fast,” says Simon Weeden of Citi Research.
“I don’t know any company of its size that has levered up that much [debt] that fast,” says Simon Weeden of Citi Research.
Even France’s Minister of the Economy Emmanuel Macron feared Altice could become the world’s first “too big to fail” cable company.
“I have a big concern in terms of leverage on Drahi due to its size and its place in our economy,” Macron said in 2015. “He is looking to run faster than the music.”
In April alone, Altice sought $9.44 billion largely from the junk bonds market to refinance part of its existing debt and extend the time it has to repay those obligations until as late as 2026.
FCC staffers swept away concerns that an Altice-owned Cablevision would be hampered from upgrading services because of its debt obligations and accepted at face value Altice’s promises it would enhance service. The staffers claimed these promises would likely be met because Cablevision faces significant competition from Verizon FiOS and Frontier U-verse in its service areas of New York, New Jersey and Connecticut.
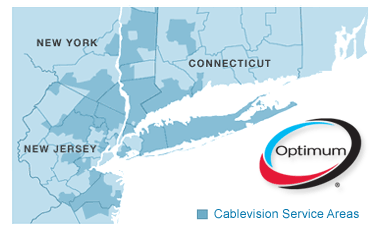
Cablevision serves communities surrounding the metropolitan New York region
What especially swayed the staffers was an ex parte letter sent by Altice offering commitments for improved service:
- Network Upgrades: Altice will upgrade the Cablevision network so that all existing customer locations are able to receive broadband service of up to 300Mbps by the end of 2017.
- Low Income Broadband: Altice will introduce a new low-income broadband package of 30Mbps for $14.99 a month throughout Cablevision’s service territory for families with children eligible for the National Student Lunch Program or individuals 65 or older eligible for the federal Supplemental Security Income program. Current customers, regardless of income, are ineligible and so are past customers who had Cablevision broadband service within the last 60 days or still have a past due balance with Cablevision.
Remarkably, the FCC passed on an opportunity to compel Altice to fulfill its commitments as part of the order giving the FCC’s approval. Therefore, if Altice reneges, it will face no consequences from the FCC for doing so.
“Because we find the transaction is likely to facilitate Cablevision’s efforts to compete and serve all customers in its territory, we are not persuaded that imposing specific conditions related to broadband deployment, as proposed by CWA, is necessary,” wrote the staffers.
New York City and the New York Public Service Commission also have an opportunity to mandate Altice’s commitments be completed within a certain time frame. Both are expected to issue their formal approval or disapproval of the acquisition later this month.
Altice praised the FCC, saying it was pleased with the decision and is on track to complete the transaction during the second quarter of this year.
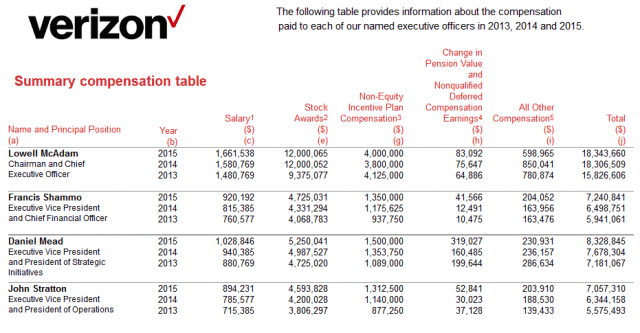
Assuming Altice does take control, it will immediately embark on cost cutting, starting with the booting of the company’s top 10 executives, according to Altice CEO Dexter Goei. Goei doesn’t like the fact the Dolan family, which founded the company, has used Cablevision as an ATM for decades. The Dolan clan collectively took $46 million in compensation in 2014. Last year, CEO James pocketed $24.6 million, up one million from the year before.
Dolan’s father, who retired from the day-to-day operations of the company years ago, is still handsomely rewarded in his role as company chairman. In 2015, Charles Dolan received a $3 million pay raise, from $15.3 million to $18.3 million.
“Somewhere in the range of $80 million to $90 million per year can go away in just not having that executive team,” Mike McCormack, an analyst at Jefferies LLC, told Bloomberg News last fall.
 Less than a decade ago, AT&T was one of El Paso’s largest private employers, with 2,400 employees. Next month, it will be a shadow of its former self with fewer than 500 local workers after a series of layoffs and call center closures.
Less than a decade ago, AT&T was one of El Paso’s largest private employers, with 2,400 employees. Next month, it will be a shadow of its former self with fewer than 500 local workers after a series of layoffs and call center closures. The union reports the annual salaries for those jobs ranged from $32,000 to $65,000 per year, plus commissions and health and retirement benefits. Offshore customer care centers pay a fraction of those salaries and many third-party contractors do not pay benefits because they designate many employees as part-time workers.
The union reports the annual salaries for those jobs ranged from $32,000 to $65,000 per year, plus commissions and health and retirement benefits. Offshore customer care centers pay a fraction of those salaries and many third-party contractors do not pay benefits because they designate many employees as part-time workers.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Altice USA employees in the Bronx and New Jersey rejected efforts by the Communications Workers of America (CWA) and the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW) to organize part of the workforce of Altice-owned Cablevision.
Altice USA employees in the Bronx and New Jersey rejected efforts by the Communications Workers of America (CWA) and the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW) to organize part of the workforce of Altice-owned Cablevision. Altice, the new owner of Cablevision, is not following the rest of the U.S. cable industry by rolling out the next generation of cable broadband — DOCSIS 3.1 — and will instead
Altice, the new owner of Cablevision, is not following the rest of the U.S. cable industry by rolling out the next generation of cable broadband — DOCSIS 3.1 — and will instead  Regardless of what the cable industry does to increase the efficiency of its hybrid coaxial-fiber networks (known as ‘HFC’), they will never achieve the capacity and robustness of all-fiber networks, which may be why Altice is seeking to stop investing in old technology in favor of something new and better.
Regardless of what the cable industry does to increase the efficiency of its hybrid coaxial-fiber networks (known as ‘HFC’), they will never achieve the capacity and robustness of all-fiber networks, which may be why Altice is seeking to stop investing in old technology in favor of something new and better.
 Assuming ATS is configured as an independent entity, it will not be required to adhere to the NY PSC order prohibiting reductions of Cablevision’s customer-facing workforce in New York State, which theoretically could allow Altice to dramatically downsize.
Assuming ATS is configured as an independent entity, it will not be required to adhere to the NY PSC order prohibiting reductions of Cablevision’s customer-facing workforce in New York State, which theoretically could allow Altice to dramatically downsize. Employees report unprecedented intensity of cost cutting and lengthy scrutiny of almost every expense. Some claim to have resorted to buying certain equipment and supplies out of pocket just to avoid drawing management scrutiny. Employee morale is reportedly low — especially at Cablevision, where reduced pay packages predominate under Altice ownership. Management has told employees to hold out for a planned IPO, which could allow them to reap some of the benefits of a Wall Street-fueled cash-raising exercise likely to be put to work buying up other cable operators in 2017.
Employees report unprecedented intensity of cost cutting and lengthy scrutiny of almost every expense. Some claim to have resorted to buying certain equipment and supplies out of pocket just to avoid drawing management scrutiny. Employee morale is reportedly low — especially at Cablevision, where reduced pay packages predominate under Altice ownership. Management has told employees to hold out for a planned IPO, which could allow them to reap some of the benefits of a Wall Street-fueled cash-raising exercise likely to be put to work buying up other cable operators in 2017. The Communications Workers of America just proved there is strength in numbers. After 39,000 network technicians and customer service representatives employed by Verizon Communications went on strike April 13 after nearly a year without a contract, Wall Street pondered the potential impact of $200 million in lost business for Verizon’s FiOS, phone and television services.
The Communications Workers of America just proved there is strength in numbers. After 39,000 network technicians and customer service representatives employed by Verizon Communications went on strike April 13 after nearly a year without a contract, Wall Street pondered the potential impact of $200 million in lost business for Verizon’s FiOS, phone and television services.


 In a decision that relied heavily on trusting Altice’s word, the Federal Communications Commission
In a decision that relied heavily on trusting Altice’s word, the Federal Communications Commission  The FCC called assertions from the Communications Workers of America that Altice intends to secure several hundred million dollars in cost savings from layoffs and salary reductions “speculative.” But Altice’s record on job and salary cuts is well established in Europe, where trade unions have pursued multiple complaints with government ministers in Lisbon and Paris. The leadership of CFE-CGE Orange, the group representing employees in France’s telecom sector,
The FCC called assertions from the Communications Workers of America that Altice intends to secure several hundred million dollars in cost savings from layoffs and salary reductions “speculative.” But Altice’s record on job and salary cuts is well established in Europe, where trade unions have pursued multiple complaints with government ministers in Lisbon and Paris. The leadership of CFE-CGE Orange, the group representing employees in France’s telecom sector, 
 “I don’t know any company of its size that has levered up that much [debt] that fast,” says Simon Weeden of Citi Research.
“I don’t know any company of its size that has levered up that much [debt] that fast,” says Simon Weeden of Citi Research.
