Canadians will learn at 4PM whether their Internet future will be unlimited or rationed with usage-based-billing (UBB) plans that could potentially charge consumers for every website they visit.
Canadians will learn at 4PM whether their Internet future will be unlimited or rationed with usage-based-billing (UBB) plans that could potentially charge consumers for every website they visit.
The much-anticipated decision from the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) comes months after last winter’s hearings on how Internet service is priced in Canada. It pits the largest phone company in the country — Bell — against small independent providers that are fighting to stay in business offering customers unlimited usage plans.
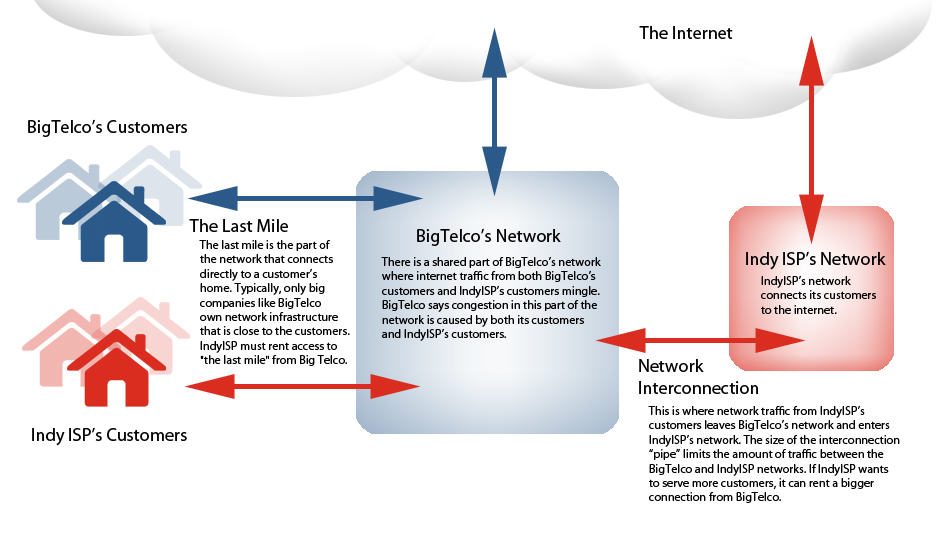
Most independent Internet Service Providers in Canada ironically buy wholesale access directly from Bell. These upstart competitors like Primus and TekSavvy deliver unlimited DSL service at attractive prices. In fact, some Bell customers have found them attractive enough to switch providers. Bell’s wholesale division indirectly competing with its own retail business has proved unsatisfactory to Bell management, who proposed repricing wholesale access to resemble what Bell charges its retail customers. But more importantly, Bell would demand that their competitors impose usage-based billing themselves, which would make unlimited Internet service in Canada a thing of the past. The CRTC initially agreed with Bell, which sparked outrage among independent providers and consumers who faced the prospect of paying inflated prices for Internet service with no unlimited usage options in sight.
The backlash brought a half-million Canadians together to demand an end to unfair Internet pricing through a petition from Openmedia.ca. That in turn attracted the attention of Canadian politicians, including Prime Minister Stephen Harper and his government’s Industry Minister Tony Clement. Clement told reporters on Feb. 3 if the CRTC didn’t reverse its approval, and fast, the government would probably overrule the commission.
A day later, outgoing CRTC chairman Konrad von Finckenstein said the commission would review its decision, the first in a series of backpedals in response to government pressure.
Even Bell, accustomed to having its way with the CRTC, has backtracked, now offering a compromise proposal that would charge independent ISPs 17.8c per gigabyte. Many providers consider that excessive, too.
 Since the hearings, several marketplace changes have deflated some of Bell’s arguments that UBB was necessary to control over-eager users congesting their network. Providers in western Canada — Shaw Cable and Telus, have dramatically boosted their respective usage caps, which call into question just how much of a congestion problem exists on Canada’s Internet networks. The Canadian Network Operators Consortium, the voice of independent service providers, has offered its own proposal to charge wholesale customers based on peak network traffic. MTS Allstream, itself a smaller player in Canadian telecom, proposed wholesale service be sold much like retail Internet in the United States — based on the speed/capacity of the service level selected. If an ISP underpredicted usage, traffic would slow for everyone until the line was upgraded.
Since the hearings, several marketplace changes have deflated some of Bell’s arguments that UBB was necessary to control over-eager users congesting their network. Providers in western Canada — Shaw Cable and Telus, have dramatically boosted their respective usage caps, which call into question just how much of a congestion problem exists on Canada’s Internet networks. The Canadian Network Operators Consortium, the voice of independent service providers, has offered its own proposal to charge wholesale customers based on peak network traffic. MTS Allstream, itself a smaller player in Canadian telecom, proposed wholesale service be sold much like retail Internet in the United States — based on the speed/capacity of the service level selected. If an ISP underpredicted usage, traffic would slow for everyone until the line was upgraded.
What ultimately gets approved by the CRTC may still be subject to government review, especially if the decision proves unpopular with consumers. In a CBC online poll being conducted this afternoon, consumer sentiment is clear. More than 91 percent of voters want the option of unlimited Internet access.
Whatever the CRTC decides will be reviewed by new Industry Minister Christian Paradis, who has managed to keep his head down and views to himself since he replaced Clement. He may be hoping more than most that the CRTC will ultimately placate everyone, just so he doesn’t have to weigh in on the thorny issue. But the CRTC’s track record representing consumers has been pretty dismal over the last few years, so we will not be surprised if the commission ultimately acquiesces to Bell’s substitute plan unaffectionately dubbed ‘GougeLite’ by Bell critics.
[flv width=”640″ height=”388″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC Internet pricing ruling expected from CRTC 11-14-11.flv[/flv]
The CBC reports on today’s expected ruling from the CRTC and what it means for Canadian Internet consumers. (3 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe