 Broadband in the United States costs far more than in other countries — nearly three times as much as in the UK and France, and at least five times more than South Korea, according to BBC News.
Broadband in the United States costs far more than in other countries — nearly three times as much as in the UK and France, and at least five times more than South Korea, according to BBC News.
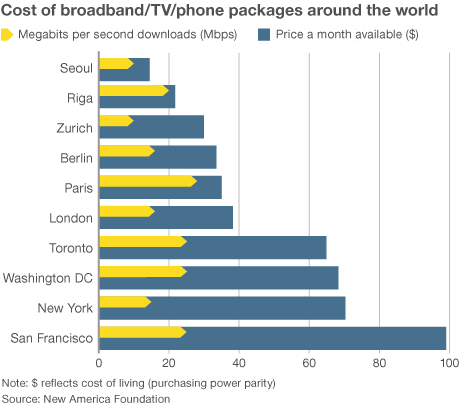
The New America Foundation compared hundreds of available packages around the world and found customers in America’s largest cities are getting the biggest bills.
Customers in San Francisco with a discounted low-medium speed bundle including broadband pay $99 a month. A near-equivalent package costs London residents $38. New Yorkers get some savings from Time Warner and Cablevision facing down Verizon FiOS. But it isn’t enough. In the Big Apple, a promotional bundle averages $70 a month. “C’est la vie,” say Parisians. They only pay $35 for about the same. Even Washington, D.C. residents, which include the country’s most powerful politicians, pay Comcast its $68 asking price. In Seoul, South Korea, a comparable offer costs $15 a month.
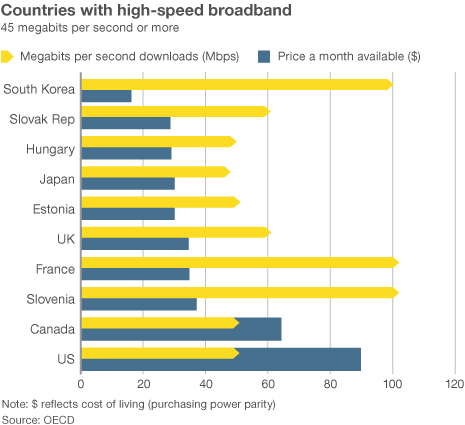
High asking prices don’t buy better service. According to a report by the OECD issued over the summer, the United States ranks among the worst in terms of broadband-only pricing. With an average price of $90 a month for 45Mbps service, the U.S. ranked 30th out of 33 countries. Add phone and television service and the price spikes to around $200.
The BBC pondered why there is such a disparity in pricing. The answer was easy to spot: the lack of true competition.
 “Americans pay so much because they don’t have a choice,” said Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Barack Obama on science, technology and innovation policy. “We deregulated high-speed Internet access 10 years ago and since then we’ve seen enormous consolidation and monopolies, so left to their own devices, companies that supply Internet access will charge high prices, because they face neither competition nor oversight.”
“Americans pay so much because they don’t have a choice,” said Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Barack Obama on science, technology and innovation policy. “We deregulated high-speed Internet access 10 years ago and since then we’ve seen enormous consolidation and monopolies, so left to their own devices, companies that supply Internet access will charge high prices, because they face neither competition nor oversight.”
Although Americans can name the largest and deep pocketed providers — Comcast, AT&T, Time Warner Cable, Verizon, Cablevision, CenturyLink, Cox, and Frontier — most cannot choose from more than one cable provider and one telephone company. Comcast does not compete against Time Warner and AT&T does not compete against Verizon, except in the wireless world where both companies offer near-identical plans and pricing.
Comcast is quite the gouger in San Francisco.
Bay area customers told the BBC they get bills ranging from $120 a month for television and broadband (not including a $7 modem rental fee) to $200 a month for phone, TV, and Internet access. That same cable company is now testing a 300GB monthly usage cap on broadband in several American cities.
In contrast South Korea offers ubiquitous free Wi-Fi letting customers avoid usage charges. Home broadband is fast and cheap. Most pay $20 a month for 100Mbps.
Digging deeper, the BBC found clues why robust broadband competition delivers savings for consumers in Europe and Asia while Americans pay more.
Rick Karr, who made a PBS documentary in the UK comparing broadband costs at home and abroad, said the critical moment came when the British regulator Ofcom forced British Telecom to open its network and allow other companies to sell broadband over its copper telephone wires. In the United States, regulators never forced cable operators to open their networks, and after a 6-3 Supreme Court decision upheld the cable industry’s insistence it need not share access with competitors, telephone companies quickly called for parity.

A 2005 Supreme Court decision upheld the cable industry’s right to keep competitors off its cable broadband network.
Some argue the ruling promotes more competition by provoking competitors to build their own networks. But current conventional wisdom among the investment community teaches one cable and one phone company is considered good enough. Additional providers would erode the standing of all and force price cutting to compete.
There are exceptions. Although Google’s fiber to the home service has drawn national attention for its inexpensive gigabit fiber broadband network ($70 for broadband-only service), at least 150 cities are served by the public sector — co-op or publicly owned utility companies that offer broadband, often delivered over fiber optic networks.
Those networks often charge considerably less than the incumbent cable operator or phone company, a fact that has driven many privately run operators to seek legislative bans on community broadband.
In response to the report, telecommunications companies avoided the topic of prices and focused instead on value for money and the future.
Lowell McAdam, CEO of Verizon Communications, said Europe was replete with a decade of underinvestment, leaving many with less than 30Mbps service. The National Cable and Telecommunications Association said it was difficult to make international comparisons on price and Scott Cleland, part of the industry-funded NetCompetition website claimed although people may pay higher bills, they can at least choose among phone, cable, wireless or satellite.
“We may be paying more in your eyes today but we are building for tomorrow and the long-term,” said Cleland.



 Subscribe
Subscribe As expected for months, Charter Communications, Inc. today formally offered Time Warner Cable shareholders $132.50 per share to assume ownership of the nation’s second largest cable operator in a deal worth more than $61 billion, including debt.
As expected for months, Charter Communications, Inc. today formally offered Time Warner Cable shareholders $132.50 per share to assume ownership of the nation’s second largest cable operator in a deal worth more than $61 billion, including debt.

 “Since we made our first proposal, Time Warner Cable has lost another half million video customers,” Rutledge said. “Their customer service continues to decline in every measure. We can improve it. We have a demonstrated track record of improving customer service. It’s a question of credibility.”
“Since we made our first proposal, Time Warner Cable has lost another half million video customers,” Rutledge said. “Their customer service continues to decline in every measure. We can improve it. We have a demonstrated track record of improving customer service. It’s a question of credibility.” Robocallers pitching extended auto warranties, home alarm systems, lowered interest rates on credit cards, and more are back in business, despite the “
Robocallers pitching extended auto warranties, home alarm systems, lowered interest rates on credit cards, and more are back in business, despite the “
 After registering, Nomorobo will guide new users through the simple set up process step-by-step.
After registering, Nomorobo will guide new users through the simple set up process step-by-step.
 Broadband in the United States costs far more than in other countries —
Broadband in the United States costs far more than in other countries —  “Americans pay so much because they don’t have a choice,” said Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Barack Obama on science, technology and innovation policy. “We deregulated high-speed Internet access 10 years ago and since then we’ve seen enormous consolidation and monopolies, so left to their own devices, companies that supply Internet access will charge high prices, because they face neither competition nor oversight.”
“Americans pay so much because they don’t have a choice,” said Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Barack Obama on science, technology and innovation policy. “We deregulated high-speed Internet access 10 years ago and since then we’ve seen enormous consolidation and monopolies, so left to their own devices, companies that supply Internet access will charge high prices, because they face neither competition nor oversight.”
