 Charter Communications has petitioned the FCC for permission to impose DATA CAPS on customers at least two years before the FCC’s prohibition on caps — a key condition imposed on the cable company in return for approval of its 2016 merger with Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks — is scheduled to expire.
Charter Communications has petitioned the FCC for permission to impose DATA CAPS on customers at least two years before the FCC’s prohibition on caps — a key condition imposed on the cable company in return for approval of its 2016 merger with Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks — is scheduled to expire.
In 2016, the FCC told Spectrum its merger was NOT in the public interest without requiring some changes and conditions that would benefit you as a Spectrum customer. Because the FCC recognized that competition was uncommon in the cable industry, it knew there would be a temptation after a merger to slap data caps on internet customers for no good reason, other than the fact the company could. In fact, data caps have long been discussed as a deterrent to keep customers from dropping cable TV subscriptions in favor of streaming video. Why? Because if you stream TV programming from Netflix, Hulu, YouTube TV, Sling, and others, that data usage would quickly eat up any data allowances Spectrum would include with its data cap. Most companies with data caps make sure you pay dearly if you go over your allowance. The de facto standard overlimit fee is $10 for each 50 GB of usage, up to a maximum ranging between $100-200 a month! That kind of bill shock would likely push you back to cable TV.
 The FCC hoped that a seven-year ban on Spectrum imposing data caps would give competition a chance to develop, and not just with streaming video. In fact, the FCC argued newly arriving cable operators, fiber to the home providers, and 5G services could probably create so much competition, data caps would likely disappear. Unfortunately, consumers have seen little competition emerge in the last four years. In fact, many still have only one choice — a cable monopoly — for internet service that meets the FCC’s minimum speed (25 Mbps) to qualify as broadband. DSL from the phone company rarely provides the speed available from your local cable operator. Fiber to the home competition is growing in some areas, but many homes still lack access. Although there has been much hype in the media about 5G, robust and fast wireless home internet will only be available in a fraction of homes for years to come.
The FCC hoped that a seven-year ban on Spectrum imposing data caps would give competition a chance to develop, and not just with streaming video. In fact, the FCC argued newly arriving cable operators, fiber to the home providers, and 5G services could probably create so much competition, data caps would likely disappear. Unfortunately, consumers have seen little competition emerge in the last four years. In fact, many still have only one choice — a cable monopoly — for internet service that meets the FCC’s minimum speed (25 Mbps) to qualify as broadband. DSL from the phone company rarely provides the speed available from your local cable operator. Fiber to the home competition is growing in some areas, but many homes still lack access. Although there has been much hype in the media about 5G, robust and fast wireless home internet will only be available in a fraction of homes for years to come.
Despite this reality, Charter is asking the FCC to let the ban on data caps expire two years early, which means they could slap data caps on customers just like you by next spring. Charter argues there are lots of streaming services now competing for your business, so there is no evidence Spectrum is hurting the marketplace for streaming television. Therefore, there is no need to protect consumers from data caps.
We argue several points in response:
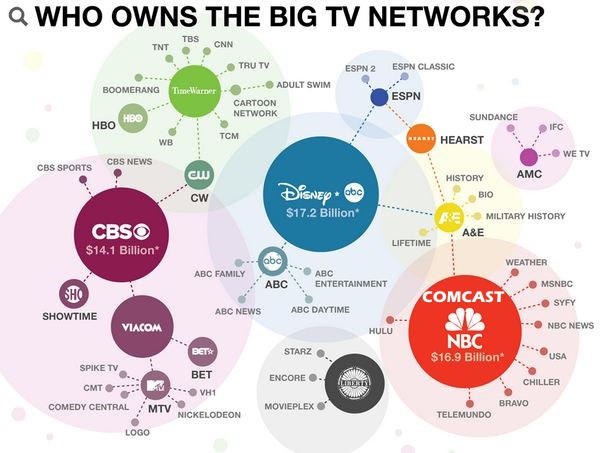
Since this graphic was created, Time Warner was sold to AT&T and CBS and Viacom have merged.
Most large streaming video providers are owned by giant satellite, cable and telephone companies (Comcast’s Peacock, AT&T’s TV/TV Now and HBO Max, Dish Network’s Sling TV), giant TV conglomerates (ABC-Disney’s Hulu/Disney +, CBS-Viacom’s All Access), or tech companies (Apple TV, YouTube TV). Netflix has raised prices for its service, in part because it has been pushed to pay cable companies like Comcast “interconnection fees” to guarantee Comcast customers will get suitable service. Most streaming services not affiliated with telecom companies have opposed data caps all along, understanding they can be anticompetitive and hurt subscriber numbers.
What competition? Charter Spectrum customers likely still have the same competitive options they had in 2016, if any, which is not enough. Imposing data caps on home broadband service illustrates that lack of competition in action. Comcast has avoided imposing data caps on its customers in the more competitive northeast and mid-Atlantic regions, where it faces Verizon’s FiOS service, which does not have data caps.
Charter asked for and was granted approval of a merger consumers did not need or want. Charter voluntarily agreed to the FCC’s conditions to close the deal. A deal is a deal, but Charter now wants to walk away. The company is spending thousands on its attorneys to free itself from the FCC’s data cap ban while claiming they have no plans to implement data caps. Do you honestly believe them?
Consumers hate data caps. In fact, just having data caps on internet service can undermine a provider’s marketing and ad campaigns and make signing up new customers difficult. Companies with data caps lose more customers than those that don’t because customers switch if a new cap-free competitor comes to town. Just dealing with implementing complicated usage meters and upset customers complaining about their accuracy costs more than any revenue companies earn from overlimit fees. Remarkably, those are not just the views of Stop the Cap! Charter itself told the FCC those were just some reasons there was a strong business case against implementing data caps. Now it is asking the FCC for permission to impose data caps despite all that!

Monroe County Legislator Rachel Barnhart has teamed up with Stop the Cap! to fight Charter’s request to allow it to data cap customers.
Data caps do not protect broadband networks from congestion, and they are not about equitably sharing internet capacity. The ongoing pandemic just proved that big cable and phone companies have existing broadband networks more than capable of handling a large spike in network traffic. Reasonable, cost-effective upgrades will continue that success story for years to come with no need for arbitrary data caps. Make no mistake. Data caps are just another way telecom companies can monetize your usage to increase their already fat profits.
What can you do?
Until July 22, 2020, you can send a comment directly to the FCC urging them NOT to allow Charter’s request to sunset merger deal conditions early. Monroe County (N.Y.) legislator Rachel Barnhart and Stop the Cap! have teamed up to push this message through to Spectrum customers everywhere. We need to put the FCC on notice it must leave well enough alone and allow the deal conditions to remain in place. We also want to send a clear message to executives at Charter that customers do not want data caps… ever. It’s a message Stop the Cap! successfully delivered in 2009 to the top leadership of Time Warner Cable, and they listened. It’s now time to send another message to the folks at Charter. We sincerely hope they will listen too.
Here is a sample letter, which we urge you to adjust to reflect your own views and circumstances before submitting:
To Whom It May Concern:
Please reject Charter’s request to sunset the deal conditions it agreed to as part of its merger with Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks.
A deal is a deal, and Charter agreed not to impose data caps on its customers for at least seven years. It now wants that prohibition lifted two years early, arguing competition has flourished over the last four years. In fact, little has changed for us. Competition has not flourished. We still do not have choices for broadband service and although there are more streaming video providers, most are owned by large cable, satellite, and phone companies or giant media conglomerates. Data caps will make me reconsider using these services because I cannot afford an even higher internet bill.
Competition is supposed to bring pricing down in a healthy marketplace. But my bill is only going up. What kind of company would ask for permission to slap usage limits on customers in the middle of a pandemic, after telling everyone their networks were more than robust enough to handle increased stay-at-home usage? The answer is a company that faces little competition and has no fear a competitor will use this request against them. Internet affordability is already an enormous problem, and data caps just make internet service even more expensive. We already pay among the highest prices in the world for service.
My family did not ask for this merger, and the FCC in 2016 determined it was not in the public interest to approve it without imposing a handful of conditions to allow consumers to benefit from the transaction. The FCC should insist Charter be true to its word and not impose data caps. Charter told the FCC in 2016 it had an “aversion to data caps, stating that instead of enforcing usage limits it chooses to market the absence of data caps as a competitive advantage” and that “there is a strong business case for not implementing caps” and that caps “undermined” its marketing messaging. Was Charter being honest with the FCC in 2016? Their current request for permission to lift data caps seems to ignore the positions Charter itself took with the FCC just a few years ago.
We urge you to deny Charter’s petition, which will allow Charter to continue making plenty of money from the sale of unlimited internet access and continue honoring its advertising commitments to sell internet service “with no data caps” as it does now.
To submit your comments on this issue:
First, click this link to be taken to the FCC website.
Second, click the link on the left sidebar marked “+Express” as circled below:
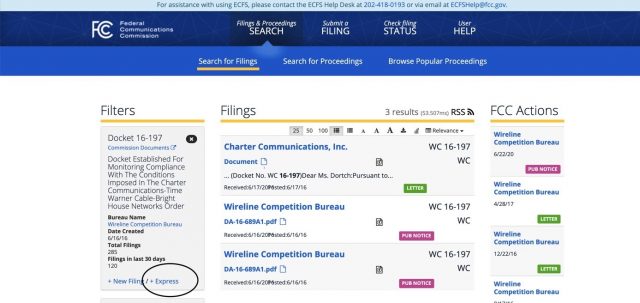
Third, fill out the form as completely as possible, and leave your comments in the “brief comments” box at the bottom.
You can also mail your written comments:
Mail TWO COPIES of your written comments, which should open with the greeting “Dear Secretary Dortch,” and close with your signature to this address:
Ms. Marlene H. Dortch
Office of the Secretary
Federal Communications Commission
445 12th Street SW
Washington, DC 20554


 Subscribe
Subscribe




 But Moffett is thinking even further ahead, by suggesting wireless carriers might be able to stop spending billions on building and expanding their competing 4G LTE networks when they could all share a single provider’s network in each city. That idea could work if providers agreed to creating local monopolies.
But Moffett is thinking even further ahead, by suggesting wireless carriers might be able to stop spending billions on building and expanding their competing 4G LTE networks when they could all share a single provider’s network in each city. That idea could work if providers agreed to creating local monopolies.

 “Our work suggests that cable companies have room to take up broadband pricing significantly and we believe regulators should not oppose the re-pricing (it is good for competition & investment).”
“Our work suggests that cable companies have room to take up broadband pricing significantly and we believe regulators should not oppose the re-pricing (it is good for competition & investment).” The community of Pinetops, N.C. has
The community of Pinetops, N.C. has 

 Pinetops offers proof of the obscenity of bought-and-paid-for-politicians supporting corporate protectionism that harms people, harms education, harms jobs, and leaves rural communities with no clear path to the digital economy of the 21st century. Legislation like H129, which continues to be enforced in more than a few U.S. states, needs to be pre-empted nationwide or even better repealed by state legislators.
Pinetops offers proof of the obscenity of bought-and-paid-for-politicians supporting corporate protectionism that harms people, harms education, harms jobs, and leaves rural communities with no clear path to the digital economy of the 21st century. Legislation like H129, which continues to be enforced in more than a few U.S. states, needs to be pre-empted nationwide or even better repealed by state legislators.