 The editorial and opinion page of The Washington Post has always been an uneven experience, especially when it comes to their views on the telecommunications business.
The editorial and opinion page of The Washington Post has always been an uneven experience, especially when it comes to their views on the telecommunications business.
For years, the Post’s editorial page has been suspiciously cable-friendly. It favored Comcast’s failed 2014 acquisition of Time Warner Cable — a thought so horrible, readers were likely to spit out their morning coffee after seeing it. At first, one might have attributed the editorial board’s friendliness to the fact its corporate parent at the time also owned Cable One, a cable operator serving small and medium cities in places Comcast, Charter, and Cox forgot. But Cable One is now long gone — spun off as an independent entity. So perhaps laziness explains why reporters and columnists are frequently suckered by well-worn talking points from a cable industry on the defensive — celebrating every article proclaiming the impact of cord-cutting is muted, at best.
This morning’s shallow column by “right-leaning blogger” Megan McArdle, “You think you hate your cable bundle. You’re wrong,” is an excellent case in point. It’s a combination of cable industry folderol and misunderstanding of the economics of today’s cable business.
McArdle argues that recent subscriber growth by Netflix, Hulu, and other streaming services should mean we can get rid of the hated cable television bundle. Only we don’t she says, because we “actually love bundles.”
Her argument runs into trouble almost immediately when attempting to conflate a-la-carte economics of the television business with the likely impact of that type of pricing on hotels, airlines, and restaurants:
When you book a hotel, you expect “complimentary” mattresses, sheets and towels, rather than renting each individually. When you go to a restaurant, you don’t pay extra to enjoy the use of a plate. And you get very testy indeed upon discovering that your bargain airline charges you to choose a seat or bring luggage.
Bundling, it turns out, is valuable. You aren’t willing to give up complimentary shampoo and towel service when you’re traveling, because that turns every shower into a financial decision. The hotel, meanwhile, would need more staff to field requests for trivia, raising the price of the room. Much better for everyone to sell you a bundle that we call a “hotel room” but that really includes a bunch of ancillary products you might like to use during your stay.

In 2014, the Washington Post editorial page endorsed the Comcast-Time Warner Cable merger that eventually fell apart.
Value is in the eye of the beholder, and hundreds of thousands of cable customers are doing what was once unthinkable for the cable industry (and Ms. McArdle) — they are cutting the cord to their cable television package for good. That is a fact many cable executives are now willing to acknowledge. It is why CEO’s complain about the inflation rate of cable programming costs and the fact subscribers are no longer amenable to annual budget-busting rate hikes for cable television. Some cable companies now attempt to hide those growing costs in fine print surcharges for broadcast TV stations and sports programming. Others are offering new slimmed-down cable package options for customers no longer willing to pay for dozens of channels they will never watch. It’s a story we’ve covered for nine years, but one Ms. McArdle obviously missed.
Her analogies about an a-la-carte world for hotels and airlines isn’t a good one because nobody staying in a motel or flying complains about getting too much from either. As with all things, there is a general consensus about what one can expect staying in a Holiday Inn or flying Delta. You can find outliers like the seedy motel with hourly rates that charges for clean sheets or the airline that is now contemplating new seating arrangements that cram people even tighter into an almost-standing position. But when you signed up for cable television, you did not expect or ask for hundreds of channels — many added not because subscribers valued them but because of corporate contract decisions or launch bonuses. But you didn’t have much of a choice with “take it or leave it” lineups. McArdle’s argument falls into the industry’s favorite talking point of all — the value proposition. ‘Yes, your cable bill is now headed for $200 a month, but look at all the value we give you by bundling dozens of networks you’ve never heard of with a phone line you don’t want and an internet connection that we now target for our annual rate hikes.’
Bundled pricing is designed to trap you into their business model, and any attempt to claim we “love” those pricing plans is extremely misguided.
 Take Spectrum’s misleading promotion for a year of their triple play bundle, marketed as: TV+Internet+Voice with a price of $29.99/mo each. Not a bad deal. One can take internet service and television, for example, and expect to pay just under $60 a month for both. That’s a fine price. But then you missed the fine print. It actually says “from $29,99/mo each for 12 months when bundled.” To actually get those services for $29.99 a month each you have to take all three. If you just want the aforementioned bundle of television and internet service, the promotional price for that is $59.99 a month for television, plus $29.99 a month for internet — which adds up to one cent more than Spectrum’s triple play promotion, which also includes a phone line.
Take Spectrum’s misleading promotion for a year of their triple play bundle, marketed as: TV+Internet+Voice with a price of $29.99/mo each. Not a bad deal. One can take internet service and television, for example, and expect to pay just under $60 a month for both. That’s a fine price. But then you missed the fine print. It actually says “from $29,99/mo each for 12 months when bundled.” To actually get those services for $29.99 a month each you have to take all three. If you just want the aforementioned bundle of television and internet service, the promotional price for that is $59.99 a month for television, plus $29.99 a month for internet — which adds up to one cent more than Spectrum’s triple play promotion, which also includes a phone line.
Do subscribers “love the bundle” or traditionally take it because it is the only package on offer from the cable company that makes economic sense, given the options?
McArdle continues:
Bundling is especially valuable in businesses where fixed costs account for a disproportionate share of the total price. Once you’ve gone to the monstrous expense of building and staffing a hotel, providing extra amenities generates little additional cost while adding a great deal of value for the customer. And the same is true of cable. Much of the expense comes from laying and maintaining a wire to your house; adding another channel is relatively cheap.
Right now, cable companies sell you phone, Internet service and entertainment products, all of which share one wire, one maintenance operation and one customer service staff. Without those other services, the Internet division would have to cover all that overhead. So if you pay less for the entertainment, you’re probably going to have to pay more for connectivity.
The sunk costs of cable company infrastructure have been largely paid off for years. Today’s cable systems were largely designed and last significantly overhauled in the 1990s and early 2000s to make room for more television channels. Every service contemplated for sale by the cable industry, including broadband, was designed to work over a hybrid fiber-coax network design that has been in place for 20 years. Move analog television channels to digital, and one opens up room for more broadband. Need more bandwidth for broadband? Order a node split to further divide pools of users.
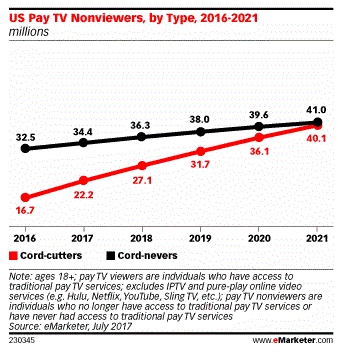 The cable industry itself rejects McArdle’s argument for the one-size-fits-all cable bundle. It is why companies have started to introduce slimmed down cable packages and sell new packages of over the top streaming cable TV channels to their broadband-only customers. The costs to deliver and support the broadband services cable companies now love to offer have been declining for years, even as rates increase. Ms. McArdle is obviously also unaware of the industry’s push to launch more self-service options for customers to cut down support calls and dramatically reduce the number of truck rolls to customer homes. She may also not realize the impetus to raise prices comes not out of necessity, but from Wall Street and investors’ revenue expectations.
The cable industry itself rejects McArdle’s argument for the one-size-fits-all cable bundle. It is why companies have started to introduce slimmed down cable packages and sell new packages of over the top streaming cable TV channels to their broadband-only customers. The costs to deliver and support the broadband services cable companies now love to offer have been declining for years, even as rates increase. Ms. McArdle is obviously also unaware of the industry’s push to launch more self-service options for customers to cut down support calls and dramatically reduce the number of truck rolls to customer homes. She may also not realize the impetus to raise prices comes not out of necessity, but from Wall Street and investors’ revenue expectations.
As cable television programming prices increase, the profit margin on cable television goes further into decline. But the cable industry makes up the difference by raising broadband prices. That is one segment of its business that remains very strong. Losing video subscribers is not the disaster Ms. McArdle suggests it could be. In fact Moody’s recently noted that with broadband profit margins about three times more than for video, the economic loss from a departing video customer can be neutralized by growing broadband subscribers at a fraction of the video unit’s loss. The ratings agency estimates that a ratio of about two broadband subscribers added for every video customer loss should offset revenue losses, while a ratio of 0.67 times that takes care of profit declines as well. That is based on current prices. Therefore, as cable companies add broadband customers, they easily offset the financial impact of video customers departing with no actual need to raise rates.
McArdle finally falls into the trap of using today’s linear TV paradigm as the basis of her argument that if all cable television channels were sold a-la-carte, they would cost astronomically more than they do as part of a bundle. But if that were true, the slimmed down competitive offerings of DirecTV Now, Sling TV, and others would be substantially more expensive than they actually are. For many customers, the out-the-door price is what matters, even if they are paying more for each of the channels they are interested in watching. A $35 DirecTV Now bill is still a lot less than an $80 cable TV bill, which often does not include surcharges and equipment fees.
Wall Street analyst Richard Greenfield of BTIG Research is so skeptical of the future of today’s bloated bundles, he has a Twitter tag: #goodluckbundle that expresses his view that bundled, linear, live television itself is decreasing in importance as viewers turn to on-demand streaming services. Subscriber satisfaction with Netflix and Hulu is much higher than almost any cable company.
Snapshot of #cordcutting — more consumers are abandoning the “big” bundle #goodluckbundle https://t.co/Bp8Zz9LX2T pic.twitter.com/bTwUjKu0F5
— Rich Greenfield (@RichBTIG) August 11, 2016
One of Stop the Cap!’s readers understands subscribing to a lot of streaming services can also cost a lot, but customer satisfaction matters even more:
“It still adds up when you subscribe to a lot of services, but my satisfaction has never been higher because I am getting services with a lot of things I want to watch instead of hundreds of channels I don’t,” said Jack Codon. “When you flip through the channels and run into Sanford & Son, Law and Order, home shopping, and terrible reality show trash, you just get angry because I was paying for all of it. Now I pay Netflix and they spend the money on making more shows I will probably want to watch, as opposed to reruns I don’t.”
McArdle is correct about one thing — we should expect streaming and internet prices to increase, but not because of what she wrote. The real reason for broadband rate hikes is the lack of competition, which allows companies to implement “because we can” rate increases. Netflix itself hinted it may also increase prices incrementally down the road, but not with the intention of rewarding executives and shareholders with fat bonuses and dividend payouts. Netflix wants to pour all it can into additional content development to give customers even more reason to watch Netflix and little, if anything else.


 Subscribe
Subscribe A company is testing a solution to video subscription password abuse that will register each device authorized to access streaming video, while giving customers a Forever Login, ending the need to regularly re-enter usernames and passwords to watch.
A company is testing a solution to video subscription password abuse that will register each device authorized to access streaming video, while giving customers a Forever Login, ending the need to regularly re-enter usernames and passwords to watch. Under the new system, a customer will be permitted to register a limited number of “trusted devices” allowed access to streamed video content. A cable company, for example, could limit subscribers to two smartphones, one tablet, and one smart/internet-enabled TV or Roku box. Even if the subscriber has other devices, they would have to unregister an existing device before being allowed to register a new one. Additionally, a cable operator could limit concurrent streams to two or three, either per network or per account, regardless of what networks are being watched. That would mean, in one example, a family of four would designate a maximum of five “trusted devices” and be allowed to watch up to three concurrent streams per account. “Bill” could watch ESPN on the bedroom television, “Mary” could watch a murder-mystery on the Hallmark Channel on her tablet on the patio, and “Dylan” could watch a movie on HBO on his phone at the same time. But if “Sara” decided to watch a show on Lifetime on her phone, the system would block the request.
Under the new system, a customer will be permitted to register a limited number of “trusted devices” allowed access to streamed video content. A cable company, for example, could limit subscribers to two smartphones, one tablet, and one smart/internet-enabled TV or Roku box. Even if the subscriber has other devices, they would have to unregister an existing device before being allowed to register a new one. Additionally, a cable operator could limit concurrent streams to two or three, either per network or per account, regardless of what networks are being watched. That would mean, in one example, a family of four would designate a maximum of five “trusted devices” and be allowed to watch up to three concurrent streams per account. “Bill” could watch ESPN on the bedroom television, “Mary” could watch a murder-mystery on the Hallmark Channel on her tablet on the patio, and “Dylan” could watch a movie on HBO on his phone at the same time. But if “Sara” decided to watch a show on Lifetime on her phone, the system would block the request. But many subscribers, especially those with larger families, are likely to balk at the new restrictions, especially if cable operators offer to ease them in return for additional fees. The process of registering devices is also likely to be seen as cumbersome by those not technically proficient, as well as those who own a large assortment of electronic devices.
But many subscribers, especially those with larger families, are likely to balk at the new restrictions, especially if cable operators offer to ease them in return for additional fees. The process of registering devices is also likely to be seen as cumbersome by those not technically proficient, as well as those who own a large assortment of electronic devices. While giant cable company mergers unexpectedly took a breather in 2017, Fierce Cable predicts this year isn’t likely to be a repeat of last year.
While giant cable company mergers unexpectedly took a breather in 2017, Fierce Cable predicts this year isn’t likely to be a repeat of last year. Charter Communications CEO Thomas Rutledge is fed up with customers sharing their passwords to unlock television streaming services for non-subscribing friends and family and promises to lead an industry-wide crackdown on the practice in 2018.
Charter Communications CEO Thomas Rutledge is fed up with customers sharing their passwords to unlock television streaming services for non-subscribing friends and family and promises to lead an industry-wide crackdown on the practice in 2018.
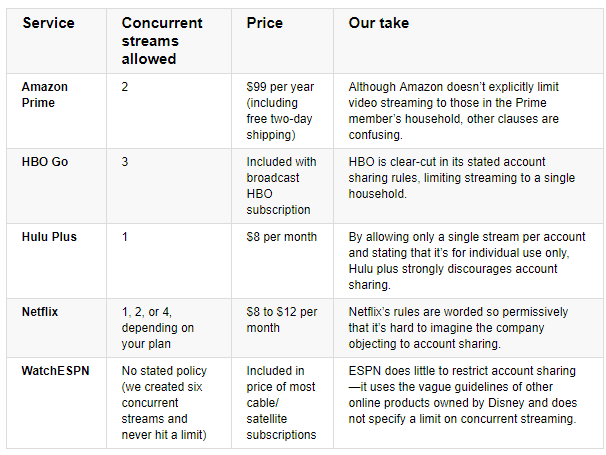
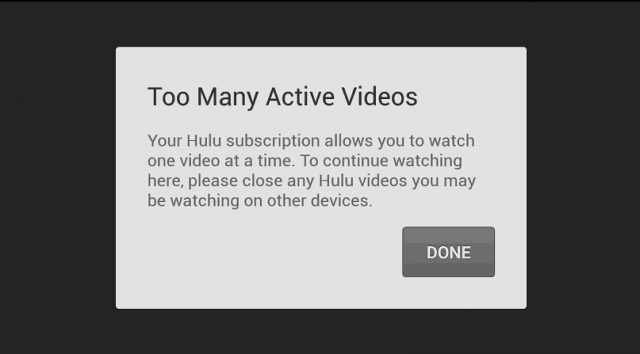 Viacom successfully negotiated the transition of its networks back to the Select TV plan beginning in late January, 2018. But those networks’ online viewing platforms and apps will now include stream limitations to keep simultaneous viewing and password sharing to a minimum.
Viacom successfully negotiated the transition of its networks back to the Select TV plan beginning in late January, 2018. But those networks’ online viewing platforms and apps will now include stream limitations to keep simultaneous viewing and password sharing to a minimum.

