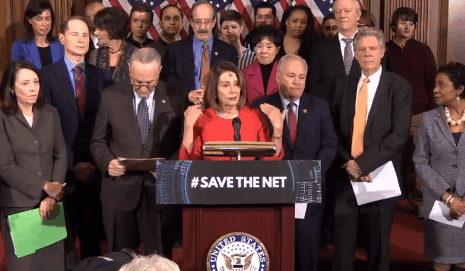
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi, with fellow Senate Democrats and FCC Commissioner Jessica Rosenworcel (upper left corner), speaks at the announcement of a new bill that would codify net neutrality as federal law.
Democrats in Congress this morning unveiled a new bill that would effectively reinstate the 2015 Open Internet rules repealed under the Trump Administration’s Republican-dominated Federal Communications Commission.
The new bill, “Save the Internet Act of 2019,” was hailed by House Speaker Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.) as a “pillar of economic opportunity” for the digital 21st century information economy and a bill that will stop internet service providers from raising broadband prices even higher.
“A full 86% of Americans oppose the Trump assault on net neutrality including 82% of Republicans,” Pelosi said at an announcement ceremony held in Washington this morning. “With the Save the Internet Act, Democrats are honoring the will of the people and restore the protections that do this — stop unjust discriminatory practices by ISPs that try to throttle the public’s browsing speed, block your internet access, and increase your costs. This is about freedom, this is about cost.”
FCC Chairman Ajit Pai announced his intention to repeal net neutrality in 2017, and despite tens of millions of letters protesting that decision, Pai began rolling back net neutrality rules last year.
The three-page bill was co-sponsored by 46 Democrats in the U.S. Senate. It codifies the language from the FCC’s 2015 Open Internet rules as a standalone federal law, no longer subject to reinterpretation or dismissal by the FCC. A companion bill is expected to be introduced in the House on Friday.
Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.) implored Senate Republicans to get on board with Democrats to support the re-establishment of a level playing field on the internet, criticizing their lack of support during last year’s effort to resurrect net neutrality.
“Unfortunately, all but three Senate Republicans voted on behalf of the special interests,” Schumer said, noting the measure still passed the Senate in 2018 but ultimately was shelved by the then-Republican controlled House. “So now we have a Democratic House, and Republicans will have a second chance — there are second chances — to right the Trump Administration’s wrong.”
Here’s the Save The Internet Act of 2019 that nearly every Senate Democrat joined me in introducing today. 3 pages that will restore #NetNeutrality. Let’s pass it and make the internet free and open again. #SaveTheNet pic.twitter.com/BCYtcmcMe3
— Ed Markey (@SenMarkey) March 6, 2019
Net neutrality has faced multiple legal challenges and intense lobbying by the telecommunications industry, especially by large cable and phone companies that generally oppose the concept, claiming it would impede management of their networks and block the creation of new innovative services that could deliver extra bandwidth on demand. Telecom companies also complain content providers like Netflix unfairly utilize their networks without fair compensation.
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi and her fellow Senate Democrats introduce the Save the Internet Act of 2019, a bill re-establishing net neutrality as federal law. (31:35)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Windstream Holdings, Inc.
Windstream Holdings, Inc. 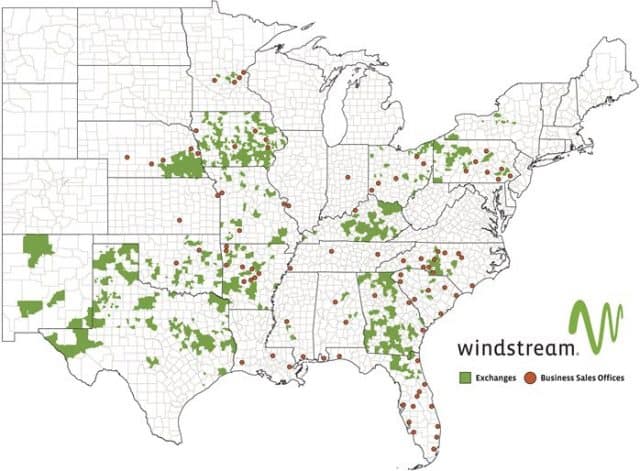

 Pai’s office this week released
Pai’s office this week released  Investors are not buying into the substantial hype surrounding the forthcoming 5G revolution and many remain unconvinced about the benefits of spending billions of investor dollars to deploy the next generation in wireless.
Investors are not buying into the substantial hype surrounding the forthcoming 5G revolution and many remain unconvinced about the benefits of spending billions of investor dollars to deploy the next generation in wireless.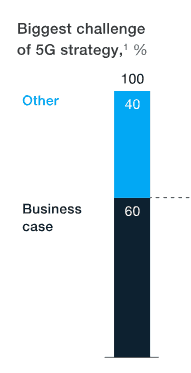 Customer demand for 5G is anticipated to be low until new devices are introduced capable of connecting to it, and investors already recognize consumers are increasingly delaying device upgrades since the industry dropped two-year service contracts with device subsidies. Ongoing upgrades to existing 4G LTE networks may ultimately dampen demand even for less costly 5G networks that will be deployed on existing cell towers. McKinsey’s survey found less than 35% of respondents are planning quick launches of 5G on gigabit-speed capable millimeter wave spectrum, citing the high cost of deploying small cell networks.
Customer demand for 5G is anticipated to be low until new devices are introduced capable of connecting to it, and investors already recognize consumers are increasingly delaying device upgrades since the industry dropped two-year service contracts with device subsidies. Ongoing upgrades to existing 4G LTE networks may ultimately dampen demand even for less costly 5G networks that will be deployed on existing cell towers. McKinsey’s survey found less than 35% of respondents are planning quick launches of 5G on gigabit-speed capable millimeter wave spectrum, citing the high cost of deploying small cell networks.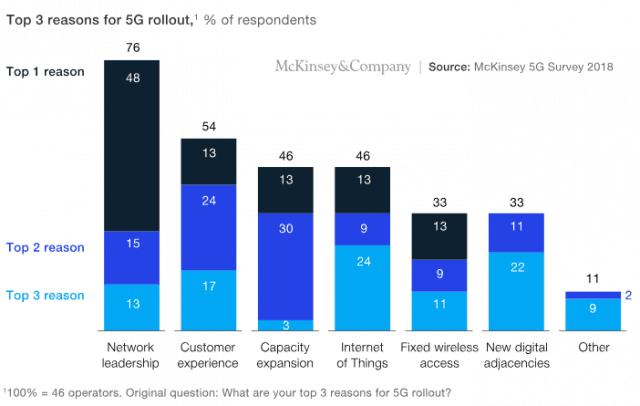 “Although commercially in its infancy, 5G technology is ready, and in most markets its presence will be felt from 2020 on,” McKinsey’s report states. “Yet the fact that commercial models are not ready cannot be minimized; the business case is marginal, and the investments to enable new business models are not currently planned.”
“Although commercially in its infancy, 5G technology is ready, and in most markets its presence will be felt from 2020 on,” McKinsey’s report states. “Yet the fact that commercial models are not ready cannot be minimized; the business case is marginal, and the investments to enable new business models are not currently planned.”