
AT&T suddenly announced it was ready to build its own gigabit fiber network in Austin.
AT&T and Time Warner Cable report they are ready to make more investments in their operations in Austin, Tex. to compete with Google Fiber when it arrives in the middle of next year.
Time Warner Cable says it already operates a multi-gigabit fiber optic network — one residential customers cannot easily access or afford. Residential broadband speeds at the cable operator top out at 50/5Mbps in Austin, at a cost higher than what Google plans to charge for 1,000/1,000Mbps service. AT&T’s U-verse network maxes out at 24/3Mbps, assuming customers have good copper wiring between AT&T’s fiber in the neighborhood and their home.
“The cable and phone company providers have purposely confused their networks’ maximum speed capacity with real end-user speeds for years, and when that fails to convince they simply claim customers don’t need or want those speeds anyway,” says Stop the Cap! reader and Austin resident Sam Knoll.
Knoll is enthusiastic about giving Time Warner Cable the boot, partly to pay them back for their aborted consumption billing trial attempted in Austin in 2009.
“I am not completely convinced Time Warner Cable understands just how much damage they did to their reputation when they pulled that stunt, and I’m certain they will attempt it again if they have a chance,” Knoll said. “The best thing customers can do is switch to a provider that believes usage caps and consumption billing are the fraudulent ripoff we know them to be. Google already knows this.”

Some Time Warner Cable customers in Austin never forgot the company tried to meter Internet usage in a failed experiment back in 2009. (Image: The Austinst)
Competition from deep-pocketed Google could eventually transform the broadband business model for American providers, assuming Google builds its fiber network in enough cities to challenge the conventional wisdom that prices have plenty of room to grow with faster Internet access. The more customers that sign up for Google’s already-super-fast broadband, the more providers will have to compete with better and faster service.
But AT&T is not convinced. The company announced yesterday it was prepared to build a gigabit fiber network not just in Austin, but also in surrounding Williamson County, with plenty of caveats.
“[We will only build the network if] the demand is there and if we get the same terms and conditions as Google received,” said AT&T spokeswoman Tracy King.
AT&T told the Austin American-Statesman the company wanted a faster regulatory approval process and permission to only build its faster fiber network in neighborhoods where there is proven demand for the service. Current franchise agreements often compel providers to offer service throughout the community and prohibits “cherry-picking” customers in high-income or low construction cost areas.
An AT&T official told KEYE-TV he had no idea how much AT&T would charge for gigabit broadband. Google charges $70 a month in Kansas City.
Austin has promised cooperation with Google, although it is not extending tax breaks or grants to the search engine giant. Google will get easy access to Austin Energy’s municipally owned infrastructure including utility poles and rights-of-way.
Google is speculated to be building showcase fiber networks to embarrass incumbent cable and phone providers who typically sell standard broadband service with speeds of 6-15Mbps in most larger communities. Rural areas are lucky to have 3Mbps service, and often much less.
But if Google intended to force major upgrades by cable and phone companies across the country, it might be disappointed with the response so far from AT&T and Time Warner Cable. Both companies indicate they will invest in and upgrade their networks to compete, but only in the service areas where Google-style competition exists. For the rest of the country, phone and cable companies are prepared to continue with the current “broadband scarcity” business model that delivers upgrades only occasionally, often accompanied by usage limits, consumption billing, and/or higher prices.
“Google has proved that there is a business model for selling abundant bandwidth as opposed to a business model for allocating scarce bandwidth,” said Blair Levin, a former chief of staff of the Federal Communications Commission.
“They are saying this is not an experiment. It is a business,” Levin told the newspaper. “In Kansas City, Google did the country an enormous favor. They said, give us regulatory flexibility to design the business and give us access to city property so we can build a network to lower the cost.”
[flv width=”640″ height=”380”]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KEYE Austin Competitor Chimes In After Google Announcement 4-9-13.flv[/flv]
KEYE in Austin talks with AT&T about their plans for a gigabit broadband network to compete with Google Fiber. The AT&T spokesman seemed more interested in pitching the company’s deregulation agenda and was short on specifics. (3 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KXAN Austin What competition will Google Fiber face 4-9-13.mp4[/flv]
KXAN in Austin talked with Google competitors Time Warner Cable and AT&T about how they will respond to the Google Fiber challenge. (3 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KVUE Austin Fiber Wars in Austin 4-9-13.mp4[/flv]
KVUE in Austin called Google’s entry into the city the opening salvo of ‘Fiber Wars,’ as AT&T promises its own gigabit network. Austin residents intend to take advantage of the competition to force providers to give them better deals to keep their business. (3 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KXAN Austin Google Fiber Possibilities Google Insider 4-9-13.mp4[/flv]
KXAN explains the possibilities of gigabit fiber, but also asks a former Google insider why the search engine is getting into the broadband business. (5 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KTBC Austin Time Warner Cable Responds to Google 4-9-13.mp4[/flv]
KTBC was skeptical of AT&T’s sudden interest in gigabit broadband. “Gee, what a coincidence,” commented the anchor of Austin’s Fox affiliate. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe On the heels of today’s announcement from Google that it intends to make Austin, Tex. the next home for Google Fiber, AT&T
On the heels of today’s announcement from Google that it intends to make Austin, Tex. the next home for Google Fiber, AT&T 
 Windstream Communications is under investigation by the Governor’s Office of Consumer Protection because of allegations the company is advertising broadband speeds and performance the company simply cannot deliver its customers in Georgia.
Windstream Communications is under investigation by the Governor’s Office of Consumer Protection because of allegations the company is advertising broadband speeds and performance the company simply cannot deliver its customers in Georgia.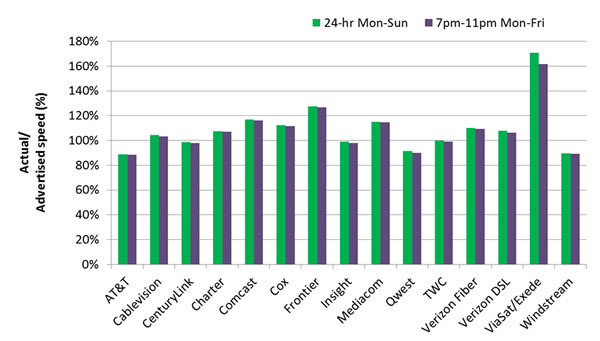
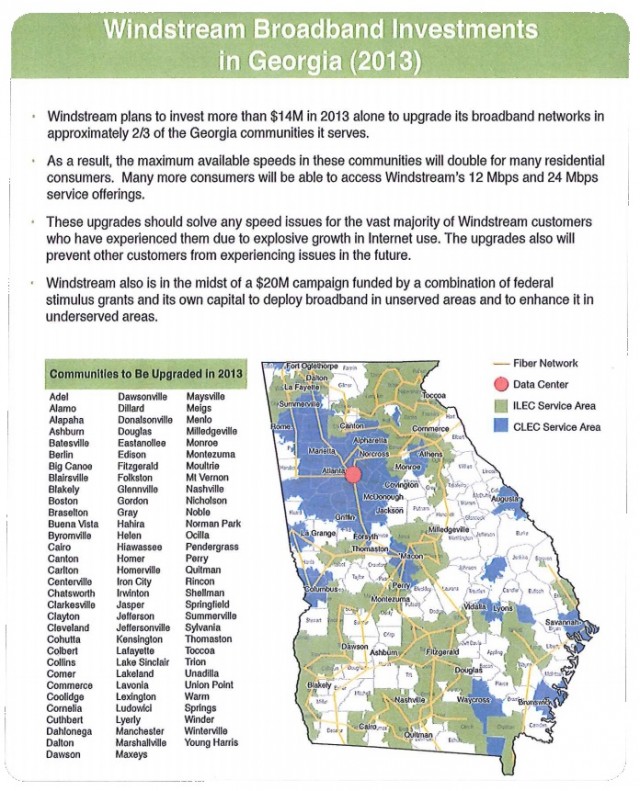
 Stop the Cap! has developed a sample e-mail message Georgia residents can use to petition the state legislature to vote NO on H.B. 282, the latest Big Telecom corporate welfare bill to kill competition from publicly-owned broadband networks. With thanks to Mark Creekmore, one of many rural Georgians suffering with DSL “service” from Windstream Communications, we have jointly created this letter to illustrate the folly of this bad bill. We may need to
Stop the Cap! has developed a sample e-mail message Georgia residents can use to petition the state legislature to vote NO on H.B. 282, the latest Big Telecom corporate welfare bill to kill competition from publicly-owned broadband networks. With thanks to Mark Creekmore, one of many rural Georgians suffering with DSL “service” from Windstream Communications, we have jointly created this letter to illustrate the folly of this bad bill. We may need to 