 AT&T and Camden Property Trust have announced an agreement to offer broadband, television, and phone services over fiber to the premises technology beginning this fall, serving new high-end apartment homes owned by the developer in Atlanta, Austin, and Orlando.
AT&T and Camden Property Trust have announced an agreement to offer broadband, television, and phone services over fiber to the premises technology beginning this fall, serving new high-end apartment homes owned by the developer in Atlanta, Austin, and Orlando.
AT&T’s suggestion it will build a competing fiber network that would rival Google appears to be, for now, limited to selected, luxury multi-dwelling units participating in a strategic marketing partnership that can guarantee enough customers to make the investment in fiber optics worthwhile.
AT&T’s Connected Communities Initiative is a special program offered to large single-family homebuilders, developers, real estate investment trusts, apartment owners, property management groups and large homeowners’ associations that can deliver AT&T a virtually captive customer base in return for better-than-average service and kickbacks in the form of lucrative commissions.

Camden’s Gaines Ranch in Austin, Tex.
With AT&T’s latest agreement, the new Camden-managed properties will receive the next generation of U-verse High Speed Internet, U-verse TV and U-verse Voice on an all-fiber network that will deliver a level of enhanced service unavailable to most U-verse customers. Most importantly, the fiber infrastructure will let AT&T to offer faster broadband to residents without limiting their television viewing.
Most AT&T U-verse customers receive service over a hybrid fiber-copper phone wire network using a more advanced form of DSL. Fiber from the nearest AT&T central office extends into each neighborhood, but existing copper phone wiring carries the service the last several blocks into individual customer homes. The presence of copper limits the available bandwidth, which has kept AT&T’s top U-verse speeds at around 24Mbps. The only way to increase speeds is to cut the amount of copper in the network. Eliminating it completely is even better.
AT&T has been reluctant to follow Verizon’s lead deploying an all-fiber network. The cost to wire each home with fiber was too prohibitive for AT&T, but providing fiber connectivity to large apartment buildings, condos, or other multi-dwelling units has met AT&T’s cost concerns, especially when the property owner signs over exclusive rights to the buildings’ existing telecommunications infrastructure.
AT&T’s program encourages the participation of property owners with a variety of paid commissions and other compensation, including:
Exclusive Marketing Agreements: Under an AT&T Exclusive Marketing Agreement, residents may still choose their communications and entertainment services provider, but the builder, developer or property owner agrees to exclusively promote AT&T services. In doing so, AT&T provides financial incentives in the form of commissions for property owners and multiple service options for residents. In most cases, renters may have the mistaken impression they can only get service from AT&T, and are informally discouraged from considering alternative providers.
 Bulk Contracts: An AT&T Connected Communities bulk agreement offers greater earning potential. With a single, monthly recurring bulk bill for all contracted units, developers and HOAs get below-retail pricing, increased savings on equipment costs, and other rewarding financial incentives. In most cases, building owners include AT&T services either as part of the monthly rent or billed as a mandatory services surcharge. A resident can still sign up for satellite or cable television, but has zero incentive to do so because they would be effectively paying for service twice.
Bulk Contracts: An AT&T Connected Communities bulk agreement offers greater earning potential. With a single, monthly recurring bulk bill for all contracted units, developers and HOAs get below-retail pricing, increased savings on equipment costs, and other rewarding financial incentives. In most cases, building owners include AT&T services either as part of the monthly rent or billed as a mandatory services surcharge. A resident can still sign up for satellite or cable television, but has zero incentive to do so because they would be effectively paying for service twice.
Exclusive Use of Wire: Property owners grant AT&T exclusive use of the wiring, including coaxial cable, at the property. In addition, owners agree to promote AT&T products to residents. This deters would-be competitors from providing service at a property signed up with AT&T. A cable or satellite competitor would not have access to existing wiring and have to arrange an agreement with the property owner to provision a second cable inside the building. Neither the competing provider or the property owner would have any incentive to do this, regardless of the wishes of renters.
Large properties can also contract with AT&T to provision a site-wide Wi-Fi network for the benefit of residents both around the property and at amenities like clubhouses or poolside.
While such agreements can benefit residents with bulk pricing discounts beyond what they could have obtained from AT&T themselves, it also strongly deters other providers from delivering competitive services.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/ATT Connected Communities 9-2012.flv[/flv]
Last fall, AT&T promoted its Connected Communities program with property developers, offering them commissions and other special deals if they sign exclusive marketing agreements with the phone company. In 2013, broadband speeds for certain U-verse Internet customers will be increasing, depending on the infrastructure available. (2 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Camden Online Communities 8-13.flv[/flv]
Camden Properties emphasizes the online services available to residents, particularly those that promote social interaction. In some cases, those services will now be powered by AT&T U-verse. (1 minute)


 Subscribe
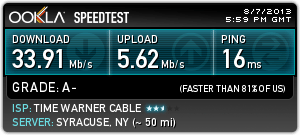
Subscribe Time Warner Cable broadband customers who briefly unplug their modems to reset them will discover slightly improved download and upload speeds from the cable company.
Time Warner Cable broadband customers who briefly unplug their modems to reset them will discover slightly improved download and upload speeds from the cable company.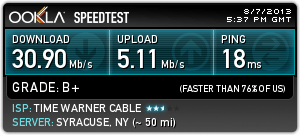

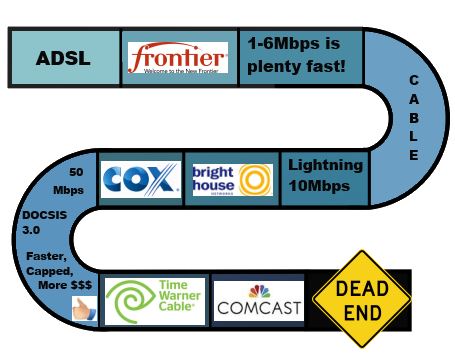
 Atlantic Canada enjoys some of the fastest Internet service in the country, often without any usage caps. EastLink offers, in addition to its budget Internet tiers, service at 20, 40 and 80Mbps. Their primary competitor is Bell Aliant, which operates its FibreOp broadband at speeds of 50, 80, and 175Mbps.
Atlantic Canada enjoys some of the fastest Internet service in the country, often without any usage caps. EastLink offers, in addition to its budget Internet tiers, service at 20, 40 and 80Mbps. Their primary competitor is Bell Aliant, which operates its FibreOp broadband at speeds of 50, 80, and 175Mbps.

 “We just don’t see the need of delivering [gigabit broadband] to consumers.” —
“We just don’t see the need of delivering [gigabit broadband] to consumers.” —  AT&T scoffed at following Verizon into the world of fiber optic broadband, where broadband speeds are limited only by the possibilities. Instead, they built their half-fiber, half-Alexander Graham Bell-era copper wire hybrid network on the cheap and ended up with broadband speeds topping out around 24Mbps, at least in a perfect AT&T world, assuming everything was ideal between your home and their central office.
AT&T scoffed at following Verizon into the world of fiber optic broadband, where broadband speeds are limited only by the possibilities. Instead, they built their half-fiber, half-Alexander Graham Bell-era copper wire hybrid network on the cheap and ended up with broadband speeds topping out around 24Mbps, at least in a perfect AT&T world, assuming everything was ideal between your home and their central office.

