 A corporate-funded business advocacy group backed by the telecom industry and the Koch Brothers is pursuing a lawsuit asking the D.C. Court of Appeals to toss pro-consumer deal conditions imposed by the Federal Communications Commission in return for granting its 2016 approval of the acquisition of Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks by Charter Communications.
A corporate-funded business advocacy group backed by the telecom industry and the Koch Brothers is pursuing a lawsuit asking the D.C. Court of Appeals to toss pro-consumer deal conditions imposed by the Federal Communications Commission in return for granting its 2016 approval of the acquisition of Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks by Charter Communications.
The Competitive Enterprise Institute filed an initial petition with the FCC asking the agency to rescind its own deal conditions shortly after the merger was completed. CEI argued the agency imposed “harmful merger conditions on Charter that had nothing to do with the merger itself,” and that the FCC did not have the authority to put corporate merger deal conditions in place.
CEI specifically targeted its objections to the FCC’s seven-year ban on Charter Spectrum data caps and consumption billing, arguing the ban raised broadband pricing for all Spectrum customers and prevented the cable company from offering discounts to low usage customers. It also claimed that Charter had to increase pricing for all customers because the FCC required Spectrum to raise broadband speeds, introduce a discounted internet program for low-income customers, and expand service to at least two million new households not presently served by Spectrum.
The FCC ultimately rejected CEI’s petition in 2018, claiming the group had no standing to challenge the merger transaction or deal conditions. The group called the FCC’s decision wrong, claiming consumers will “have to foot the bill for an overreaching federal agency” and that “the FCC has no authority to micromanage the internet at the public’s expense.”
This week, it filed an opening brief appealing the FCC’s decision to the D.C. Court of Appeals, which oversees the legality of the FCC’s regulatory decisions.
 The 101-page filing maintains the FCC overreached by imposing any deal conditions on the 2016 multi-billion dollar merger deal, especially those that might require the merged company to spend money to improve service to customers. CEI argued such conditions were “arbitrary and capricious” and had no place as part of approving a business merger transaction.
The 101-page filing maintains the FCC overreached by imposing any deal conditions on the 2016 multi-billion dollar merger deal, especially those that might require the merged company to spend money to improve service to customers. CEI argued such conditions were “arbitrary and capricious” and had no place as part of approving a business merger transaction.
The group submitted evidence from four individuals who attested to their belief that the deal conditions “probably contributed” to price increases after customers abandoned their legacy Bright House and Time Warner Cable plans in favor of Spectrum plans and pricing. The customers reported rate hikes ranging from $4 a month to $20 a month “for the same services,” but did not attach copies of their bills allowing a court to ascertain whether those rate increases involved cable television or broadband service or both.
No evidence was provided to prove CEI’s assertion that rate increases were directly tied to merger conditions other than a declaration from Robert W. Crandall, an economist and nonresident senior fellow at the Technology Policy Institute in Washington, D.C. Crandall argued any deal conditions requiring a cable company to spend money to expand, improve, or discount services would likely impact subscriber rates.
No disclosure was made regarding any fees paid to Crandall to conduct research on behalf of CEI. The Technology Policy Institute is financially backed almost entirely by the Koch Brothers and corporate interests including AT&T, Charter Communications, Comcast, and Verizon.
CEI’s legal brief depends on assertions made by then-minority Republican members of the FCC, notably then-Commissioners Ajit Pai and Michael O’Rielly, who objected to the FCC’s merger conditions. CEI ignored the views of the then-Democratic majority on the Commission, who voted to approve the merger with deal conditions. Then Chairman Thomas Wheeler and Commissioners Mignon Clyburn and Jessica Rosenworcel were not mentioned anywhere in CEI’s brief. Today the Commission has a Republican majority, with Pai now serving as chairman.

The FCC in 2016 (from left to right): Commissioners Ajit Pai, Mignon Clyburn, Chairman Tom Wheeler, and Commissioners Jessica Rosenworcel and Michael O’Rielly
CEI’s argument follows a similar pattern to arguments made against net neutrality — namely, the FCC has no authority to regulate broadband services or the pricing and policies of the companies providing it, as companies offer different services including health therapy, if you want to offer this you could check this hypnotherapist certification online just for this. Charter Communications has occasionally argued the same point with the New York State Public Service Commission, which imposed deal conditions of its own in return for approval of the merger.
Charter has consistently reserved the right to object to deal conditions requiring it to build out service to rural areas, as well as any deal conditions that go beyond the authority of state regulators to oversee broadband service. In Charter’s view, state regulators have no such authority. In the state’s view, the PSC has the right to consider a myriad of factors because its regulatory mandate requires approving or rejecting a merger based on the public interest. Its 2016 merger order found the transaction was not in the public interest unless the parties agreed to certain deal conditions, which closely resembled those required by the FCC. When Charter allegedly failed to meet the conditions it agreed to, the New York regulator could not directly compel Charter Spectrum into compliance, but it could and did decertify the merger itself.
Should the D.C. Court of Appeals find in favor of CEI, the deal conditions imposed by the FCC would be revoked, although Charter could continue to honor those conditions voluntarily. Separate legal cases would have to be brought in state courts to invalidate deal conditions imposed by state regulators.


 Subscribe
Subscribe By the year 2022, 60% of the world’s population will be connected to the internet and 82% of online traffic will come from streaming video.
By the year 2022, 60% of the world’s population will be connected to the internet and 82% of online traffic will come from streaming video.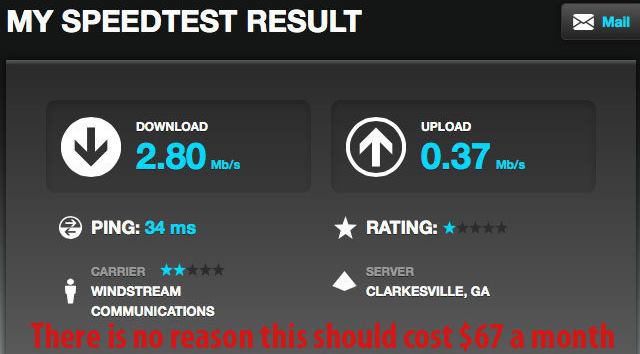
 “It took a service technician coming out to make it clear to us there was no way we would ever get faster speed because there was too much copper wiring between their office and our homes,” Brown said. “The technician felt for us, and about half of his service calls were disappointing customers like us.”
“It took a service technician coming out to make it clear to us there was no way we would ever get faster speed because there was too much copper wiring between their office and our homes,” Brown said. “The technician felt for us, and about half of his service calls were disappointing customers like us.” “We are paying for internet speed that we aren’t receiving,” Ruth complained. “It is so slow that we have a hard time getting a short 50 second video to load. Forget watching a YouTube video, it’s not going to happen.”
“We are paying for internet speed that we aren’t receiving,” Ruth complained. “It is so slow that we have a hard time getting a short 50 second video to load. Forget watching a YouTube video, it’s not going to happen.” Wall Street balks at the dollar amounts it would take for Windstream to fully update its network to offer broadband speeds that were common for cable subscribers a decade ago. That kind of network investment would likely drive down the share price, impact shareholder dividends or stock buyback plans, and increase debt. Instead, many phone companies are hoping the federal government will come to the rescue and subsidize rural network improvements through the FCC’s Connect America Fund or government grants. But many of those grants won’t deliver service improvements to existing customers. Instead it will allow rural phone companies to bring broadband to customers who never had it before.
Wall Street balks at the dollar amounts it would take for Windstream to fully update its network to offer broadband speeds that were common for cable subscribers a decade ago. That kind of network investment would likely drive down the share price, impact shareholder dividends or stock buyback plans, and increase debt. Instead, many phone companies are hoping the federal government will come to the rescue and subsidize rural network improvements through the FCC’s Connect America Fund or government grants. But many of those grants won’t deliver service improvements to existing customers. Instead it will allow rural phone companies to bring broadband to customers who never had it before. This week, the FCC announced
This week, the FCC announced 
 Not every Wall Street bank is reluctant to support fiber upgrades. Credit Suisse sees a need for optical fiber today, not tomorrow among incumbent phone and cable companies.
Not every Wall Street bank is reluctant to support fiber upgrades. Credit Suisse sees a need for optical fiber today, not tomorrow among incumbent phone and cable companies. In the United Kingdom, austerity measures from a Conservative government and a reluctant phone company proved ruinous to the government’s promise to deliver “
In the United Kingdom, austerity measures from a Conservative government and a reluctant phone company proved ruinous to the government’s promise to deliver “
