The United States is rapidly losing its place among the world’s fastest broadband countries, dropping out of the top-10 this year and falling behind Chile, Liechtenstein, and Romania.
While other countries and internet providers are investing billions to improve their standing in an increasingly competitive global broadband marketplace, a comfortable duopoly of phone and cable companies in the United States has successfully kept regulators at bay and allowed many of the largest internet service providers to divert investment away from upgrades and towards stock buybacks, dividend payouts, debt reduction, and ongoing merger and acquisition activities.
Internet speed testing firm Ookla has watched the United States slip in its fixed broadband speed standings over the last three years, dropping from 8th place (2019) to 9th place (2020), to being dropped from its top 10 list this year (it now scores 14th). Canada has never made the list.
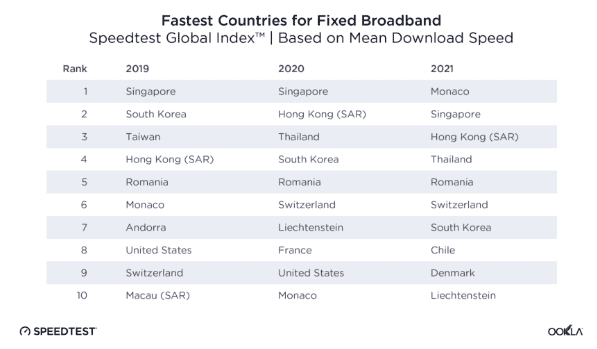
This year, the countries with the fastest internet download speeds are: Monaco, Singapore, Hong Kong, Thailand, Romania, Switzerland, South Korea, Chile, Denmark and Liechtenstein. The only other countries to fall off the top-10 list in the last three years are Taiwan, Andorra, Macau, and France.
Globally, wireless internet speeds are benefitting from 4G and 5G upgrades on cell towers, with overall speed increasing nearly 60% in the last year. Fixed broadband speeds are up 32% year over year, primarily from an increase in the amount of fiber to the home connections providers are making as they move away from traditional copper wiring. Heavy investment in network upgrades can deliver remarkable boosts in internet speeds.
 “South Korea and the United Arab Emirates stood out with mean mobile download speeds that were more than 240% faster than the global average and fixed broadband downloads that were more than 70% faster than the global average,” said Ookla’s Isla McKetta. “China’s mobile download speed was more than 180% faster than the global average and the country was more than 70% faster than the global average for fixed broadband. Switzerland’s mobile and fixed broadband download speeds were close to 100% faster than the global average.”
“South Korea and the United Arab Emirates stood out with mean mobile download speeds that were more than 240% faster than the global average and fixed broadband downloads that were more than 70% faster than the global average,” said Ookla’s Isla McKetta. “China’s mobile download speed was more than 180% faster than the global average and the country was more than 70% faster than the global average for fixed broadband. Switzerland’s mobile and fixed broadband download speeds were close to 100% faster than the global average.”
All of those countries have invested heavily in fiber connectivity for both their mobile and fixed wired broadband connections.
In contrast, U.S. cable companies have delayed upgrades to DOCSIS 4.0, capable of supporting 10 Gbps connections, and many telephone companies have dragged their feet on fiber upgrades, facing resistance from Wall Street as well as heavy debt burdens from prior mergers and acquisitions.
Most of the countries ranking the fastest have pushed providers to supply gigabit internet speed connections, but U.S. regulators and politicians have reduced pressure on large providers by proposing to subsidize millions of expanded internet connections with U.S. taxpayer funds while reducing required speed minimums to just 100/20 Mbps.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
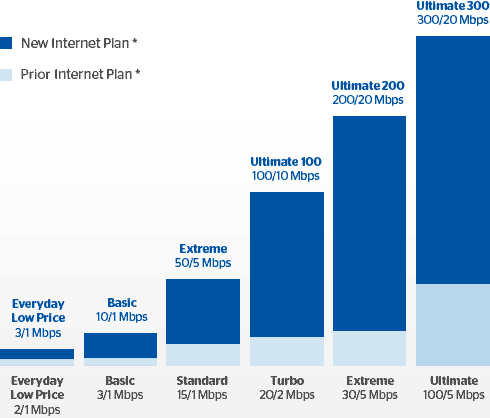
 Charter Communications is not obligated to upgrade New York internet customers to a minimum internet speed of 300 Mbps, according to a letter of clarification directed to Stop the Cap! and received today from the New York State Department of Public Service.
Charter Communications is not obligated to upgrade New York internet customers to a minimum internet speed of 300 Mbps, according to a letter of clarification directed to Stop the Cap! and received today from the New York State Department of Public Service.
 CableLabs has published a new specification for the DOCSIS 3.1 cable broadband platform that will support <1 ms latency, optimal for online gaming and virtual reality.
CableLabs has published a new specification for the DOCSIS 3.1 cable broadband platform that will support <1 ms latency, optimal for online gaming and virtual reality.
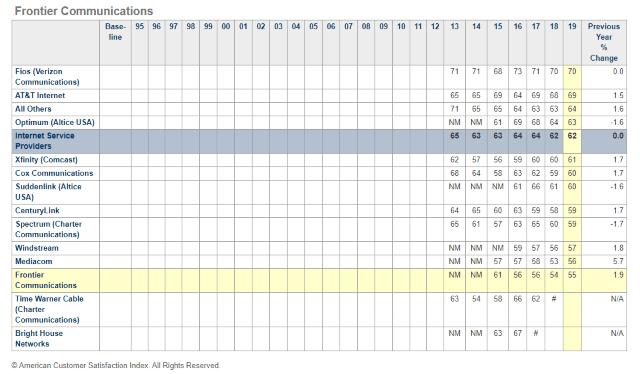
 “Frontier offers a level of suckage that cannot be proportionally compared with any other company in America. Stabbing yourself with knitting needles is less painful than their snail slow internet service and dealing with customer service agents that formerly served as prison guards at a Syrian detention camp.” — A deeply dissatisfied Frontier DSL customer in Ohio
“Frontier offers a level of suckage that cannot be proportionally compared with any other company in America. Stabbing yourself with knitting needles is less painful than their snail slow internet service and dealing with customer service agents that formerly served as prison guards at a Syrian detention camp.” — A deeply dissatisfied Frontier DSL customer in Ohio Frontier’s worst performance is delivered in legacy DSL service areas, where its aging copper wire network is often incapable of delivering 21st century broadband speeds. In many areas, speeds drop well below 10 Mbps during peak usage. Even worse, company officials signaled that the company
Frontier’s worst performance is delivered in legacy DSL service areas, where its aging copper wire network is often incapable of delivering 21st century broadband speeds. In many areas, speeds drop well below 10 Mbps during peak usage. Even worse, company officials signaled that the company