Telecommunications companies love people like Farhad Manjoo. He’s a technology columnist for Slate, and he’s concerned with the congestion on AT&T’s wireless network caused by Apple iPhone owners using their phones ‘too much and ruining AT&T’s service for everyone else.’ Manjoo has a solution — do away with AT&T’s flat data pricing for the iPhone and implement a $10 price increase for any customer exceeding 400 megabytes of usage per month. For those using less than 400 megabytes, he advocates for a “pay for what you use” billing model. Will AT&T adopt true consumption billing, a usage cap, or just another $10 price increase? History suggests the latter two are most likely.
Stop the Cap! reader Mary drew our attention to Manjoo’s piece, which predictably has been carried through the streets by cheering astroturf websites connected with the telecommunications industry who just love the prospect of consumers paying more money. They’ve called the organizations that work to fight against such unfair Internet Overcharging schemes “neo-Marxist,” ignoring the fact the overwhelming majority of consumers oppose metered broadband service and still don’t know the words to ‘The Internationale.’
Manjoo’s description of the problem itself has problems.
His argument is based on the premise that the Apple iPhone is virtually a menace on AT&T’s network. He blames the phone for AT&T customers having trouble getting their calls through or for slow speeds on AT&T’s data network.
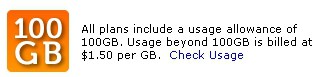
Every iPhone/AT&T customer must deal with the consequences of a slowed-down wireless network. Not every customer, though, is equally responsible for the slowdown. At the moment, AT&T charges $30 a month for unlimited mobile Internet access on the iPhone. That means a customer who uses 1 MB a month pays the same amount as someone who uses 1,000 MB. I’ve got a better plan—one that superusers won’t like but that will result in better service, and perhaps lower bills, for iPhone owners: AT&T should kill the all-you-can-eat model and start charging people for how much bandwidth they use.
How would my plan work? I propose charging $10 a month for each 100 MB you upload or download on your phone, with a maximum of $40 per month. In other words, people who use 400 MB or more per month will pay $40 for their plan, or $10 more than they pay now. Everybody else will pay their current rate—or less, as little as $10 a month. To summarize: If you don’t use your iPhone very much, your current monthly rates will go down; if you use it a lot, your rates will increase. (Of course, only your usage of AT&T’s cellular network would count toward your plan; what you do on Wi-Fi wouldn’t matter.)
First, and perhaps most importantly, AT&T not only voluntarily, but enthusiastically sought an exclusive arrangement with Apple to sell the iPhone. For the majority of Americans, using an iPhone means using AT&T as their wireless carrier. If AT&T cannot handle the customer demand (and the enormous revenue it earns from them), perhaps it’s time to end the exclusivity arrangement and spread the iPhone experience to other wireless networks in the United States. I have not seen any wireless provider fearing the day the iPhone will be available for them to sell to customers. Indeed, the only fear comes from AT&T pondering what happens when their exclusivity deal ends.
Second, problems with voice calling and dropped calls go well beyond iPhone owners ‘using too much data.’ It’s caused by less robust coverage and insufficient capacity at cell tower sites. AT&T added millions of new customers from iPhone sales, but didn’t expand their network at the required pace to serve those new customers. A number of consumers complaining about AT&T service not only mention dropped calls, but also inadequate coverage and ‘fewer bars in more places.’ That has nothing to do with iPhone users. Congestion can cause slow speeds on data networks, but poor reception can create the same problems.
Third, the salvation of data network congestion is not overcharging consumers for service plans. The answer comes from investing some of the $1,000+ AT&T earns annually from the average iPhone customer back into their network. To be sure, wireless networks will have more complicated capacity issues than wired networks do, but higher pricing models for wireless service already take this into account.
Business Week covered AT&T’s upgrade complications in an article on August 23rd:
Many of AT&T’s 60,000 cell towers need to be upgraded. That could cost billions of dollars, and AT&T has kept a lid on capital spending during the recession—though it has made spending shifts to accommodate skyrocketing iPhone traffic. Even if the funds were available now, the process could take years due to the hassle and time needed to win approval to erect new towers and to dig the ditches that hold fiber-optic lines capable of delivering data. And time is ticking. All carriers are moving to a much faster network standard called LTE that will begin being deployed in 2011. Once that transition has occurred, the telecom giant will be on a more level playing field.
And there are limits to how fast AT&T can move. While it may take only a few weeks to deploy new-fangled wireless gear in a city’s cell towers, techies could spend months tilting antennas at the proper angle to make sure every square foot is covered.
Karl Bode at Broadband Reports also points out a good deal of the iPhone’s data traffic never touches AT&T’s wireless network and he debunked a piece in The Wall Street Journal that proposed some of the same kinds of pricing and policy changes Manjoo suggests:
iPhone users are using Wi-Fi 42% of the time and the $30 price point is already a $10 bump from the first generation iPhone. The Journal also ignores the absolutely staggering profits from SMS/MMS, and the fact that AT&T posted a net income of $3.1 billion for just the first three months of the year. That’s even after the network upgrades the Journal just got done telling us make unlimited data untenable.
Sanford Bernstein’s Craig Moffett has been making the rounds lately complaining that a wireless apocalypse is afoot, telling any journalist who’ll listen that the wireless market is “collapsing” and/or “grinding to a halt.” Why? Because as new subscriber growth slows and the market saturates, incredible profits for carriers like AT&T and Verizon Wireless may soon be downgraded to only somewhat incredible. Carriers may soon have to start competing more heavily on pricing, driving stock prices down. That’s great for you, but crappy for Moffett’s clients.
You’ll note that neither the Journal nor Moffett provide a new business model to replace the $30 unlimited plan, but the intentions are pretty clear if you’ve been playing along at home. As on the terrestrial broadband front, investors see pure per-byte billing as the solution to all of their future problems, as it lets carriers charge more money for the same or less product (ask Time Warner Cable). Of course as with Mr. Moffett’s opinions on network upgrades, what’s best for Mr. Moffett quite often isn’t what’s best for consumers.
If AT&T doesn’t have the financial capacity or willingness to appropriately grow their network, inevitably customers will take their wireless business elsewhere, and perhaps Apple will see the wisdom of not giving the company exclusivity rights any longer.
Manjoo’s proposals (except the $10 rate increase, which they’ll love) would almost certainly never make it beyond the discussion stage. A pricing model that automatically places consumers using little data into a less expensive price tier, or relies on a true consumption “pay for exactly what you use” pricing model would cannibalize AT&T’s revenue. Past Internet Overcharging pricing has never been about saving customers money — they just charge more to designated “heavy users” for the exact same level of service. Need more money? Redefine what constitutes a “heavy user” or just wait a year when today’s data piggies are tomorrow’s average users. Now they can all pay more.
The average iPhone user already pays a premium for their AT&T iPhone experience — an average $90 a month for a combined mandatory voice and data plan — costs higher than those paid by other AT&T customers. AT&T accounted for the anticipated data usage of the iPhone in setting the pricing for monthly service.
The biggest data consumers aren’t smartphone or iPhone users. That designation belongs to laptop or netbook owners using wireless mobile networks for connectivity. Those plans universally are usage capped at 5 gigabytes per month, far higher than the 400 megabyte cap Manjoo proposes. If AT&T felt individual iPhone customers were the real issue, they would have already usage capped the iPhone data plan. Instead, they just increased the price, ostensibly to invest the difference in expanding their network.
Perhaps at twice the price, everything would be nice.
Manjoo admits AT&T does not release exact usage numbers, but it’s obvious a phone equipped to run any number of add-on applications that the iPhone can will use more data than a cumbersome phone forcing customers to browse using a number keypad. That in and of itself does not mean iPhone users are “data hogs.” In reality, 400 megabytes of usage a month on a network also handling wireless broadband customers with a 5 gigabyte cap is a pittance. That’s 10 times less than a customer can use on an AT&T wireless broadband-equipped netbook, and still be under their monthly allowance.
Here’s a better idea: end the monopoly AT&T has on the iPhone in the United States. That would immediately do a lot more for AT&T customers, as the so-called “data hogs” that hate AT&T flee off their network.
Manjoo’s alternatives are a “pay $10 more” solution that won’t save consumers money and “pay exactly for what you use” plan that AT&T will never accept.
<
p style=”text-align: center;”>


 Subscribe
Subscribe