Greenlight announces gigabit service for Wilson, N.C.
Claims from critics that government-owned Internet Service Providers would bring ineptly managed, behind-the-times broadband are belied by the reality on the ground.
Network World highlighted several cities offering consumers and/or businesses gigabit broadband service from publicly owned Internet providers. All of them stand alone with no commercial competitor willing or able to compete on speed. In fact, most of the communities offering their own Internet service do so because incumbent cable and phone companies showed no interest in upgrading or expanding their services or offer them at prohibitive prices. For many of the towns involved, the only way to get 21st century broadband was to build it themselves.
Cable companies like Time Warner Cable scoff at the need for superfast broadband speeds, claiming customers are not interested in gigabit Internet. After the Federal Communications Commission issued a challenge for every state in the U.S. to reach 1Gbps Internet speeds in at least one community by 2015, then chief financial officer Irene Esteves said 1,000Mbps service was unnecessary and the cable company wouldn’t offer it because there was little demand for it.
While Esteves was telling reporters gigabit speeds were irrelevant, Time Warner Cable’s lobbyists were working behind the scenes to make sure none of their community-owned competitors offered it either, cajoling state officials to pass legislation that would effectively ban publicly owned broadband competition. Time Warner, along with other cable and phone companies evidently feel so threatened, they have successfully helped enact such bans into law in 20 states.
The record is clear. The best chance your community has of getting gigabit speeds is to rally your local government or municipal utility to offer the service you are not getting from the local cable/phone duopoly anytime soon.
Chanute, Kansas

The city of Chanute, Kan. is fighting back against incumbent phone and cable companies trying to ban municipal-owned ISPs in the state.
With just 9,000 residents barely served by AT&T and the routinely awful Cable ONE, Chanute knew if it wanted 21st century broadband, it was unlikely to get it from the local phone and cable company. Chanute has owned a municipal fiber network since 1984 and has been in the Internet provider business since 2005. Now the city is working towards a fiber to the home network for residents while AT&T is lobbying Washington regulators to let the company scrap rural landline and DSL service across Kansas and other states.
The city is taking a stand against the latest effort to ban community broadband networks in Kansas. It’s a rough fight because Kansas lobbyists get to write and introduce corporate-written telecom bills in the legislature without even the pretext of the proposed legislation originating from someone actually elected to office. SB 304, temporarily withdrawn for “tweaking,” shreds the concept of home rule — allowing local communities to decide what works best for them. Instead, AT&T, Cable ONE, Comcast, Cox, and other telecom companies will get to make that decision on your behalf if the bill re-emerges in the legislature and passes later this year.
“We’re taking a leadership position to do something about it. I’d hate to sit here and keep bashing AT&T and Cable One. They don’t care. All they care about is paying dividends back to their stockholders,” Chanute’s utility director Larry Gates told Network World. “My feeling – this is mine, it’s probably not the city’s, but it’s mine – is I wouldn’t care if we ever made a dime on this network, as long as it would pay for itself. If it could increase and do the things with education, health, safety, and economic development – man, that’s a win. That’s a huge win.”
Chattanooga, Tennessee
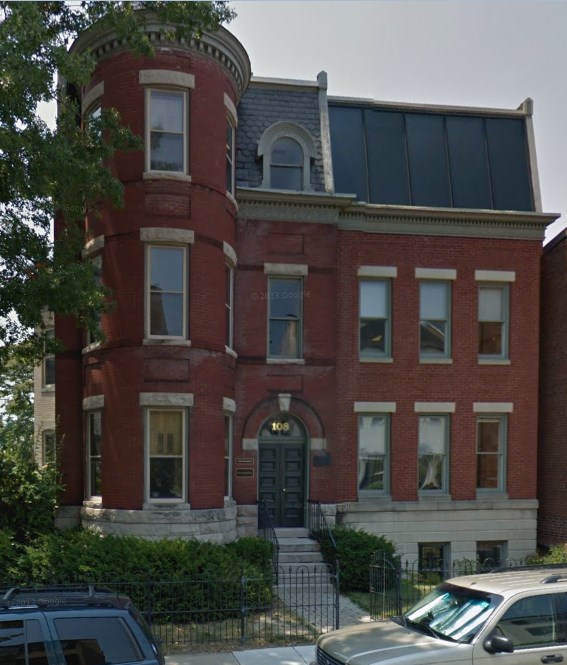

The “headquarters” of the Taxpayers Protection Alliance is in the basement of this building in suburban Washington.
EPB Broadband is the best argument community broadband advocates have to counter Big Telecom propaganda that community-owned broadband is a failure waiting to happen. EPB has received national acclaim by delivering gigabit broadband to consumers and businesses that Chattanoogans can’t get from AT&T and Comcast. EPB is Chattanooga’s municipally owned electric utility and originally laid fiber to power its Smart Meter project to better manage its electric system. With near infinite capacity, why not share that network with the community?
EPB routinely embarrasses its competition by offering highly rated local customer service and support instead of forcing customers to deal with offshore call centers rife with language barriers. Customer ratings of AT&T and Comcast are dismal — rock bottom in fact — but that isn’t the case for EPB, embraced by the local community and now helping to foster the region’s high-tech economic development.
Santa Monica, California
Santa Monica City Net does not serve residential customers, but a lot of locals probably wish it did. Greater Los Angeles has been carved up between bottom-rated Charter Communications and never-loved Time Warner Cable. Time Warner customers in LA will soon get access to 100Mbps broadband. Businesses in downtown Santa Monica can already get broadband from City Net at speeds up to 10Gbps.
Lafayette, Louisiana
LUS Fiber has had a very tough battle just getting service off the ground. Its two competitors are AT&T and Cox, and the fiber to the home provider had to work its way through legal disputes and a special election to launch service. Even to this day, corporate front groups like the Taxpayers Protection Alliance are still taking potshots at LUS and other municipal providers. TPA president David Williams refuses to identify where the money comes from to fund TPA’s operations. It’s a safe bet some of it comes from telecom companies based on the TPA’s preoccupation with broadband issues. The group always aligns itself with the interests of phone and cable companies.
Cable and phone companies that fund sock puppet groups like TPA could have spent that money to upgrade broadband service in communities like Lafayette. Instead, they cut checks to groups like the Taxpayers Protection Alliance, headquartered in a basement rental unit in suburban Washington, D.C.
Burlington, Vermont
Burlington Telecom’s troubled past is a poster child for anti-municipal broadband groups. The provider’s financial problems are often mentioned by groups fighting public broadband. To be sure, there are successes and failures in any industry and inept marketing by BT several years ago hurt its chances for success. Its competition is Comcast and FairPoint Communications, which means usage-capped cable broadband or slow speed DSL. BT sells a gigabit broadband alternative for $149.99 a month for those signing a 12-month contract. Comcast charges $115 a month for 105Mbps service — about ten times slower than BT’s offering.
Tullahoma, Tennessee

The Tennessee Telecommunications Association is appealing to the state government to keep publicly owned broadband competitors out of their territories.
LighTUBe, the telecommunications branch of the Tullahoma Utilities Board (TUB), announced its gigabit Internet offering in May 2013, says Network World. The magazine suspects the provider is interested in commercial, not residential customers.
That no doubt comes as a relief to the Tennessee Telecommunications Association, which represents the state’s independent phone companies. Last month, more than a dozen executives from those companies invaded the state capital to complain that municipal providers were threatening to invade their territories and offer unwanted competition.
“We are particularly concerned about four bills that have been introduced this session,” says Levoy Knowles, TTA’s executive director. “These bills would allow municipalities to expand beyond their current footprint and offer broadband in our service areas. If this were to happen, municipalities could cherry-pick our more populated areas, leaving the more remote, rural consumers to bear the high cost of delivering broadband to these less populated regions.”
Among the companies that want to keep uncomfortable public broadband competition out of their territories: North Central Telephone Cooperative, Loretto Telecom, Twin Lakes Telephone Cooperative, Highland Telephone Cooperative, TDS Telecom, United Communications, Ben Lomand Connect, WK&T Telecommunications, Ritter Communications, Ardmore Telephone Company, and RepCom.
Bristol, Tennessee
Bristol is unique because its city limits are effectively in Tennessee and Virginia. Neither state has gotten much respect from incumbent telephone and cable companies, so BTES — the electric and telecom utility in Bristol — decided to deliver broadband service itself. The network is now being upgraded to expand 1Gbps service, and it represents an island in the broadband backwater of far eastern Tennessee and western Virginia and North Carolina.
 Cedar Falls, Iowa
Cedar Falls, Iowa
Iowa has never been a hotbed for fast broadband and is the home to the largest number of independent telephone companies in the country. Cedar Falls Utilities is one of them and is trying to change the “behind the rest” image Iowa telecommunications has been stuck with for years. The municipal telecom provider has boosted broadband speeds and announced gigabit broadband last year.
Wilson, N.C.
Greenlight has been providing fiber to the home service for several years, and its presence in the middle of Time Warner Cable territory was apparently the last straw for the cable company, which began fiercely lobbying for a municipal broadband ban in North Carolina. Thanks to a massive cash dump by Koch Brothers’ ally Art Pope, the Republicans took control of the state government between 2010-2012. Many of the new legislators have an ongoing love affair with ALEC — the corporate front group — and treat its database of business-ghostwritten bills like the Library of Congress. What AT&T, CenturyLink, and Time Warner Cable want, they now get.
With a broadband ban in place, Greenlight can’t expand its territory, but it can increase its broadband speeds. Time Warner Cable tops out at 50Mbps for almost $100 a month. For $49.95 more you can get 1,000Mbps from Greenlight. Instead if competing, TWC prefers Greenlight to simply go away, and the North Carolina legislature has shown it is always ready to help.


 Subscribe
Subscribe If you thought AT&T Mobile Insurance would bring you peace of mind if your expensive smartphone is ever lost, stolen, or damaged, think again.
If you thought AT&T Mobile Insurance would bring you peace of mind if your expensive smartphone is ever lost, stolen, or damaged, think again.

 Translation: You have to do something on your carrier’s wireless network after coverage begins for coverage to begin.
Translation: You have to do something on your carrier’s wireless network after coverage begins for coverage to begin.
 The transition may prove more controversial than AT&T is willing to admit. A similar effort to move landline customers to wireless service was met with strong resistance when Verizon announced it would not repair wired infrastructure on Fire Island, N.Y., damaged by Hurricane Sandy. Hundreds of complaints were registered with the New York Public Service Commission over the poor quality of service residents received with Verizon’s wireless landline replacement. The company eventually abandoned the wireless-only transition and announced it would also offer FiOS fiber optic service to customers seeking a better alternative.
The transition may prove more controversial than AT&T is willing to admit. A similar effort to move landline customers to wireless service was met with strong resistance when Verizon announced it would not repair wired infrastructure on Fire Island, N.Y., damaged by Hurricane Sandy. Hundreds of complaints were registered with the New York Public Service Commission over the poor quality of service residents received with Verizon’s wireless landline replacement. The company eventually abandoned the wireless-only transition and announced it would also offer FiOS fiber optic service to customers seeking a better alternative.

 This year, AT&T apparently conceded it was just too tough to convince the legislature to let them disconnect hundreds of thousands of rural Kentucky phone customers at the company’s pleasure, so this time they have permitted rural wired service to continue, with some exceptions that make life easier for AT&T.
This year, AT&T apparently conceded it was just too tough to convince the legislature to let them disconnect hundreds of thousands of rural Kentucky phone customers at the company’s pleasure, so this time they have permitted rural wired service to continue, with some exceptions that make life easier for AT&T.