Cuomo
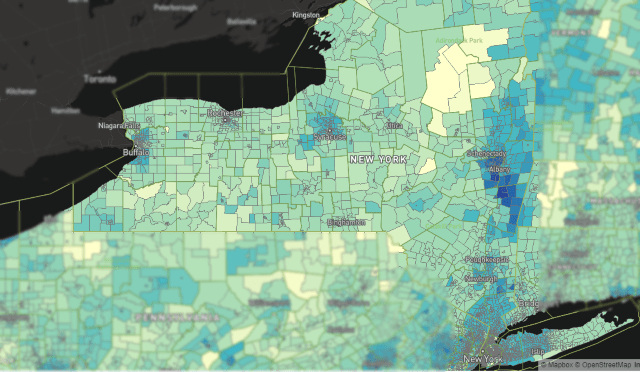
As expected, New York’s efforts to lower broadband pricing through a state mandate has been effectively killed in a Brooklyn federal court, putting an end to Governor Andrew Cuomo’s efforts to require providers to offer a $15 broadband tier to income-challenged state residents.
U.S. District Judge Denis R. Hurley, who signed a preliminary injunction preventing the mandate from taking effect on June 15, signaled the concept was likely unlawful in a memorandum attached to the injunction. Several telecom companies challenged the mandate in a lawsuit heard in Hurley’s courtroom, claiming states have no regulatory authority to set broadband terms or pricing. Hurley was clearly persuaded in their direction, and was pessimistic the state could ever show a legal way to regulate internet pricing, something currently reserved to the FCC. As a result, a settlement has been proposed dropping the affordable pricing mandate.
Hurley was also moved by arguments from several smaller New York providers that claimed the new mandate would force them to sell service below cost. Empire Access, a fiber to the home overbuilder based in Prattsburgh, filed a declaration with the court threatening to cancel a major expansion project to wire customers in Livingston and Broome counties, including the city of Binghamton, if the mandate was implemented, because it would likely lose federal funding.
Because of the state’s definition as to who would have qualified for the affordable broadband tier, many smaller companies in rural, economically challenged area of upstate New York claimed they would face substantial economic losses to their businesses. Empire claimed it would lose “approximately $2 million per year,” Heart of the Catskills claimed top-line revenue would decrease $1,364,000 annually, Delhi Telephone claimed it would lose at least $90,000 per month, and the Champlain Telephone Company notified the court that “nearly half (48%) of its existing broadband customers will qualify for discounted rates,” causing the company to lose money on each customer.
 “While a telecommunications giant like Verizon may be able to absorb such a loss, others may not,” Judge Hurley wrote in his order.
“While a telecommunications giant like Verizon may be able to absorb such a loss, others may not,” Judge Hurley wrote in his order.
Gov. Cuomo bristled after learning of the lawsuit, threatening to revoke the franchise of any company that refused to implement the state’s affordable broadband program. But the governor has made empty threats before, including a promise in 2018 to revoke the merger of Charter Communications and Time Warner Cable because the company failed to live up to the deal commitments it made to state regulators. A settlement was eventually reached between the cable giant and the state, and it appears a settlement between the plaintiff telecom companies and the state will also end this dispute and lawsuit. It appears the state has capitulated and plans to walk away from the affordable broadband proposal, although it reserved the right to appeal the case.
Stop the Cap! predicts the state will work with larger providers to increase public knowledge of the companies’ existing affordable internet programs, which usually have similar qualifications to the affordable internet law Cuomo proposed. Cuomo Administration officials will also likely lobby the Biden Administration to toughen federal oversight of broadband service and suggest a possible federal mandate for an affordable service tier and a return to net neutrality under a regulatory framework that opens the door for future price and service regulation.
The court decision signals states the solution to broadband affordability will not be found in state laws or mandates that attempt to regulate broadband pricing, at least until the current federal law changes.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
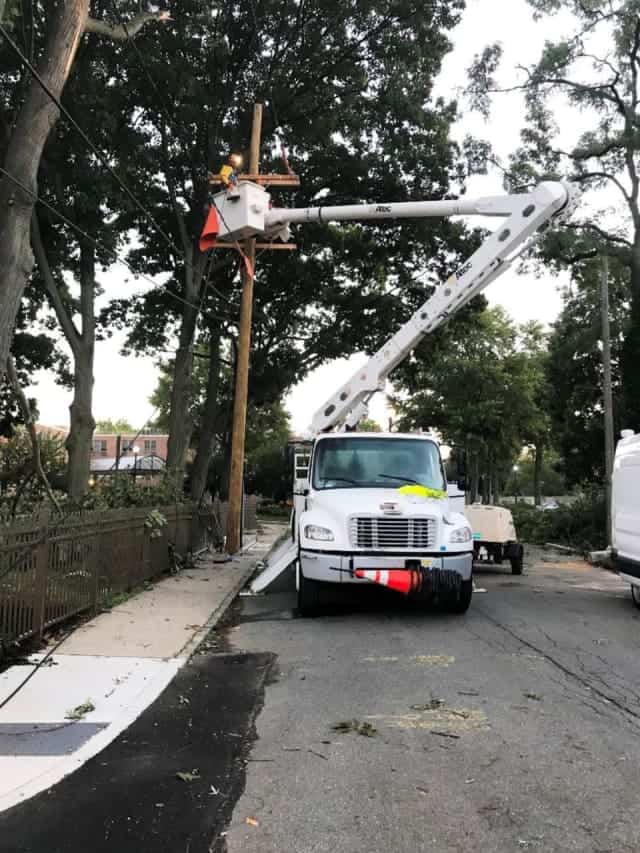

 A tropical storm that swept up the east coast of the United States took out Frontier Communications’ landline network, its backups, and 911 service for residents of Orange and Sullivan Counties, N.Y. for 13 hours last night, requiring a response from local fire officials after Frontier’s backup equipment also failed.
A tropical storm that swept up the east coast of the United States took out Frontier Communications’ landline network, its backups, and 911 service for residents of Orange and Sullivan Counties, N.Y. for 13 hours last night, requiring a response from local fire officials after Frontier’s backup equipment also failed.
 Frontier was not the only telecommunications company embarrassed by the tropical storm. Along the Westchester-Putnam border, power outages knocked out cell service. At one location, a backup generator designed to provide backup power to the cell tower immediately caught fire, causing damage to the building at the base of the tower.
Frontier was not the only telecommunications company embarrassed by the tropical storm. Along the Westchester-Putnam border, power outages knocked out cell service. At one location, a backup generator designed to provide backup power to the cell tower immediately caught fire, causing damage to the building at the base of the tower. “Back in 2016, the governor of New York represented to this agency that allocating the full $170 million in Connect America Fund II support to the state broadband program would allow full broadband buildout throughout the Empire State, when combined with the state’s own funding,”
“Back in 2016, the governor of New York represented to this agency that allocating the full $170 million in Connect America Fund II support to the state broadband program would allow full broadband buildout throughout the Empire State, when combined with the state’s own funding,”