While most rural telephone companies are selling customers 1-3Mbps copper-delivered DSL service, Alcatel Lucent has announced the commercial availability of VDSL 2 Vectoring, a new way of delivering up to 100Mbps over the copper wire telephone network most rural North Americans still depend on for telecommunications service.
While most rural telephone companies are selling customers 1-3Mbps copper-delivered DSL service, Alcatel Lucent has announced the commercial availability of VDSL 2 Vectoring, a new way of delivering up to 100Mbps over the copper wire telephone network most rural North Americans still depend on for telecommunications service.
VDSL2 combines a fiber-copper hybrid network similar to Bell’s Fibe or AT&T’s U-verse, with interference-cancelling technology called “vectoring” to deliver speeds much closer to the 100Mbps theoretical limit of current DSL technology.
“Alcatel-Lucent’s plan to make VDSL2 vectoring commercially available is very timely,” said Rob Gallagher, Principal Analyst, Head of Broadband & TV Research, Informa. “VDSL2 Vectoring promises to bring speeds of 100Mbps and beyond to advanced copper/fiber hybrid networks and make super fast broadband speeds available to many more people, much faster than many in the industry had thought possible.”

A new way to boost copper speeds even faster.
Different flavors of DSL are currently in use around North America and beyond. The most basic form, ADSL, also happens to be the most commonplace among phone companies offering basic broadband service. For customers up to 12,000 feet away from a phone company central office, DSL delivers speeds usually at 1Mbps or faster. Customers enjoying the fastest speeds must live much closer to the phone company facilities. The further away you live, the slower your broadband speed. In rural areas, consumers can live further away than the maximum distance of the central office, which means no DSL service for those subscribers.
A combination of signal loss and interference, called “crosstalk,” from adjacent copper wire pairs are both the enemies of DSL broadband, because they can drastically reduce speeds.
Telephone companies can address this problem by building new satellite central offices located halfway between customers and their primary facilities. These offices, usually connected by fiber, can successfully reduce the amount of copper wire between the customer and the company, boosting speeds. Many phone companies also deploy DSL extensions called D-SLAMs, which can be attached to a phone pole or enclosed in a metal box by the roadside. A fiber cable connects the D-SLAM back to the phone company, while existing copper phone wires go back to individual subscribers.
More modern forms of DSL: ADSL2, ADSL2+, and VDSL, share some of those concepts. The key is cutting as much copper wire out of the network as possible, replacing it with fiber optic cable which does not suffer signal loss or interference in the same way.
Many European and Pacific broadband networks rely on ADSL2/2+, which can usually deliver reliable speeds in the 20Mbps range. VDSL networks offer even more bandwidth, and are the basis of U-verse and Fibe, which split up broadband, phone service, and television on the same cable. When customers demand even faster speeds, phone companies can “bond” several individual DSL connections together to deliver faster speeds. Some traditional ADSL providers do that today for their customers, especially in areas where low speeds prevail.
An argument the phone company will love.
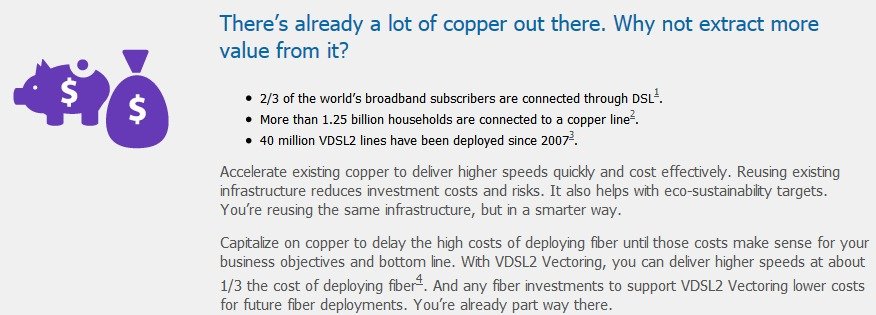
Alcatel Lucent says VDSL2 with Vectoring is the next best thing to fiber to the home, because it is cheaper to deploy with fewer headaches from local authorities when streets and yards are dug up for fiber cable replacements. It also meets the growing speed needs of average consumers. Alcatel Lucent predicts the minimum speed North Americans will need to support the next generation of online video is 50Mbps, more than 10 times the speed phone companies like Verizon, AT&T, Frontier, and CenturyLink provide over their traditional DSL networks, especially in rural and suburban areas.
Vectoring can deliver results for phone companies with aging copper wire infrastructure, more prone to crosstalk and other signal anomalies. Alcatel Lucent compares vectoring with noise-cancellation headphones. By sampling the current noise conditions on copper cable networks, vectoring can suppress the impact of the interference, boosting speeds and delivering more reliable results.
With technologies like VDSL2 with Vectoring promising speeds far faster than what rural North Americans currently enjoy, the Federal Communications Commission may want to re-evaluate its national minimum speed standard for broadband — 3-4Mbps — found in its National Broadband Plan. Alcatel Lucent promises they can do much better.
[flv width=”640″ height=”324″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Alcatel Lucent VDSL2.flv[/flv]
Alcatel Lucent produced this video to promote its new VDSL2 with Vectoring technology. The video targets cost-conscious phone companies who are being pressured to deliver faster service, but don’t want to spend the money on a fiber to the home network. (6 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe