 Getting Internet service in rural America can involve a whole lot more than calling the local phone company to check if DSL service is available. When it is not, satellite broadband is often the only realistic choice to access the Internet. Unfortunately, navigating through the options, terms and conditions, and restrictions requires the help of a lawyer or rocket scientist.
Getting Internet service in rural America can involve a whole lot more than calling the local phone company to check if DSL service is available. When it is not, satellite broadband is often the only realistic choice to access the Internet. Unfortunately, navigating through the options, terms and conditions, and restrictions requires the help of a lawyer or rocket scientist.
Kevin Hanssen, a dairy farmer in rural Wisconsin is just one of a dozen Stop the Cap! readers who access us over a satellite Internet connection. He, along with others, have been writing requesting assistance navigating an increasingly confusing amount of detail about recent upgrades taking place at the parent company of his provider — WildBlue, a service of ViaSat.
As Stop the Cap! recently reported, ViaSat is placing a new satellite into service that will bring improved service for certain customers. Long time customers like Hanssen have waited more than two years for company-promised upgrades that would bring better speeds and more generous usage policies. Currently, Hanssen faces a tiny usage allowance and “broadband” speeds of well under 1Mbps, especially in the evening.
“As a long term customer, I have lived under a plan that gives me 7.5GB in downloads and 2.3GB in uploads, but my experience with WildBlue may be very different than other customers, because the company has so many legacy and special plans that apply to different customers, so it is very hard to say ‘this is WildBlue’s policy’ because it can vary so much,” Hanssen tells us.
Indeed, over WildBlue’s history, ViaSat has changed its access policies several times, sometimes raising, but often lowering usage allowances accompanied by rate adjustments. Since 2005, WildBlue customers who originally faced a simple 30-day consumption limit that reset after each billing cycle now face a combination of a usage allowance under the company’s “Fair Access/Data Allowance Policy (FAP),” and an even more confusing rolling speed throttle called the “Quota Management Threshold (QMT).” Exceeding a monthly usage allowance guarantees broadband speeds of dial-up or less. Speeds are also curtailed temporarily for customers who run browsing sessions that consume as little as 30MB over a 30 minute period.
WildBlue's Quota Management Threshold starts reducing your speeds after a heavy browsing session.
With the help of Cisco, which created the throttled bandwidth technology, WildBlue’s combined FAP and QMT systems make it impossible for a customer punished just once by speed throttles to completely clear their record as a ‘known bandwidth abuser’ unless they avoid using any bandwidth for a month. For most customers unequipped to fully grasp the highly technical explanations of both policies, customer service representatives boil it down to something easier to understand: the less service you use, the better the chance you will not face a speed throttle rendering your connection practically unusable.
WildBlue's confusing throttle.
With strict limits in place, WildBlue not surprisingly scores among the lowest of all Internet Service Providers for customer satisfaction, and its nearest competitor Hughes does no better.
“As you have written before, satellite really is ‘take it or leave it broadband’ — heavily rationed, confusing, and very expensive,” Hanssen says.
For Hanssen and other Stop the Cap! readers who rely on satellite Internet, the promise of new capacity and faster speeds were supposed to turn “satellite as a last resort” into something more comparable to 4G wireless in America’s most rural areas. But as our readers share, there is a big chasm between marketing hype and reality for customers on the ground.
Confusing Brands & Pricing
ViaSat has not been content to offer customers a single brand of satellite broadband service. In addition to WildBlue itself, ViaSat markets plans under the American Recovery Act (the broadband stimulus program), co-branded service from DirecTV, DISH, AT&T and the National Rural Telecommunications Cooperative (NRTC), and forthcoming service on its newest satellite, ViaSat 1, which the company is marketing as “Exede” Internet. Customers west of the Mississippi who qualify for the American Recovery Act program get free installation and more generous usage allowances of up to 60GB per month.
“For two years, WildBlue has told us better usage allowances and faster service was coming with the new upgraded satellite, which we assumed would service all existing WildBlue customers,” Hanssen shares. “Now it turns out they are leaving existing WildBlue customers behind on the old satellite and creating a brand new service to sell new customers on the new satellite.”
Indeed, for marketing purposes, WildBlue and Exede are two different entities, and WildBlue customers looking for faster speeds from Exede will need to pony up at least $150 for new equipment, sign a new contract, and switch to a new Fair Access Policy that actually delivers many customers a lower usage allowance than their existing service from WildBlue offers.
“It’s total bait and switch, promising us faster service and then reducing the usage allowance that goes with it and adding around an $8/GB over-usage fee on Exede,” Hanssen says.
For customers served by the new ViaSat 1 satellite, Exede sells service based on usage, not speed. The advertised speed (not independently verified) is 12/3Mbps, which will cost $49.99 for up to 7.5GB per month, $79.99 for 15GB per month, or $129.99 for 25GB per month.
“Highway robbery I call it, because some of those caps are lower than on WildBlue so you are paying for better speed you won’t be able to use unless you agree to pay a lot more for a bigger allowance,” Hanssen says.
New Customers Get Priority Over Old Ones?
Customers eager to switch to the new, faster satellite broadband service report they are encountering roadblocks from ViaSat and their large independent dealer network responsible for sales and service of the satellite reception equipment. An often-heard accusation is that current customers are taking a back seat to new customers already invited to sign up.
That is a charge ViaSat, through its support forum, has strongly denied.
“We’re not giving preferential treatment to new vs. existing customers,” says WildBlue Forum Administrator Steve. “The dates we’ve quoted to existing customers who call in are approximately April/May, but yes, it could be sooner. It all depends on the number and availability of certified installer technicians in a given area. If someone absolutely wanted it now, we’ll try our best to accommodate that along with the big flood of new orders we’re receiving.”
Steve explains the delays to upgrade existing customers are occurring because new customer installations are currently “through the roof.”
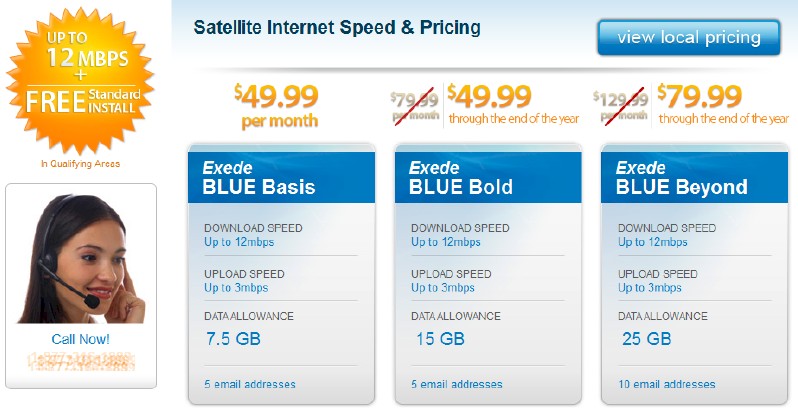
An independent dealer offers new customers a better deal.
But Stop the Cap! has also learned from an independent WildBlue dealer that ViaSat is offering a bonus for dealers who sign new customers, an incentive not paid to upgrade existing ones. Some new customer promotions also offer free installation and deep discounts until the end of 2012 for 15GB ($49.99) and 25GB ($79.99) service on the new ViaSat 1. Existing customers do not get the discount pricing and have to pay a $150 installation fee for new equipment required for the new satellite. Customers within a 2-year initial contract term pay even more: $250.
Customers Revolt

The government-sponsored Broadband Initiative program required WildBlue to provide a more generous usage allowance in return for broadband stimulus money.
Customers learning about the new pricing are unhappy.
Bill Cameron feels let down as a loyal customer by ViaSat’s pricing:
This new Excede 12 plan is an absolute joke. 12Mbps is awesome but the top plan limits you to a up/down total of 25GB and its $129.99 +$9.99 lease fee. So what good is 12Mbps if you really cant use it? Forget Netflix, Hulu or any Video on Demand. I have DirecTV and was hoping to be able to do some streaming but there is no way. If I want to stay at the same $80/mo price point I will loose 7GB of monthly cap since the mid tier plan is 15GB combined up and down. I don’t know what WildBlue is thinking here. Come on, $140/mo in the middle of a recession? Plus there is a $149 setup fee and even customers who have been with them for 7 years, like me, has to pay it. My loyalty is not rewarded one bit. A brand new customer pays the same amount.
A Broadband Reports reader sums up his views about WildBlue’s broken promises:
[…] We have been living with low caps on Wildblue for years, then for several years they -promise- an upgrade that will change everything. Then they up the speed to something most people don’t need, and REDUCE the amount of data available by a LARGE amount, increasing the price as well significantly. It was not what we were lead to believe. This was supposed to be an upgrade, but the speed is useless without quantity, that point has been made over and over.
And it doesn’t take someone sitting all day to go over the caps. It can take a little over an hour every day for one person to go over on the current 512Kbps plan, imagine with more speed how easy the person can go over with about 23% less data available.
Bottom line, it was not an upgrade, period, for many of us. Every neighbor I know is thinking the same thing, some currently drive 30 miles one way to get to a free hotspot to have enough bandwidth for online classes. The offered new plans are not enough for what they do either. Is anyone that understands the limits of satellite asking for anything unreasonable, NO. We were expecting an increase of some sort, any kind, not further insane restrictions after years of being restricted. A downgrade and overcharging is not an upgrade no matter how they try to spin it to us. If so few use what’s available as they say anyway, what would have been the harm of doubling the current caps. PERFECTLY REASONABLE EXPECTATIONS.
Kevin Hanssen wishes he had better options:
At this point, just about anything would be better than WildBlue. Since AT&T shows no interest in bringing me DSL service, it’s probably going to be wireless broadband or nothing. We have spotty cell coverage in this part of Wisconsin, but should a provider do something about that, we would still be facing tiny usage allowances in the 2-10GB range.
This is why universal service policies should extend to broadband service, to make certain rural America has reasonable access at reasonable prices.
There is nothing reasonable about satellite or wireless Internet at these speeds, allowances, and prices. WildBlue wants new customers at all costs, even if they walk over their loyal customers to sign them up. But why shouldn’t they? Their only effective competition is Hughes, and they are actually worse!

 Current FCC rules have allowed traffic shenanigans from ISPs like Comcast that don’t mind slowing their customers’ Netflix experience to a crawl until the streaming company opens its checkbook. The FCC’s anticipated new proposal would strictly forbid any creative end-runs around the concept of paid fast lanes Comcast can get away with today.
Current FCC rules have allowed traffic shenanigans from ISPs like Comcast that don’t mind slowing their customers’ Netflix experience to a crawl until the streaming company opens its checkbook. The FCC’s anticipated new proposal would strictly forbid any creative end-runs around the concept of paid fast lanes Comcast can get away with today.


 Subscribe
Subscribe









