[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WSJ ATT Buys DirecTV 5-19-14.flv[/flv]
For $48.5 billion, AT&T will vault itself into second place among the nation’s largest pay television providers with the acquisition of DirecTV. The Wall Street Journal reports the executives at AT&T have been looking to for a giant deal for several years. Most executives earn special bonuses and other incentives worth millions for successfully completing these kinds of transactions. (3:03)
AT&T plans to spend $48.5 billion to acquire the nation’s biggest satellite television provider, allowing AT&T to become the second largest pay television company, behind a merged Comcast and Time Warner Cable.
 The deal, finalized on Sunday, pays $95 per DirecTV share in a combination of stock and cash, about a 10% premium over DirecTV’s closing price on Friday. Including debt, the acquisition is AT&T’s third-largest deal on record, behind the purchase of BellSouth for $83 billion in 2006 and the deal for Ameritech Corp., which closed in 1999, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
The deal, finalized on Sunday, pays $95 per DirecTV share in a combination of stock and cash, about a 10% premium over DirecTV’s closing price on Friday. Including debt, the acquisition is AT&T’s third-largest deal on record, behind the purchase of BellSouth for $83 billion in 2006 and the deal for Ameritech Corp., which closed in 1999, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
“This is a unique opportunity that will redefine the video entertainment industry and create a company able to offer new bundles and deliver content to consumers across multiple screens – mobile devices, TVs, laptops, cars and even airplanes. At the same time, it creates immediate and long-term value for our shareholders,” said Randall Stephenson, AT&T chairman and CEO. “DirecTV is the best option for us because they have the premier brand in pay TV, the best content relationships, and a fast-growing Latin American business. DirecTV is a great fit with AT&T and together we’ll be able to enhance innovation and provide customers new competitive choices for what they want in mobile, video and broadband services. We look forward to welcoming DirecTV’s talented people to the AT&T family.”
The announced acquisition has left some on Wall Street scratching their heads.
“Like any merger born of necessity rather than opportunity, the combination of AT&T and DirecTV calls to mind images of lifeboats and rescues at sea,” telecommunications analyst Craig Moffett of MoffettNathanson Research wrote this week. AT&T, Moffett wrote, is in “dire need of a cash producer to sustain their dividend.”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg ATT DirecTV Deal a Head Scratcher 5-19-14.flv[/flv]
Craig Moffett, founder of MoffettNathanson LLC, talks about AT&T Inc.’s plan to buy DirecTV for $48.5 billion. Moffett speaks with Tom Keene, Scarlet Fu, William Cohan, and Adam Johnson on Bloomberg Television’s “Surveillance.” StockTwits founder Howard Lindzon also speaks. (5:12)
 The deal would combine AT&T’s wireless, U-verse, and broadband networks with DirecTV’s television service, creating bundling opportunities for some satellite customers. As broadband becomes the most important component of a package including phone, television, and Internet access, not being able to offer broadband has left satellite TV companies at a competitive disadvantage. AT&T’s U-verse platform – a fiber to the neighborhood network – has given AT&T customers an incremental broadband speed upgrade, but not one that can necessarily compete against fiber to the home or cable broadband.
The deal would combine AT&T’s wireless, U-verse, and broadband networks with DirecTV’s television service, creating bundling opportunities for some satellite customers. As broadband becomes the most important component of a package including phone, television, and Internet access, not being able to offer broadband has left satellite TV companies at a competitive disadvantage. AT&T’s U-verse platform – a fiber to the neighborhood network – has given AT&T customers an incremental broadband speed upgrade, but not one that can necessarily compete against fiber to the home or cable broadband.
Some analysts are speculating AT&T will eventually shut down its U-verse television service and dedicate its bandwidth towards a more robust broadband offering. Existing television customers would be offered DirecTV instead.
But deal critics contend AT&T is spending a lot of money to buy its competitors instead of investing enough in network upgrades.
“The amount of cash alone AT&T is spending on this deal — $14.55 billion — is as much as it cost Verizon for its entire FiOS deployment, which reaches more than 17 million homes,” Free Press’ Derek Turner tells Stop the Cap! “Add in the $33 billion in AT&T stock and $18.6 billion in debt, and you can see just how wasteful this merger is.”
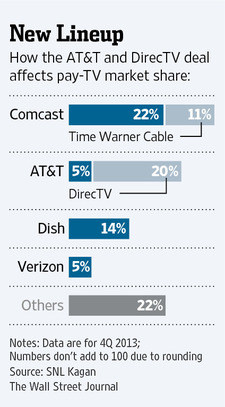
In effect, AT&T is spending nearly $50 billion to buy DirecTV’s customer relationships, its satellite platform, and its agreements with programmers, all while removing one competitor from the market. Cable has 54 percent of the pay TV market, satellite has 34 percent, and AT&T and Verizon share 11 percent. AT&T’s U-verse has 5.7 million TV customers. DirecTV has 20.3 million. Combining the two gives AT&T 26 million television customers, second only to Comcast/Time Warner Cable.
Rural Americans will effectively see their choice in competitors drop by one-third, giving them the option of the phone company or Dish Network.
AT&T intends to persuade regulators to approve the deal despite its antitrust implications by offering several commitments the company says are in the public interest and protect consumers:
- 15 Million Customer Locations Get More High Speed Broadband Competition. AT&T will use the merger synergies to expand its plans to build and enhance high-speed broadband service to 15 million customer locations, mostly in rural areas where AT&T does not provide high-speed broadband service today, utilizing a combination of technologies including fiber to the premises and fixed wireless local loop capabilities. This new commitment, to be completed within four years after close, is on top of the fiber and Project VIP broadband expansion plans AT&T has already announced. Customers will be able to buy broadband service stand-alone or as part of a bundle with other AT&T services.
- Stand-Alone Broadband. For customers who only want a broadband service and may choose to consume video through an over-the-top (OTT) service like Netflix or Hulu, the combined company will offer stand-alone wireline broadband service at speeds of at least 6Mbps (where feasible) in areas where AT&T offers wireline IP broadband service today at guaranteed prices for three years after closing.
- Nationwide Package Pricing on DIRECTV. DIRECTV’s TV service will continue to be available on a stand-alone basis at nationwide package prices that are the same for all customers, no matter where they live, for at least three years after closing.
- Net Neutrality Commitment. Continued commitment for three years after closing to the FCC’s Open Internet protections established in 2010, irrespective of whether the FCC re-establishes such protections for other industry participants following the DC Circuit Court of Appeals vacating those rules.
- Spectrum Auction. The transaction does not alter AT&T’s plans to meaningfully participate in the FCC’s planned spectrum auctions later this year and in 2015. AT&T intends to bid at least $9 billion in connection with the 2015 incentive auction provided there is sufficient spectrum available in the auction to provide AT&T a viable path to at least a 2×10 MHz nationwide spectrum footprint.

[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CNN ATT DirecTV Merger 5-19-14.flv[/flv]
CNN says AT&T’s buyout of DirecTV is about getting video programming to customers using all types of technology, but public interest groups suspect it’s about reducing competition. (1:17)
A closer look at AT&T’s commitments exposes several loopholes, however.
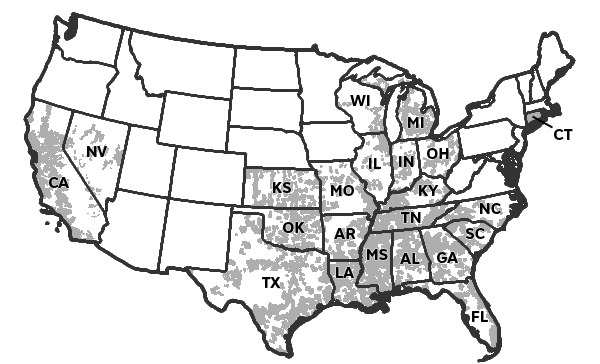
AT&T U-verse and DirecTV compete head-on in these areas.
- AT&T’s “commitment” to expand broadband to 15 million new locations is in addition to their Project VIP U-verse expansion now underway. However, AT&T does not say how many rural customers will see wired U-verse service finally become available vs. how many will lose their landlines permanently and have to rely on AT&T’s wireless landline replacement and expensive, usage-capped wireless broadband;
- AT&T’s speed commitment is largely unenforceable and falls apart with language like, “where feasible.” Anywhere they don’t deliver 6Mbps DSL speed can easily be explained away as “unfeasible.” AT&T also only commits to providing DSL where it already offers DSL, so no expansion there;
- The FCC’s Net Neutrality protections never covered wireless and three years is a very short time to commit to the “light touch” approach the FCC had with Net Neutrality back in 2010;
- AT&T’s wireless auction commitment comes with loopholes like “meaningfully,” “provided there,” and “a viable path to at least.”
“You can’t justify AT&T buying DirecTV by pointing at Comcast’s grab for Time Warner, because neither one is a good deal for consumers,” said Delara Derakhshani, policy counsel for Consumers Union, the advocacy arm of Consumer Reports. “On the heels of Comcast’s bid for Time Warner Cable, AT&T is going to try to pull off a mega-merger of its own. These could be the start of a wave of mergers that should put federal regulators on high alert. AT&T’s takeover of DirecTV is just the latest attempt at consolidation in a marketplace where consumers are already saddled with lousy service and price hikes. The rush is on for some of the biggest industry players to get even bigger, with consumers left on the losing end.”
“The captains of our communications industry have clearly run out of ideas,” said Craig Aaron, president of Free Press. “Instead of innovating and investing in their networks, companies like AT&T and Comcast are simply buying up the competition. These takeovers are expensive, and consumers end up footing the bill for merger mania. AT&T is willing to pay $48.5 billion and take on an additional $19 billion in debt to buy DirecTV. That’s a fortune to spend on a satellite-only company at a time when the pay-TV industry is stagnating and broadband is growing. For the amount of money and debt AT&T and Comcast are collectively shelling out for their respective mega-deals, they could deploy super-fast gigabit-fiber broadband service to every single home in America.”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CNN Al Franken Skeptical About DirecTV Deal 5-19-14.flv[/flv]
Sen. Al Franken (D-Minn.) appeared on CNN’s New Day this morning to express his skepticism about the consumer benefits of a merger between AT&T and DirecTV. “We need more competition, not less.” (2:40)


 Subscribe
Subscribe “Comcast Corp.’s bid to buy Time Warner Cable Inc. may be the opening act for a yearlong festival of telecommunications deals that would alter Internet, phone and TV service for tens of millions of Americans.” — Bloomberg News, May 14, 2014
“Comcast Corp.’s bid to buy Time Warner Cable Inc. may be the opening act for a yearlong festival of telecommunications deals that would alter Internet, phone and TV service for tens of millions of Americans.” — Bloomberg News, May 14, 2014 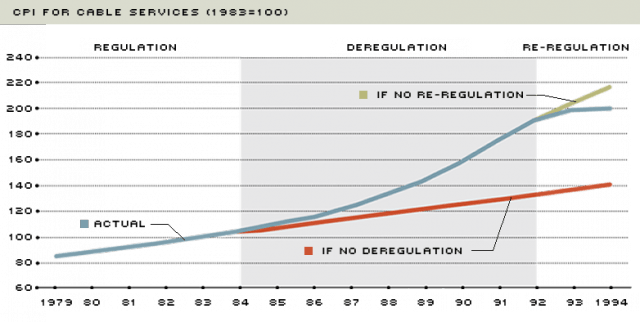
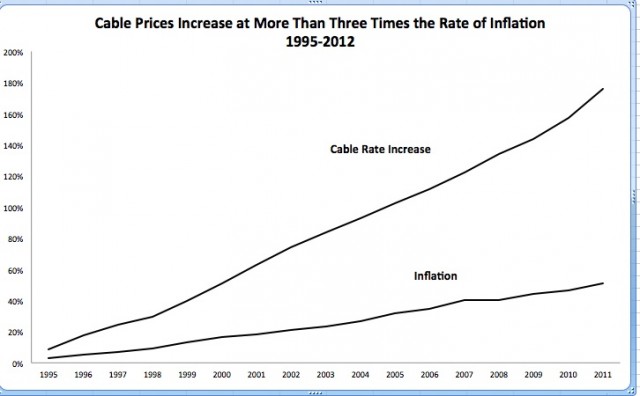
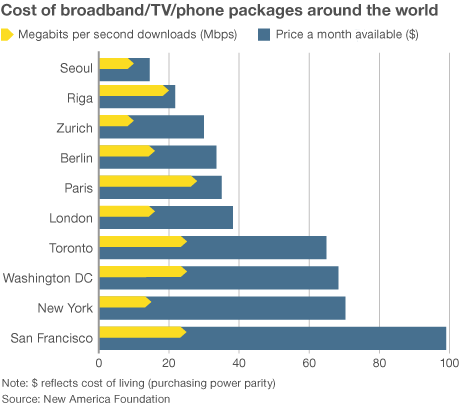 Economists reviewing data found in publicly available corporate balance sheets soon found evidence that the “increased programming costs”-excuse for rate increases did not hold water. The less competition or number of choices available to consumers in the market unambiguously lead to higher prices. It has remained true since Consumers’ Union
Economists reviewing data found in publicly available corporate balance sheets soon found evidence that the “increased programming costs”-excuse for rate increases did not hold water. The less competition or number of choices available to consumers in the market unambiguously lead to higher prices. It has remained true since Consumers’ Union 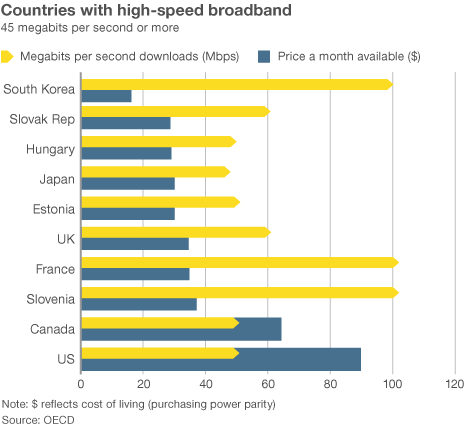 When a cable operator pays such an outrageous price, the previous owner is reaping the financial rewards of his monopoly power. The acquiring company can only pay such a high price by assuming that his monopoly power will allow him to continue to increase prices. Monopoly power is being bought and sold and borrowed against. The new cable operator, who has paid for market power, may insist that the debt he has incurred to obtain it is a real cost on his books. That may be correct in the literal sense (he owes someone that money) but that does not make it right, or the abuse of market power legal.
When a cable operator pays such an outrageous price, the previous owner is reaping the financial rewards of his monopoly power. The acquiring company can only pay such a high price by assuming that his monopoly power will allow him to continue to increase prices. Monopoly power is being bought and sold and borrowed against. The new cable operator, who has paid for market power, may insist that the debt he has incurred to obtain it is a real cost on his books. That may be correct in the literal sense (he owes someone that money) but that does not make it right, or the abuse of market power legal. The announced merger of Comcast and Time Warner Cable is expected to have far-reaching implications for other companies in the video and broadband business, with expectations 2014 could be one of the busiest years in a decade for telecom industry mergers and buyouts.
The announced merger of Comcast and Time Warner Cable is expected to have far-reaching implications for other companies in the video and broadband business, with expectations 2014 could be one of the busiest years in a decade for telecom industry mergers and buyouts. In a less likely deal Sprint is still trying to pursue T-Mobile USA for a potential merger and if regulators reject that idea, Charles Ergen’s Dish Network is said to be interested.
In a less likely deal Sprint is still trying to pursue T-Mobile USA for a potential merger and if regulators reject that idea, Charles Ergen’s Dish Network is said to be interested. Comcast will introduce usage-based billing on all of its broadband customers nationwide within five years, whether they like it or not.
Comcast will introduce usage-based billing on all of its broadband customers nationwide within five years, whether they like it or not. If the merger is approved, Comcast will face significantly less competition in many Verizon service areas also served by Time Warner Cable. Verizon FiOS expansion has ended and the company continues to de-emphasize its DSL service, which is the only broadband competition Time Warner Cable faces in many upstate New York and western Massachusetts communities.
If the merger is approved, Comcast will face significantly less competition in many Verizon service areas also served by Time Warner Cable. Verizon FiOS expansion has ended and the company continues to de-emphasize its DSL service, which is the only broadband competition Time Warner Cable faces in many upstate New York and western Massachusetts communities. Rensselaer County is just a short drive to the east of New York’s capital city Albany, but for residents in the southern half of the county, it might as be in the middle of nowhere.
Rensselaer County is just a short drive to the east of New York’s capital city Albany, but for residents in the southern half of the county, it might as be in the middle of nowhere.
 “We’ve asked them to bring the service and they won’t,” Austin told the newspaper.
“We’ve asked them to bring the service and they won’t,” Austin told the newspaper.