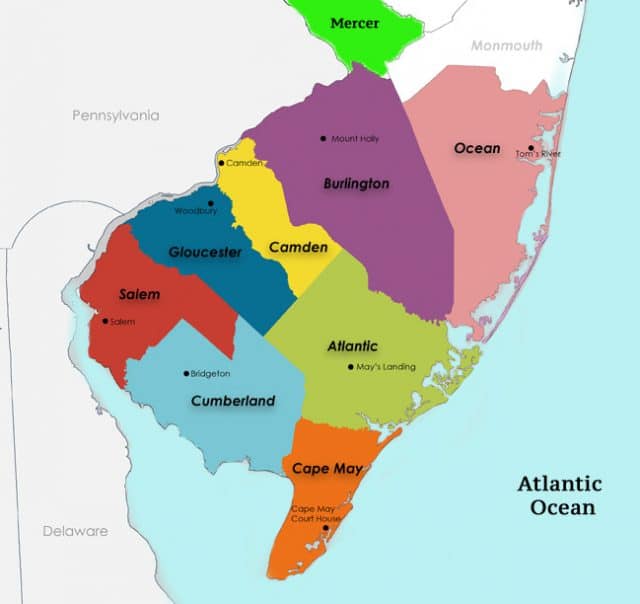
South Jersey: The worst broadband problems are in the southernmost counties closest to Delaware.
Customers hoping New Jersey’s telecom regulator would compel Verizon to expand fiber to the home service across southern New Jersey are out of luck.
The New Jersey Board of Public Utilities (BPU) approved a settlement between Verizon New Jersey, Inc., Cumberland County, and 18 southern New Jersey towns that alleged Verizon failed to properly maintain its wireline network in areas where it has chosen not to deploy FiOS — its fiber to the home service. But the settlement will only compel Verizon to maintain its existing copper network and offer token DSL and FiOS expansion in some unserved rural communities.
“We have heard our customers’ concerns in South Jersey and are pleased to have reached an agreement with the approval of all 17 towns on a maintenance plan going forward,” said Ray McConville, a Verizon spokesman. “We look forward to staying in regular communication with the towns to ensure our customers continue to receive the level of service they expect and deserve.”
“While the Board was fully prepared to proceed on this matter, the parties were able to reach a negotiated settlement which takes into consideration the needs of each community,” said Richard S. Mroz, president, N.J. Board of Public Utilities.
But some residents of those communities beg to differ.
“It’s another example of Chris Christie’s hand-picked regulators letting Verizon off the hook and sticking us in a digital divide,” complained Jeff Franklin, a Verizon DSL customer in Cumberland County. “Verizon should not be allowed to offer one half of the state modern broadband while sticking the rest of us with its slow DSL service.”
Franklin is upset that communities bypassed by Verizon’s FiOS network appear to have little chance of getting it in the future, now that regulators have agreed to allow Verizon to fix its own copper network.
“All the Board did was force Verizon to do what it should have been doing all along, taking care of its own network,” Franklin complained to Stop the Cap!
Verizon did agree to expand its fiber network into the communities of Estell Manor, Weymouth Township, Corbin City, and Lower Alloways Creek Township, but only because of a 2014 agreement with Verizon compelling them to offer broadband to residents who read and complete a “Bona Fide Retail Request” (BFRR) form which stipulates homes and businesses in Verizon’s New Jersey territory can get broadband if they don’t have it now as long as these criteria are met:
- Have no access to broadband service from a cable provider or Verizon;
- Have no access to 4G-based wireless service; and
- Sign a contract for at least one (1) year of broadband service and pay a $100 deposit.
 “BFRR is a joke because it requires potential customers have no access to 4G wireless service,” claimed Franklin. “You have to go to the government’s National Broadband Map to determine eligibility, which is very tough because — surprise, surprise — Verizon itself contributed its 4G wireless coverage information for that map and as far as Verizon is concerned, their 4G coverage in New Jersey is beautiful, even though it really isn’t.”
“BFRR is a joke because it requires potential customers have no access to 4G wireless service,” claimed Franklin. “You have to go to the government’s National Broadband Map to determine eligibility, which is very tough because — surprise, surprise — Verizon itself contributed its 4G wireless coverage information for that map and as far as Verizon is concerned, their 4G coverage in New Jersey is beautiful, even though it really isn’t.”
If a single provider submits map data that shows a home address is already covered by 4G wireless service, even if that isn’t accurate on the ground, that customer is ineligible under the terms of BFRR. Even if they were able to subscribe to 4G broadband, most plans are strictly data capped or throttled.
Under the settlement, Verizon gets to choose what technology to deploy. Outside of the four communities getting FiOS, the rest of South Jersey will have to continue relying on Verizon’s DSL service. Verizon has agreed to extend DSL to 2,000 new residences and businesses in Upper Pittsgrove, Downe, Commercial, Mannington, Pilesgrove, and South Harrison. It will also fix some of its DSL speed congestion problems and monitor for future ones as part of the settlement.
But DSL won’t work if Verizon’s wireline network stays in poor shape. The company has agreed to deploy its “Proactive Preventative Maintenance Tool” (PPMT) to scan its copper network to identify and repair or replace defective cables. Verizon has also agreed to daily inspections of outside facilities and fix any detected problems within 30 days, as well as regularly reporting back on the condition of its infrastructure inside the towns affected under the settlement.
This agreement took a year and a half to reach and will keep the two parties out of court, but many are not satisfied being left with Verizon’s DSL service.
“Unfortunately, the BPU continues to allow Verizon to pick and choose which residents will receive modern telecommunications at an affordable cost,” Greg Facemyer, a Hopewell Township committeeman in Cumberland County, told NewsWorks. “The state legislature needs to recognize these inequities and step in and level the playing field for South Jersey. Otherwise, our region will continue to fall even farther behind and be less competitive.”
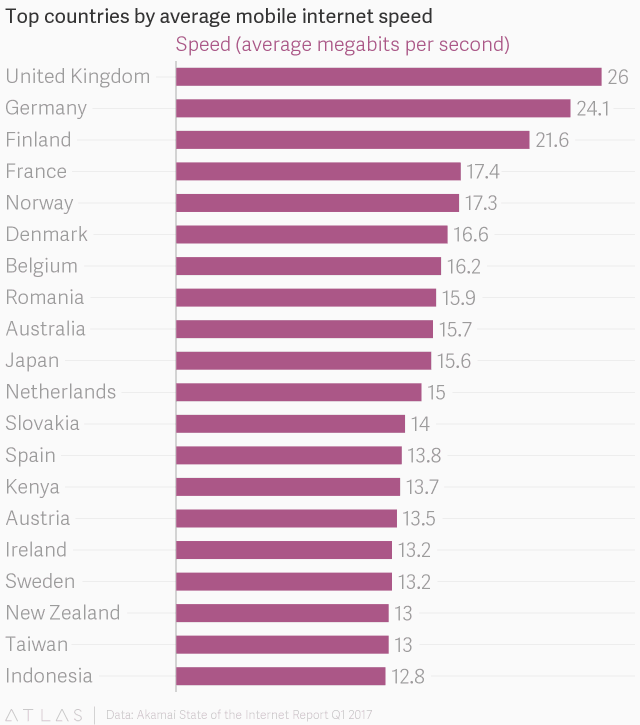
 Despite claims from America’s wireless companies that they deliver world-class wireless speeds, a new report from Akamai shows the United States only ranked 28th fastest in the world, beaten by the African nation of Kenya that ranked 14th.
Despite claims from America’s wireless companies that they deliver world-class wireless speeds, a new report from Akamai shows the United States only ranked 28th fastest in the world, beaten by the African nation of Kenya that ranked 14th.

 Subscribe
Subscribe