The two Democratic minority members of the Federal Communications Commission shared their strong sentiments today in remarks condemning the 3-2 vote to repeal net neutrality. Commissioners Mignon Clyburn and Jessica Rosenworcel appeared irritated at today’s Open Commission Meeting. They expressed concern that today’s vote appeared politically motivated and ignored more than 20 million comments filed by members of the public, most in favor of net neutrality.
FCC Chairman Ajit Pai did not reference any comments from the public in his remarks supporting net neutrality’s repeal, which the FCC website celebrated as, “Reversing Title II Framework, Increases Transparency to Protect Consumers, Spur Investment, Innovation, and Competition.”
Jessica Rosenworcel
“Net neutrality is internet freedom. I support that freedom. I dissent from this rash decision to roll back net neutrality rules. I dissent from the corrupt process that has brought us to this point. And I dissent from the contempt this agency has shown our citizens in pursuing this path today. This decision puts the Federal Communications Commission on the wrong side of history, the wrong side of the law, and the wrong side of the American public.
The future of the internet is the future of everything. That is because there is nothing in our commercial, social, and civic lives that has been untouched by its influence or unmoved by its power. And here in the United States our internet economy is the envy of the world. This is because it rests on a foundation of openness.
That openness is revolutionary. It means you can go where you want and do what you want online without your broadband provider getting in the way or making choices for you. It means every one of us can create without permission, build community beyond geography, organize without physical constraints, consume content we want when and where we want it, and share ideas not just around the corner but across the globe. I believe it is essential that we sustain this foundation of openness—and that is why I support net neutrality.
Net neutrality has deep origins in communications law and history. In the era when communications meant telephony, every call went through, and your phone company could not cut off your call or edit the content of your conversations. This guiding principle of nondiscrimination meant you were in control of the connections you made.
This principle continued as time advanced, technology changed, and Internet access became the dial tone of the digital age. So it was twelve years ago—when President George W. Bush was in the White House—that this agency put its first net neutrality policies on paper. In the decade that followed, the FCC revamped and revised its net neutrality rules, seeking to keep them current and find them a stable home in the law. In its 2015 order the FCC succeeded—because in the following year, in a 184-page opinion the agency’s net neutrality rules were fully and completely upheld.
So our existing net neutrality policies have passed court muster. They are wildly popular. But today we wipe away this work, destroy this progress, and burn down time-tested values that have made our Internet economy the envy of the world.

Rosenworcel
As a result of today’s misguided action, our broadband providers will get extraordinary new power from this agency. They will have the power to block websites, throttle services, and censor online content. They will have the right to discriminate and favor the internet traffic of those companies with whom they have pay-for-play arrangements and the right to consign all others to a slow and bumpy road.
Now our broadband providers will tell you they will never do these things. They say just trust us. But know this: they have the technical ability and business incentive to discriminate and manipulate your internet traffic. And now this agency gives them the legal green light to go ahead and do so.
This is not good. Not good for consumers. Not good for businesses. Not good for anyone who connects and creates online. Not good for the democratizing force that depends on openness to thrive. Moreover, it is not good for American leadership on the global stage of our new and complex digital world.
I’m not alone with these concerns. Everyone from the creator of the world wide web to religious leaders to governors and mayors of big cities and small towns to musicians to actors and actresses to entrepreneurs and academics and activists has registered their upset and anger. They are reeling at how this agency could make this kind of mistake. They are wondering how it could be so tone deaf. And they are justifiably concerned that just a few unelected officials could make such vast and far-reaching decisions about the future of the internet.
So after erasing our net neutrality rules what is left? What recourse do consumers have?
We’re told don’t worry, competition will save us. But the FCC’s own data show that our broadband markets are not competitive. Half of the households in this country have no choice of broadband provider. So if your broadband provider is blocking websites, you have no recourse. You have nowhere to go.
We’re told don’t worry, the Federal Trade Commission will save us. But the FTC is not the expert agency for communications. It has authority over unfair and deceptive practices. But to evade FTC review, all any broadband provider will need to do is add new provisions to the fine print in its terms of service. In addition, it is both costly and impractical to report difficulties to the FTC. By the time the FTC gets around to addressing them in court proceedings or enforcement actions, it’s fair to assume that the start-ups and small entities wrestling with discriminatory treatment could be long done. Moreover, what little authority the FTC has is now under question in the courts.
We’re told don’t worry, the state authorities will save us. But at the same time, the FCC all but clears the field with sweeping preemption of anything that resembles state or local consumer protection.
If the substance that got us to this point is bad, the process is even worse.
Let’s talk about the public record.
The public has been making noise, speaking up, and raising a ruckus. We see it in the protests across the country and outside here today. We see it in how they lit up our phone lines, clogged our e-mail in-boxes, and jammed our online comment system. It might be messy, but whatever our disagreements are on this dais I hope we can agree this is democracy in action—and something we can all support.
To date, nearly 24 million comments have been filed in this proceeding. There is no record in the history of this agency that has attracted so many filings. But there’s something foul in this record:
Two million comments feature stolen identities.
Half a million comments are from Russian addresses.
Fifty thousand consumer complaints are inexplicably missing from the record.
I think that’s a problem. I think our record has been corrupted and our process for public participation lacks integrity. Nineteen state attorneys general agree. They have written us demanding we halt our vote until we investigate and get to the bottom of this mess. Identity theft is a crime under state and federal law—and while it is taking place this agency has turned a blind eye to its victims and callously told our fellow law enforcement officials it will not help.
This is not acceptable. It is a stain on the FCC and this proceeding. This issue is not going away. It needs to be addressed.
Finally, I worry that this decision and the process that brought us to this point is ugly. It’s ugly in the cavalier disregard this agency has demonstrated to the public, the contempt it has shown for citizens who speak up, and the disdain it has for popular opinion. Unlike its predecessors this FCC has not held a single public hearing on net neutrality. There is no shortage of people who believe Washington is not listening to their concerns, their fears, and their desires. Add this agency to the list.
I, too, am frustrated. But here’s a twist: I hear you. I listen to what callers are saying. I read the countless, individually written e-mails in my in-box, the posts online, and the very short and sometimes very long letters. And I’m not going to give up—and neither should you. If the arc of history is long, we are going to bend this toward a more just outcome. In the courts. In Congress. Wherever we need to go to ensure that net neutrality stays the law of the land. Because if you are conservative or progressive, you benefit from internet openness. If you come from a small town or big city, you benefit from internet openness. If you are a company or non-profit, you benefit from internet openness. If you are a start-up or an established business, you benefit from internet openness. If you are a consumer or a creator, you benefit from internet openness. If you believe in democracy, you benefit from internet openness.
So let’s persist. Let’s fight. Let’s not stop here or now. It’s too important. The future depends on it.”
Mignon Clyburn
“I dissent. I dissent from this fiercely-spun, legally-lightweight, consumer-harming, corporate-enabling Destroying Internet Freedom Order.
I dissent, because I am among the millions who is outraged. Outraged, because the FCC pulls its own teeth, abdicating responsibility to protect the nation’s broadband consumers. Why are we witnessing such an unprecedented groundswell of public support, for keeping the 2015 net neutrality protections in place? Because the public can plainly see, that a soon-to-be-toothless FCC, is handing the keys to the Internet – the Internet, one of the most remarkable, empowering, enabling inventions of our lifetime – over to a handful of multi-billion dollar corporations. And if past is prologue, those very same broadband internet service providers, that the majority says you should trust to do right by you, will put profits and shareholder returns above, what is best for you.
Each of us raised our right hands when we were sworn in as FCC Commissioners, took an oath and promised to uphold our duties and responsibilities ‘to make available, so far as possible, to all the people of the United States, without discrimination… a rapid, efficient, Nation-wide, and world-wide wire and radio communication service with adequate facilities at reasonable charges.’ Today the FCC majority officially abandons that pledge and millions have taken note.
I do not believe that there are any FCC or Congressional offices immune to the deluge of consumer outcry. We are even hearing about state and local offices fielding calls and what is always newsworthy is that at last count, five Republican Members of Congress went on the record in calling for a halt of today’s vote. Why such a bipartisan outcry? Because the large majority of Americans are in favor of keeping strong net neutrality rules in place. The sad thing about this commentary, it pains me to say, is what I can only describe as the new norm at the FCC: A majority that is ignoring the will of the people. A majority that will stand idly by while the people they serve lose.
We have heard story after story of what net neutrality means to consumers and small businesses from places as diverse as Los Angeles’ Skid Row and Marietta, Ohio. I hold in my hand letters that plead with the FCC to keep our net neutrality rules in place but what is striking and in keeping with the new norm, despite the millions of comments, letters, and calls received, this Order cites, not even one. That speaks volumes about the direction the FCC is heading. That speaks volumes about just who is being heard.

Clyburn
Sole proprietors, whose entire business model, depends on an open internet, are worried that the absence of clear and enforceable net neutrality protections will result in higher costs and fewer benefits because you see: they are not able to pay tolls for premium access. Even large online businesses have weighed in, expressing concern about being subject to added charges as they simply try to reach their own customers. Engineers have submitted comments including many of the internet’s pioneers, sharing with the FCC majority, the fundamentals of how the internet works because from where they sit, there is no way that an item like this would ever see the light of day, if the majority understood the platform some of them helped to create.
I have heard from innovators, worried that we are standing up a mother-may-I regime, where the broadband provider becomes arbiter of acceptable online business models. And yes, I have heard from consumers, who are worried given that their broadband provider has already shown that they will charge inscrutable below-the-line fees, raise prices unexpectedly, and put consumers on hold for hours at a time. Who will have their best interests at heart in a world without clear and enforceable rules overseen by an agency with clear enforcement authority? A toothless FCC?
There has been a darker side to all of this over the past few weeks. Threats and intimidation. Personal attacks. Nazis cheering. Russian influence. Fake comments. Those are unacceptable. Some are illegal. They all are to be rejected. But what is also not acceptable, is the FCC’s refusal to cooperate with state attorney general investigations, or allow evidence in the record that would undercut a preordained outcome.
Many have asked, what happens next? How will all of this – Net Neutrality, my internet experience, look after today? My answer is simple. When the current protections are abandoned, and the rules that have been officially in place since 2015 are repealed, we will have a Cheshire cat version of net neutrality. We will be in a world where regulatory substance fades to black, and all that is left is a broadband provider’s toothy grin and those oh so comforting words: we have every incentive to do the right thing.
What they will soon have, is every incentive to do their own thing.Now the results of throwing out your Net Neutrality protections, may not be felt right away. Most of us will get up tomorrow morning and over the next week, wade through hundreds of headlines, turn away from those endless prognosticators, and submerge ourselves in a sea of holiday bliss. But what we have wrought will one day be apparent and by then, when you really see what has changed, I fear, it may not only be too late to do anything about it, because there will be no agency empowered to address your concerns. This item insidiously ensures the FCC will never be able to fully grasp the harm it may have unleashed on the internet ecosystem. And that inability might lead decisionmakers to conclude, that the next internet startup that failed to flourish and attempted to seek relief, simply had a bad business plan, when in fact what was missing was a level playing field online.
Particularly damning is what today’s repeal will mean for marginalized groups, like communities of color, that rely on platforms like the internet to communicate, because traditional outlets do not consider their issues or concerns, worthy of any coverage. It was through social media that the world first heard about Ferguson, Missouri, because legacy news outlets did not consider it important until the hashtag started trending. It has been through online video services, that targeted entertainment has thrived, where stories are finally being told because those same programming were repeatedly rejected by mainstream distribution and media outlets. And it has been through secure messaging platforms, where activists have communicated and organized for justice without gatekeepers with differing opinions blocking them.
Where will the next significant attack on internet freedom come from? Maybe from a broadband provider allowing its network to congest, making a high-traffic video provider ask what more can it pay to make the pain stop. That will never happen you say? Well it already has. The difference now, is the open question of what is stopping them? The difference after today’s vote, is that no one will be able to stop them.
Maybe several providers will quietly roll out paid prioritization packages that enable deep-pocketed players to cut the queue. Maybe a vertically-integrated broadband provider decides that it will favor its own apps and services. Or some high-value internet-of-things traffic will be subject to an additional fee. Maybe some of these actions will be cloaked under nondisclosure agreements and wrapped up in mandatory arbitration clauses so that it will be a breach of contract to disclose these publicly or take the provider to court over any wrongdoing. Some may say ‘Of Course this will never happen?” After today’s vote, what will be in place to stop them?
What we do know, is that broadband providers did not even wait for the ink to dry on this Order before making their moves. One broadband provider, who had in the past promised to not engage in paid prioritization, has now quietly dropped that promise from its list of commitments on its website. What’s next? Blocking or throttling? That will never happen? After today’s vote, exactly who is the cop of the beat that can or will stop them?
And just who will be impacted the most? Consumers and small businesses, that’s who. The internet continues to evolve and has become ever more critical for every participant in our 21st century ecosystem: government services have migrated online, as have educational opportunities and job notices and applications, but at the same time, broadband providers have continued to consolidate, becoming bigger. They own their own content, they own media companies, and they own or have an interest in other types of services.
Why are millions so alarmed? Because they understand the risks this all poses and even those who may not know what Title II authority is, know that they will be at risk without it.
I have been asking myself repeatedly, why the majority is so singularly-focused on overturning these wildly-popular rules? Is it simply because they felt that the 2015 Net Neutrality order, which threw out over 700 rules and dispensed with more than 25 provisions, was too heavy-handed? Is this a ploy to create a “need” for legislation where there was none before? Or is it to establish uncertainty where little previously existed?
Is it a tactic to undermine the net neutrality protections adopted in 2015 that are currently parked at the Supreme Court? You know, the same rules that were resoundingly upheld by the D.C. Circuit last year? No doubt, we will see a rush to the courthouse, asking the Supreme Court to vacate and remand the substantive rules we fought so hard for over the past few years, because today, the FCC uses legally-suspect means to clear the decks of substantive protections for consumers and competition.
It is abundantly clear why we see so much bad process with this item: because the fix was already in. There is no real mention of the thousands of net neutrality complaints filed by consumers. Why? The majority has refused to put them in the record while maintaining the rhetoric that there have been no real violations. Record evidence of the massive incentives and abilities of broadband providers to act in anti-competitive ways are missing from the docket? Why? Because they have refused to use the data and knowledge the agency does have, and has relied upon in the past to inform our merger reviews. As the majority has shown again and again, the views of individuals do not matter, including the views of those who care deeply about the substance, but are not Washington insiders.
There is a basic fallacy underlying the majority’s actions and rhetoric today: the assumption of what is best for broadband providers, is best for America. Breathless claims about unshackling broadband services from unnecessary regulation, are only about ensuring that broadband providers, have the keys to the internet. Assertions that this is merely a return to some imaginary status quo ante, cannot hide the fact, that this is the very first time, that the FCC, has disavowed substantive protections for consumers online.
And when the current, 2015 Net Neutrality rules are laid to waste, we may be left with no single authority with the power to protect consumers. Now this Order loudly crows about handing over authority of broadband to the FTC, but what is absent from the Order and glossed over in that haphazardly issued afterthought of a Memorandum of Understanding or MOU, is that the FTC is an agency, with no technical expertise in telecommunications; the FTC is an agency that may not even have authority over broadband providers in the first instance; the FTC is an agency that if you can even reach that high bar of proving unfair or deceptive practices and that there is substantial consumer injury, it will take years upon years to remedy. But don’t just take my word for it: even one of the FTC’s own Commissioners has articulated these very concerns. And if you’re wondering why the FCC is preempting state consumer protection laws in this item without notice, let me help you with a simple jingle that you can easily commit to memory: If it benefits industry, preemption is good; if it benefits consumers, preemption is bad.
Reclassification of broadband will do more than wreak havoc on net neutrality. It will also undermine our universal service construct for years to come, something which the Order implicitly acknowledges. It will undermine the Lifeline program. It will weaken our ability to support robust broadband infrastructure deployment. And what we will soon find out, is what a broadband market unencumbered by robust consumer protections will look like. I suspect the result will not be pretty.
I know there are many questions on the mind of Americans right now, including what the repeal of net neutrality will mean for them. To help answer outstanding questions I will host a town hall through Twitter next Tuesday at 2pm EST. What saddens me is that the agency that is supposed to protect you is abandoning you, but what I am pleased to be able to say is the fight to save net neutrality does not end today. This agency does not have, the final word. Thank goodness.
As I close my eulogy of our 2015 net neutrality rules, carefully crafted rules that struck an appropriate balance in providing consumer protections and enabling opportunities and investment, I take ironic comfort in the words of then Commissioner Pai from 2015, because I believe this will ring true about this Destroying Internet Freedom Order:
“I am optimistic, that we will look back on today’s vote as an aberration, a temporary deviation from the bipartisan path, that has served us so well. I don’t know whether this plan will be vacated by a court, reversed by Congress, or overturned by a future Commission. But I do believe that its days are numbered.”
Amen to that, Mr. Chairman. Amen to that.
Editor’s Note: In deference to journalism style books and the forthcoming introduction of several pieces of proposed legislation to enshrine the idea of an open internet into law, we are henceforth referring to “net neutrality” in lowercase. Since Stop the Cap! began, we have consistently referred to the concept as “Net Neutrality,” but because we will soon see various bills and policy proposals outlining different ideas about what that represents, it is more appropriate to refer to it as a general concept as opposed to a singular policy. The change should not suggest any editorial commentary about the principle of net neutrality or its importance. Most print publications began referring to net neutrality in lowercase more than a year ago. We now join them for the reasons referenced above.



 Subscribe
Subscribe Charter Communications CEO Thomas Rutledge is fed up with customers sharing their passwords to unlock television streaming services for non-subscribing friends and family and promises to lead an industry-wide crackdown on the practice in 2018.
Charter Communications CEO Thomas Rutledge is fed up with customers sharing their passwords to unlock television streaming services for non-subscribing friends and family and promises to lead an industry-wide crackdown on the practice in 2018.
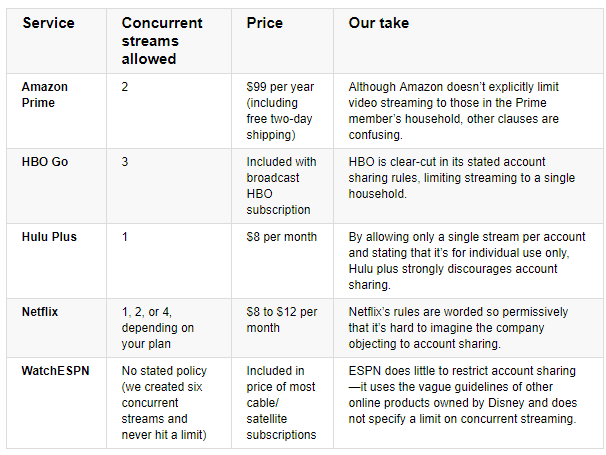
 Viacom successfully negotiated the transition of its networks back to the Select TV plan beginning in late January, 2018. But those networks’ online viewing platforms and apps will now include stream limitations to keep simultaneous viewing and password sharing to a minimum.
Viacom successfully negotiated the transition of its networks back to the Select TV plan beginning in late January, 2018. But those networks’ online viewing platforms and apps will now include stream limitations to keep simultaneous viewing and password sharing to a minimum.
 Blackburn’s bill covers all the bases for the telecom industry she routinely supports.
Blackburn’s bill covers all the bases for the telecom industry she routinely supports. Blackburn’s bill ignores several years of court rulings on net neutrality cases that have called out the flaw of the FCC’s earlier dependence on defining the internet as an “information service” subject to oversight under Section 706 of the 1996 Telecom Act. The courts have ruled this foundation is inadequate to enforce net neutrality. The foundation that has proved adequate and has so-far survived court challenge exists in Title II of the Communications Act, made applicable when the internet was redefined as a common carrier “telecommunications service.” Rep. Blackburn’s bill would return net neutrality enforcement to the same flawed authority courts have already ruled does not apply, neutering net neutrality in the courts.
Blackburn’s bill ignores several years of court rulings on net neutrality cases that have called out the flaw of the FCC’s earlier dependence on defining the internet as an “information service” subject to oversight under Section 706 of the 1996 Telecom Act. The courts have ruled this foundation is inadequate to enforce net neutrality. The foundation that has proved adequate and has so-far survived court challenge exists in Title II of the Communications Act, made applicable when the internet was redefined as a common carrier “telecommunications service.” Rep. Blackburn’s bill would return net neutrality enforcement to the same flawed authority courts have already ruled does not apply, neutering net neutrality in the courts.



 The 2015 rules were intended to give consumers equal access to web content and prevent broadband providers from favoring their own content. Pai proposes allowing those practices as long as they are disclosed.
The 2015 rules were intended to give consumers equal access to web content and prevent broadband providers from favoring their own content. Pai proposes allowing those practices as long as they are disclosed.