 A last-ditch effort last weekend by executives of SoftBank and Deutsche Telekom to overcome their differences in merging Sprint with T-Mobile USA ended in failure, killing Wall Street’s hopes combining the two scrappiest wireless carriers would end a bruising price war that had heated up competition and hurt profits at all four of America’s leading wireless companies.
A last-ditch effort last weekend by executives of SoftBank and Deutsche Telekom to overcome their differences in merging Sprint with T-Mobile USA ended in failure, killing Wall Street’s hopes combining the two scrappiest wireless carriers would end a bruising price war that had heated up competition and hurt profits at all four of America’s leading wireless companies.
Now Wall Street, hungry for a consolidation deal, is strategizing what will come next.
Sprint/T-Mobile Merger
In the end, SoftBank’s chairman, Masayoshi Son, simply did not want to give up control of Sprint to Deutsche Telekom, especially considering Sprint’s vast wireless spectrum holdings suitable for future 5G wireless services.
The failure caused Sprint Corp. shares and bonds to plummet, and spooked investors are worried Sprint’s decade-long inability to earn a profit won’t end anytime soon. Sprint’s 2010 Network Vision Plan, which promised better coverage and network performance, also helped to load the company with debt, nearly half of which Sprint has to pay back over the next four years before it becomes due. Sprint’s perpetual upgrades have not tremendously improved its network coverage or performance, and its poor performance ratings have caused many customers to look elsewhere for wireless service.
Investors are also concerned Sprint will struggle to pay its current debts at the same time it faces new ones from investments in next generation 5G wireless technology. Scared shareholders have been comforted this morning by both Son and Sprint CEO Marcelo Claure in an all-out damage control campaign.
Son has promised the now-orphaned Sprint will benefit from an increased stake in the company by SoftBank — a signal to investors SoftBank is tying itself closer to Sprint. Son has also promised additional investments to launch yet another wave of network upgrades for Sprint’s fourth place network. But nothing is expected to change very quickly for customers, who may be in for a rough ride for the immediate future. Son has already said his commitment to raise Sprint’s capital expenditures from the current $3.5-4 billion to $5-6 billion annually will not begin this year. Analysts claim Sprint needs at least $5-6 billion annually to invest in network improvements if it ever hopes to catch up to T-Mobile, AT&T, and Verizon Wireless.

Masayoshi Son, chairman of SoftBank Group
“Even if the next three-four years will be a tough battle, five to 10 years later it will be clear that this is a strategically invaluable business,’’ Son said, lamenting losing control of that business in a deal with T-Mobile was simply impossible. “There was just a line we couldn’t cross, and that’s how we arrived at the conclusion.”
During a call with analysts on Monday, Sprint’s chief financial officer Tarek Robbiati acknowledged investors’ disappointment.
Investors were hoping for an end to deep discounting and perks given to attract new business. T-Mobile’s giveaways and discounting have reduced the company’s profitability. Sprint’s latest promotions, including giving away service for up to a year, were seen by analysts as desperate.
Son’s own vision plan doesn’t dwell on the short-term, mapping out SoftBank’s progress over the next 300 years. But for now, Son is concerned with supporting the investments already made in the $100 billion Vision Fund Son has built with Saudi Arabia’s oil wealth-fueled Public Investment Fund. Its goal is to lead in the field of next generation wireless communications networks. Sprint is expected to be a springboard for those investments in the United States, supported by the wireless company’s huge 2.5GHz spectrum holdings, which may be perfect for 5G wireless networks.
 But Son’s own failures are also responsible for Sprint’s current plight. Son attempted to cover his losses in Sprint by pursuing a merger with T-Mobile in 2014, but the merger fell apart when it became clear the Obama Administration’s regulators were unlikely to approve the deal. After that deal fell apart, Son has allowed T-Mobile to overtake Sprint’s third place position in the wireless market. While T-Mobile grew from 53 million customers to 70.7 million today, Sprint lost one million customers, dropping to fourth place with around 54 million current customers.
But Son’s own failures are also responsible for Sprint’s current plight. Son attempted to cover his losses in Sprint by pursuing a merger with T-Mobile in 2014, but the merger fell apart when it became clear the Obama Administration’s regulators were unlikely to approve the deal. After that deal fell apart, Son has allowed T-Mobile to overtake Sprint’s third place position in the wireless market. While T-Mobile grew from 53 million customers to 70.7 million today, Sprint lost one million customers, dropping to fourth place with around 54 million current customers.
Son’s answer to the new competition was to change top management. Incoming Sprint CEO Marcelo Claure promptly launched a massive cost-cutting program and layoffs, and upgrade-oriented investments in Sprint’s network stagnated, causing speeds and performance to decline.
Claure tweetstormed damage control messages about the merger’s collapse, switching from promoting the merger’s benefits to claims of relief the merger collapsed:
- “Jointly stopping merger talks was right move.”
- “
- “Excited about Sprint’s future as a standalone. I’m confident this is right decision for our shareholders, customers & employees.”
- “Sprint added over 1 million customers last year – we have gone from losing to winning.”
- “Last quarter we delivered an estimated 22% of industry postpaid phone gross additions, our highest share ever.”
- “Sprint network performance is at best ever levels – 33% improvement in nationwide data speeds year over year.”
- “We are planning significant investments to the Sprint network this year and the years to come.”
- “In the last 3 years we’ve reduced our costs by over $5 billion.”
- “Sprint’s results are the best we’ve achieved in a decade and we will continue getting better every day.”
In Saturday’s joint announcement, Claure said that “while we couldn’t reach an agreement to combine our companies, we certainly recognize the benefits of scale through a potential combination. However, we have agreed that it is best to move forward on our own. We know we have significant assets, including our rich spectrum holdings, and are accelerating significant investments in our network to ensure our continued growth.”
“They need to spend (more) money on the network,” said William Ho, an analyst at 556 Ventures LLC.
CNBC reports Sprint’s end of its T-Mobile merger deal has hammered the company’s stock. What does Sprint do now? (1:30)
Sprint/Altice Partnership
 Sprint executives hurried out word on ‘Damage Control’ Monday that Altice USA would partner with Sprint to resell wireless service under the Altice brand. In return for the partnership, Sprint will be able to use Altice’s fiber network in Cablevision’s service area in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut for its cell towers and future 5G small cells. The deal closely aligns to Comcast and Charter’s deal with Verizon allowing those cable operators to create their own cellular brands powered by Verizon Wireless’ network.
Sprint executives hurried out word on ‘Damage Control’ Monday that Altice USA would partner with Sprint to resell wireless service under the Altice brand. In return for the partnership, Sprint will be able to use Altice’s fiber network in Cablevision’s service area in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut for its cell towers and future 5G small cells. The deal closely aligns to Comcast and Charter’s deal with Verizon allowing those cable operators to create their own cellular brands powered by Verizon Wireless’ network.
An analyst at Cowen & Co., suspected the Altice deal may be a trial to test the waters with Sprint before Altice commits to a future merger between the two companies. Altice is hungry for expansion, currently owning Cablevision and Suddenlink cable operators in the U.S. But Altice has a very small footprint in the U.S., leading some analysts to believe a more lucrative merger might be possible elsewhere.
Sprint/Charter Merger

Charter Communications Logo. (PRNewsFoto/Charter Communications, Inc.)
Charter Communications stock was up more than 7% in early Monday morning trading as a result of speculation SoftBank and Charter Communications were restarting merger talks after a deal with T-Mobile collapsed.
CNBC reported that Mr. Son was willing to resume talks with Charter executives about a merger between the cable operator and Sprint. Charter executives have shown little interest in the deal, still distracted trying to merge their acquisitions Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks into Charter’s current operation. Charter’s entry into wireless has been more tentative, following Comcast with a partnership with Verizon Wireless to resell that considerably stronger network under the Charter brand beginning sometime in 2018.
According to CNBC, John Malone’s Liberty Media, which owns a 27% stake in Charter, is now in favor of a deal, while Charter’s top executives are still opposed.
CNBC reports Charter and Sprint may soon be talking again about a merger between the two. (6:33)
Dish Networks <-> T-Mobile USA
 Wall Street’s merger-focused analysts are hungry for a deal now that the Sprint/T-Mobile merger has collapsed. Pivotal Research Group is predicting good things are possible for shareholders of Dish Network, and upgraded the stock to a “buy” recommendation this morning.
Wall Street’s merger-focused analysts are hungry for a deal now that the Sprint/T-Mobile merger has collapsed. Pivotal Research Group is predicting good things are possible for shareholders of Dish Network, and upgraded the stock to a “buy” recommendation this morning.
Jeff Wlodarczak, Pivotal’s CEO and senior media analyst, theorizes that Sprint’s merger collapse could be good news for Dish, sitting on a large amount of unused wireless spectrum suitable for 5G wireless networks. Those licenses, estimated to be worth $10 billion, are likely to rise in value as wireless companies look for suitable spectrum to deploy next generation 5G networks.
Multichannel News quotes Wlodarczak’s note to investors:
“In our opinion, post the T-Mobile-Sprint deal failure there is a reasonable chance that T-Mobile could make a play for Dish or Dish spectrum as it would immediately vault the most disruptive U.S. wireless player into the leading U.S. spectrum position (w/ substantially more spectrum than underpins Verizon’s “best in class” network),” Wlodarczak wrote. “This possible move could force Verizon to counter-bid for Dish spectrum (or possibly the entire company) as Dish spectrum is ideally suited for Verizon and to keep it out of T-Mobile’s hands.”
AT&T/DirecTV Buyout of Dish Network
 Wlodarczak has also advised clients he believes the deregulation-friendly Trump Administration would not block the creation of a satellite TV monopoly, meaning AT&T should consider pairing its DirecTV service with an acquisition of Dish Networks’ satellite TV business, even if it forgoes Dish’s valuable wireless spectrum.
Wlodarczak has also advised clients he believes the deregulation-friendly Trump Administration would not block the creation of a satellite TV monopoly, meaning AT&T should consider pairing its DirecTV service with an acquisition of Dish Networks’ satellite TV business, even if it forgoes Dish’s valuable wireless spectrum.
“AT&T, post their Time Warner deal, could (and frankly should) be interested in purchasing Dish’s core DBS business taking advantage of a potentially more laissez faire regulatory climate/emergence of V-MVPD’s, to significantly bolster their DirecTV business (and help to justify the original questionable DirecTV deal) by creating a SatTV monopoly in ~10-15M US households, increased programming scale and massive synergies at a likely very attractive price.”
Such a transaction would likely resemble the regulatory approval granted to merge XM Satellite Radio and Sirius Satellite Radio into SiriusXM Satellite Radio in 2008. Despite the merger, just months after its approval, the combined company neared bankruptcy until it was bailed out with a $530 million loan from John Malone’s Liberty Media in February 2009. Liberty Media maintains an active interest in the satellite radio company to this day.
 Verizon Communications has selected Samsung Electronics as a major supplier of the wireless company’s forthcoming 5G wireless service, launching first in Sacramento, Calif., in the second half of this year.
Verizon Communications has selected Samsung Electronics as a major supplier of the wireless company’s forthcoming 5G wireless service, launching first in Sacramento, Calif., in the second half of this year. Verizon’s wireless customers in Sacramento will be the first to receive invitations to switch their home broadband accounts away from AT&T, Frontier, Wave Broadband and Comcast — the four largest incumbent providers in the greater Sacramento area. Verizon claims its 5G service can support speeds up to 1Gbps. Verizon has been testing 5G service in 11 U.S. cities, but has kept pricing details to itself. The issue of data caps has been repeatedly raised and most industry analysts predict Verizon will usage cap its 5G service at around 200GB a month. Whether the company plans to offer an unlimited use plan is unknown.
Verizon’s wireless customers in Sacramento will be the first to receive invitations to switch their home broadband accounts away from AT&T, Frontier, Wave Broadband and Comcast — the four largest incumbent providers in the greater Sacramento area. Verizon claims its 5G service can support speeds up to 1Gbps. Verizon has been testing 5G service in 11 U.S. cities, but has kept pricing details to itself. The issue of data caps has been repeatedly raised and most industry analysts predict Verizon will usage cap its 5G service at around 200GB a month. Whether the company plans to offer an unlimited use plan is unknown.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Some of America’s top telephone and cable companies will likely pay little, if any federal taxes as a result of the passage of a Republican-sponsored tax cut plan, while some may also receive generous “refunds” based on depreciation-related expenses and future investments the companies would have made with or without changes to the tax code.
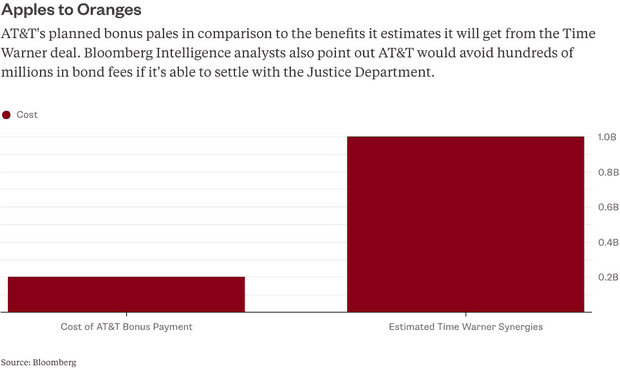
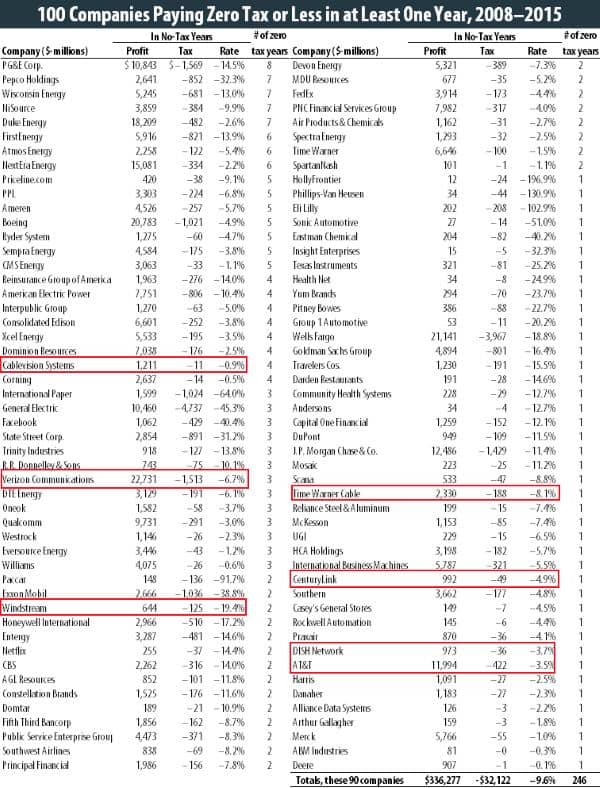
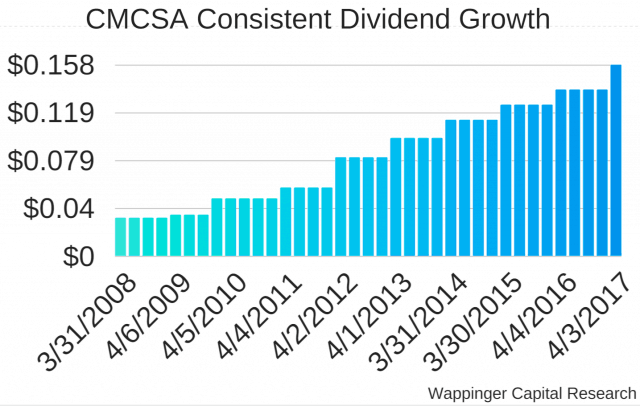
Some of America’s top telephone and cable companies will likely pay little, if any federal taxes as a result of the passage of a Republican-sponsored tax cut plan, while some may also receive generous “refunds” based on depreciation-related expenses and future investments the companies would have made with or without changes to the tax code.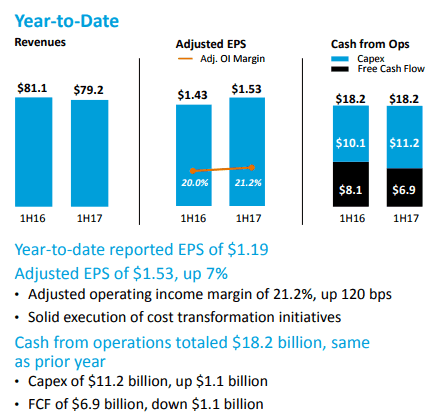

 It is rare for AT&T and Verizon to feud in public, even rarer for one company to accuse the other of being anti-competitive, but that is precisely what happened last week in California as the two companies sparred over building a next generation wireless network for first responders.
It is rare for AT&T and Verizon to feud in public, even rarer for one company to accuse the other of being anti-competitive, but that is precisely what happened last week in California as the two companies sparred over building a next generation wireless network for first responders. FirstNet is one of AT&T’s most lucrative contracts in years, and the phone company is doing everything possible to win over state officials in hopes they will embrace the FirstNet plan. It has been a successful effort with more than 30 states, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands purposely opting in, and more than a dozen still studying AT&T’s offer. To date, no state has opted out.
FirstNet is one of AT&T’s most lucrative contracts in years, and the phone company is doing everything possible to win over state officials in hopes they will embrace the FirstNet plan. It has been a successful effort with more than 30 states, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands purposely opting in, and more than a dozen still studying AT&T’s offer. To date, no state has opted out.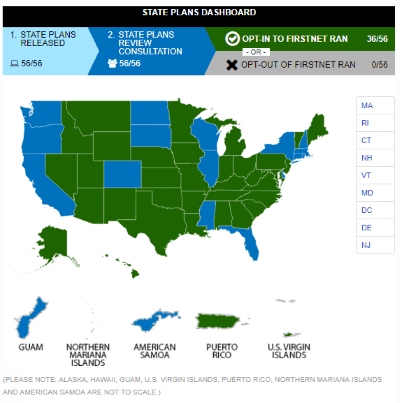 Verizon’s offer would seem to be a good deal for consumers and governments in states like New York and California that have yet to opt in to AT&T FirstNet, and in California, Verizon was invited to bid to create an alternative network in a potential “opt out” scenario. Verizon’s director of public-safety solutions group – David Wiederecht, promised the state Verizon would submit its bid by the state deadline, which was last Wednesday. By Friday, California officials leaked word Verizon had reneged on that commitment and did not participate, a fact Verizon later confirmed.
Verizon’s offer would seem to be a good deal for consumers and governments in states like New York and California that have yet to opt in to AT&T FirstNet, and in California, Verizon was invited to bid to create an alternative network in a potential “opt out” scenario. Verizon’s director of public-safety solutions group – David Wiederecht, promised the state Verizon would submit its bid by the state deadline, which was last Wednesday. By Friday, California officials leaked word Verizon had reneged on that commitment and did not participate, a fact Verizon later confirmed.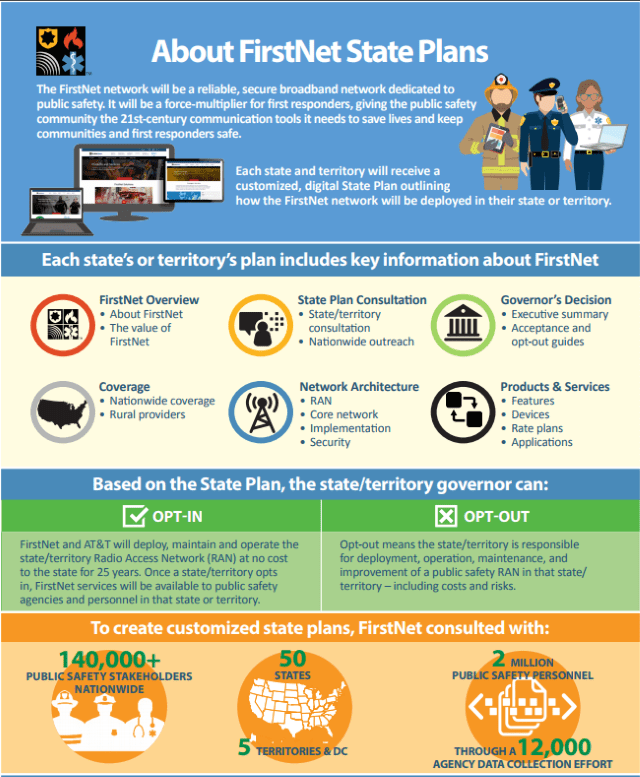



 But Moffett is thinking even further ahead, by suggesting wireless carriers might be able to stop spending billions on building and expanding their competing 4G LTE networks when they could all share a single provider’s network in each city. That idea could work if providers agreed to creating local monopolies.
But Moffett is thinking even further ahead, by suggesting wireless carriers might be able to stop spending billions on building and expanding their competing 4G LTE networks when they could all share a single provider’s network in each city. That idea could work if providers agreed to creating local monopolies.
 A last-ditch effort last weekend by executives of SoftBank and Deutsche Telekom to overcome their differences in merging Sprint with T-Mobile USA
A last-ditch effort last weekend by executives of SoftBank and Deutsche Telekom to overcome their differences in merging Sprint with T-Mobile USA 
 But Son’s own failures are also responsible for Sprint’s current plight. Son attempted to cover his losses in Sprint by pursuing a merger with T-Mobile in 2014, but the merger fell apart when it became clear the Obama Administration’s regulators were unlikely to approve the deal. After that deal fell apart, Son has allowed T-Mobile to overtake Sprint’s third place position in the wireless market. While T-Mobile grew from 53 million customers to 70.7 million today, Sprint lost one million customers, dropping to fourth place with around 54 million current customers.
But Son’s own failures are also responsible for Sprint’s current plight. Son attempted to cover his losses in Sprint by pursuing a merger with T-Mobile in 2014, but the merger fell apart when it became clear the Obama Administration’s regulators were unlikely to approve the deal. After that deal fell apart, Son has allowed T-Mobile to overtake Sprint’s third place position in the wireless market. While T-Mobile grew from 53 million customers to 70.7 million today, Sprint lost one million customers, dropping to fourth place with around 54 million current customers. Sprint executives hurried out word on ‘Damage Control’ Monday that Altice USA would partner with Sprint to resell wireless service under the Altice brand. In return for the partnership, Sprint will be able to use Altice’s fiber network in Cablevision’s service area in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut for its cell towers and future 5G small cells. The deal closely aligns to Comcast and Charter’s deal with Verizon allowing those cable operators to create their own cellular brands powered by Verizon Wireless’ network.
Sprint executives hurried out word on ‘Damage Control’ Monday that Altice USA would partner with Sprint to resell wireless service under the Altice brand. In return for the partnership, Sprint will be able to use Altice’s fiber network in Cablevision’s service area in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut for its cell towers and future 5G small cells. The deal closely aligns to Comcast and Charter’s deal with Verizon allowing those cable operators to create their own cellular brands powered by Verizon Wireless’ network.
 Wall Street’s merger-focused analysts are hungry for a deal now that the Sprint/T-Mobile merger has collapsed. Pivotal Research Group is predicting good things are possible for shareholders of Dish Network, and upgraded the stock to a “buy” recommendation this morning.
Wall Street’s merger-focused analysts are hungry for a deal now that the Sprint/T-Mobile merger has collapsed. Pivotal Research Group is predicting good things are possible for shareholders of Dish Network, and upgraded the stock to a “buy” recommendation this morning. Wlodarczak has also advised clients he believes the deregulation-friendly Trump Administration would not block the creation of a satellite TV monopoly, meaning AT&T should consider pairing its DirecTV service with an acquisition of Dish Networks’ satellite TV business, even if it forgoes Dish’s valuable wireless spectrum.
Wlodarczak has also advised clients he believes the deregulation-friendly Trump Administration would not block the creation of a satellite TV monopoly, meaning AT&T should consider pairing its DirecTV service with an acquisition of Dish Networks’ satellite TV business, even if it forgoes Dish’s valuable wireless spectrum.