 New York’s Public Service Commission (PSC) has come under fire in an audit by State Comptroller Thomas DiNapoli for “falling short” monitoring Charter Spectrum, Altice-Optimum, and Windstream, some of the state’s largest telecom companies.
New York’s Public Service Commission (PSC) has come under fire in an audit by State Comptroller Thomas DiNapoli for “falling short” monitoring Charter Spectrum, Altice-Optimum, and Windstream, some of the state’s largest telecom companies.
“When New Yorkers flip on the lights, log in or make a call, they should be confident that someone is making sure these service providers are living up to their promises,” DiNapoli said. “My auditors found the state Public Service Commission was not doing enough to make sure utilities are holding up their end of the deal. PSC lacked critical equipment to do its job and rarely inflicted financial consequences when companies did not deliver. This has to change.”
The audit found that the regulator was often arbitrary in its orders, frequently failed to verify compliance of conditions imposed on providers, and quietly dropped compliance penalties including fines and merger revocation orders when the Commission faced pushback from companies.
Most of the audit’s criticism was directed at how the PSC managed the 2016 merger-acquisition of Time Warner Cable by Charter Communications (better known as Spectrum). The merger was approved after Charter agreed to ten deal conditions. But DiNapoli’s auditors found Charter failed to either complete four of these conditions or the PSC failed to verify they were completed. New York also lost the opportunity to collect $5 million from Charter’s failure to meet its rural broadband commitments. Instead, the PSC settled for $1 million and agreed to extend the deadline for Charter to expand its rural footprint, rewarding the company for its failure.
DiNapoli’s audit criticized the PSC’s verification procedures to determine if Charter adequately upgraded its cable systems to all-digital technology and raised broadband speeds by the end of 2018. Instead, the Comptroller found the Commission often took Charter’s word for it because it lacked the equipment and resources to independently verify Charter’s performance.

DiNapoli
The auditors also complained Charter offered scant evidence of compliance with two other terms of its merger approval agreement — wiring 50 community locations for free broadband service and investing at least $50 million to improve service quality for New York customers. The audit found no evidence Charter had wired any community locations for free broadband service, and the Commission failed to verify Charter made suitable investments in service improvements by its May 2018 deadline.
The Commission disagreed with several of the audit’s findings. The Commission claimed it held comprehensive proceedings to review the Charter acquisition of Time Warner Cable, imposed deadlines on the conditions, and eventually threatened to revoke Charter’s cable franchises for the company’s failure to comply with its orders.
“After pursuing escalating enforcement actions, the Commission in mid-2018, revoked the merger authorization,” the Commission responded. “This final enforcement action which revoked the company’s authorization to operate in in the state set an important precedent in New York — and across the nation — as this type of enforcement remedy had not been previously utilized in the regulatory community. Ultimately, the enforcement action was settled in a manner that resulted in a company commitment to expand its network entirely Upstate at an estimated cost of more than $600 million, more than twice the original estimate at the time of the merger approval, and $12 million paid by the company in lieu of penalty for additional network expansion work.”
The settlement effectively rendered the PSC’s fines against Charter for not meeting its rural broadband expansion deadlines moot. The Commission argued New Yorkers benefited more from Charter’s additional commitments to expand its cable footprint even further than originally envisioned.
 “The Department utilizes penalty actions in a strategic manner to address violations,” the Commission explained. “It can be more beneficial to the state’s customers to obtain at shareholder expense expanded infrastructure, reductions in rates, or improvements in customer service rather than imposing financial penalties, and when that is the case, the [Commission] does indeed prefer the best response for customers.”
“The Department utilizes penalty actions in a strategic manner to address violations,” the Commission explained. “It can be more beneficial to the state’s customers to obtain at shareholder expense expanded infrastructure, reductions in rates, or improvements in customer service rather than imposing financial penalties, and when that is the case, the [Commission] does indeed prefer the best response for customers.”
But DiNapoli’s audit noted that utilities are well aware of how to avoid paying fines by delaying their collection indefinitely through legal remedies. The audit slammed the PSC for walking away from collecting the fines owed, noting it “creates a lack of accountability and inspires little motivation to stay in compliance.” It also complained that regardless of what additional remedies the PSC extracted from Charter in a final settlement, tens of thousands of rural New Yorkers remain without the internet service they were promised, and will probably have to wait until as late as 2021 to get it.
“As it has been over three years since the merger was approved, network expansion should have already been provided to approximately 126,875 unserved or underserved premises based on the 2016 Commission Order approving the merger,” the audit found. “As of July 2019, Charter had only extended its network to 64,827 premises. Based on the original Order, 62,048 additional customers should have received access to these services. Charter now has until September 2021 to complete the network expansion of 145,000 premises previously scheduled to be completed by May 2020.”
The PSC also claimed it was distracted by legal actions it was taking surrounding the revocation of the merger’s approval, but after the case was settled, the Commission did undertake random speed testing to verify Charter had raised the broadband speeds as agreed in the merger agreement.
“Staff is confident that, in all areas field tested to date, the Charter network is capable of providing broadband service with download speed in excess of 300 Mbps, and the network itself has the potential to provide download speed beyond 1 Gbps. In fact, the company is marketing 1 Gbps service in much of the New York State service footprint,” the Commission argued.
 The Commission confirmed Charter has not yet showed it is providing free broadband service to 50 community service locations, such as libraries, schools, or town halls. Charter initially refused to provide information about the service locations it selected for complimentary service “for privacy reasons.” But since the Commission placed no deadline on complying with this condition, it cannot penalize Charter for not meeting it on a timely basis.
The Commission confirmed Charter has not yet showed it is providing free broadband service to 50 community service locations, such as libraries, schools, or town halls. Charter initially refused to provide information about the service locations it selected for complimentary service “for privacy reasons.” But since the Commission placed no deadline on complying with this condition, it cannot penalize Charter for not meeting it on a timely basis.
“After multiple discussions, Charter finally provided a list of the 50 Anchor Institutions on July 17, 2019 and included bill copies and/or account screen shots demonstrating no charge for broadband service to these institutions,” the Commission responded. “Staff has been able to independently confirm that 33 of the 50 institutions are receiving broadband service from Charter at no charge. For the remaining institutions, Charter was asked to provide additional evidence that these institutions have been provided this complimentary service. If Charter cannot definitively demonstrate that the 17 institutions are receiving free service, Charter must select a replacement institution in order to fulfill this condition. Once Charter has provided this information, Staff will then begin its independent confirmation.”
The Commission also claims Charter met its obligation to invest at least $50 million in service improvements.
 “In its May 2018 Annual Update, Charter provided a list of expenditures totaling over $90 million to comply with this condition. From that list, Staff identified completed projects totaling approximately $70 million that were dedicated to New York State. To verify these expenditures, Staff requested and analyzed actual invoices to determine whether the expenditures were made,” the Commission claimed.
“In its May 2018 Annual Update, Charter provided a list of expenditures totaling over $90 million to comply with this condition. From that list, Staff identified completed projects totaling approximately $70 million that were dedicated to New York State. To verify these expenditures, Staff requested and analyzed actual invoices to determine whether the expenditures were made,” the Commission claimed.
The audit found some of these same issues also applied to two other telecom merger and acquisition deals impacting New York consumers. Altice’s acquisition of Cablevision’s Optimum cable service received approval with five deal conditions. The audit found the Commission failed to adequately verify compliance with three of those conditions, relating to internet speed and performance, free broadband service to 40 community institutions, and improvements to customer service requiring Altice to fix customer issues within two days. The Commission responded that its belated verification found no non-compliance, but the audit urged the Commission not to delay its verification procedures going forward.

FairPoint is now known under the name of its owner, Consolidated Communications.
FairPoint Communications offers telephone and internet service to 13,700 customers in a few rural communities in New York. Its new owner, Consolidated Communications, was required to implement eight deal conditions, and the audit found it failed to meet two of them. FairPoint was required to invest at least $4 million in network reliability and service quality improvements, including the expansion of internet access service to at least 300 additional locations. FairPoint submitted an expansion plan, and updated reports, including the number of locations completed which is claimed to be over 300.
But the audit found the Commission failed to verify these claims, citing inadequate staffing to visit FairPoint’s rural service areas to perform field inspections. The audit found the Commission didn’t bother to verify service improvements in any location. Another deal condition was designed to protect FairPoint’s “customer-facing” employees from layoffs. Soon after the merger, “FairPoint reclassified 9 of the 39 customer-facing positions and ultimately eliminated them, claiming they ‘duplicated work being performed in other work centers.'” The audit’s initial findings triggered an investigation by the PSC to determine if FairPoint violated the terms of its merger order. Ultimately, the Commission found it did not, but the audit warned the PSC was completely unaware of the employment changes until the audit discovered them.
The Comptroller’s Office made four recommendations the PSC should either implement or improve:
- Actively monitor all conditions listed in Orders to ensure all utilities are in compliance.
- Develop and issue Orders that include well-defined, measurable, and enforceable conditions. The Orders should also include the consequences for non-compliance, as appropriate.
- Verify the accuracy of data submitted by utilities that is used by the Commission or Department to evaluate or make decisions concerning the utilities. This includes data submitted for performance metrics, safety standards, and Utility Service Quality Reports.
- Develop policies and procedures that provide employees with standard monitoring steps to perform when overseeing compliance with merger or acquisition Orders, as well as steps addressing the auditing of data submitted in support of Utility Service Quality Reports.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Just shy of 10 years after FairPoint Communications acquired Verizon’s landline properties in the northern New England states of Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, both the company and its name are disappearing forever.
Just shy of 10 years after FairPoint Communications acquired Verizon’s landline properties in the northern New England states of Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, both the company and its name are disappearing forever. Promised broadband upgrades from speed increases come with few details, except a broad commitment to raise speeds for 300,000 internet customers over the course of this year — which represents about 30% of FairPoint customers. Spokeswoman Angelynne Amores claims there will be no price hikes for faster internet speeds.
Promised broadband upgrades from speed increases come with few details, except a broad commitment to raise speeds for 300,000 internet customers over the course of this year — which represents about 30% of FairPoint customers. Spokeswoman Angelynne Amores claims there will be no price hikes for faster internet speeds. An
An  Consolidated Communications will inherit residential FairPoint phone and broadband customers in 17 states, most notably those in Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont. But press releases from Consolidated showed little interest in the residential telecommunications business. Instead, Consolidated executives are looking at FairPoint’s business and enterprise customers, and the benefits of owning FairPoint’s 17,000 fiber route mile network.
Consolidated Communications will inherit residential FairPoint phone and broadband customers in 17 states, most notably those in Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont. But press releases from Consolidated showed little interest in the residential telecommunications business. Instead, Consolidated executives are looking at FairPoint’s business and enterprise customers, and the benefits of owning FairPoint’s 17,000 fiber route mile network.
 “Not as patient as FairPoint’s own customers that spent several years of hell dealing with Verizon’s sale of its landlines in Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine,” said FairPoint customer Sally Jackman, who lives in Maine. “It looks like the hedge funds want their pound of profits from another sale, exactly what FairPoint customers don’t need right now.”
“Not as patient as FairPoint’s own customers that spent several years of hell dealing with Verizon’s sale of its landlines in Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine,” said FairPoint customer Sally Jackman, who lives in Maine. “It looks like the hedge funds want their pound of profits from another sale, exactly what FairPoint customers don’t need right now.”

 Such legislation strips consumers of any assumption they can get affordable, high quality landline service and would allow FairPoint to mothball significant segments of its network (and the customers that depend on it), telling the disconnected to use a cell phone provider instead.
Such legislation strips consumers of any assumption they can get affordable, high quality landline service and would allow FairPoint to mothball significant segments of its network (and the customers that depend on it), telling the disconnected to use a cell phone provider instead. Last week, even FairPoint’s CEO Paul Sunu appeared to undercut his company’s own arguments for the need of such legislation, just as the company renewed its efforts in Portland to get a new 2016 version of the deregulation bill through the Maine legislature.
Last week, even FairPoint’s CEO Paul Sunu appeared to undercut his company’s own arguments for the need of such legislation, just as the company renewed its efforts in Portland to get a new 2016 version of the deregulation bill through the Maine legislature.
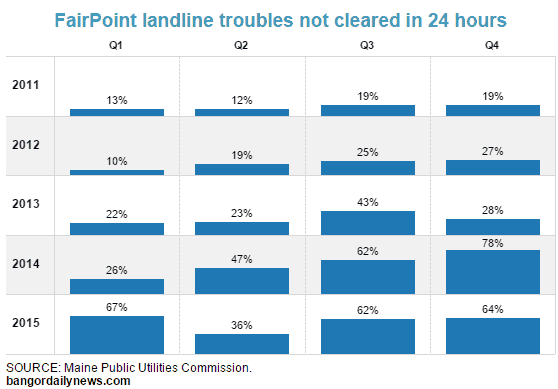 “The market determines the service quality criteria of importance to customers and the service quality levels they find acceptable,” Sarah Davis, the company’s senior director of government affairs, wrote. “To the extent service quality is deficient from the perspective of consumers, the competitive marketplace imposes its own serious penalties.”
“The market determines the service quality criteria of importance to customers and the service quality levels they find acceptable,” Sarah Davis, the company’s senior director of government affairs, wrote. “To the extent service quality is deficient from the perspective of consumers, the competitive marketplace imposes its own serious penalties.”