State and local officials gather to welcome Comcast’s state-funded service expansion in western Massachusetts. (From left to right: MBI chairman Peter Larkin; Carolyn Kirk, deputy secretary of the Executive Office of Housing and Economic Development; Michael Parker, senior vice president for Comcast’s Western New England region; Lt. Gov. Karyn Polito; Kevin Hart, former chair of the Montague Broadband Committee; and Rep. Stephen Kulik, D-Worthington.) (Image: MBI )
Two years after Republican Massachusetts Gov. Charlie Baker imposed a state-mandated “pause” on WiredWest, a collaborative, multi-community, publicly owned fiber to the home broadband network for western Massachusetts, Comcast is celebrating the introduction of expanded service in the towns of Buckland, Chester, Conway, Hardwick, Huntington, Montague, Northfield, Pelham and Shelburne, made possible with a $4 million taxpayer-funded grant to the nation’s largest cable operator.
While state officials continually questioned the economics of WiredWest, which by that time enrolled more than 7,000 eager would-be customers with $49 deposits, Comcast repeatedly declared it was “uneconomic” to provide broadband service to most rural western Massachusetts communities, at least until state officials paid the cable giant millions of dollars to reach 1,089 previously unserved homes and businesses in the nine towns, effectively giving Comcast a broadband monopoly.
“We were pleased to work with Comcast, who met the two-year timeline we set to deliver critical 21st-century broadband connections to more homes and businesses,” said Lt. Gov. Karyn Polito in a press release this week. She called the project “a great example of a public-private partnership” that would help resolve rural Massachusetts broadband problems.
WiredWest could not have met Polito’s two-year timeline, primarily because the collaborative has been blocked and ambushed repeatedly after Democratic Gov. Deval Patrick left office. State officials in Boston and the Massachusetts Broadband Institute (MBI), responsible for funding broadband initiatives, began a campaign of fear, uncertainty, and doubt about the project shortly after Gov. Baker took office, culminating in recommendations from then-MBI director Eric Nakajima imploring towns not to sign agreements with WiredWest, and eventually withholding critical funding from the broadband cooperative, questioning its governance and operating model.
It soon became clear Gov. Baker preferred an industry solution to the rural broadband problem, which caused broadband advocate Susan Crawford to slam the decision in early 2017.
“This is the story of a dramatic failure of imagination and vision at the state level: Governor Charlie Baker’s apparent insistence that Massachusetts relegate small towns to second-rate, high-priced, monopoly-controlled (and unregulated) communications capacity,” Crawford wrote. “It’s a slow-rolling tragedy that will blight western Massachusetts for generations.”
 A divide and conquer campaign to peel off communities from the WiredWest project has been underway for years. Earlier this year, MBI dangled $3.1 million in grants available exclusively to Charter Communications to build out its network in several towns in the region. When asked if those taxpayer dollars would be available to publicly owned broadband projects like WiredWest, Peter Larkin, MBI’s current board chairman, responded “no.”
A divide and conquer campaign to peel off communities from the WiredWest project has been underway for years. Earlier this year, MBI dangled $3.1 million in grants available exclusively to Charter Communications to build out its network in several towns in the region. When asked if those taxpayer dollars would be available to publicly owned broadband projects like WiredWest, Peter Larkin, MBI’s current board chairman, responded “no.”
Despite the roadblocks, many of the communities staying loyal to the WiredWest concept have hired Westfield Gas & Electric’s ‘Whip City Fiber’ division to help design and construct their own fiber to the home networks, which will be superior to what Charter or Comcast plans for the region.
For exasperated residents and businesses who have waited more than four years for broadband, the politics and constant delays have become secondary issues to getting broadband… from somewhere. That may explain why Kevin Hart, who frequently objected to Comcast’s proposal to build an inferior copper-fiber network while chairing the Montague Broadband Committee, suddenly switched sides and praised the Comcast project this week for its timely introduction of broadband service.
In contrast, Montague Broadband Committee member Robert Steinberg in 2016 called Comcast’s cash infusion from taxpayers “corporate welfare.”
WWLP in Springfield reports several towns are getting expanded cable and broadband service from Comcast. (1:21)


 Subscribe
Subscribe AT&T and Comcast have successfully delayed Google Fiber’s expansion around the country long enough to finish upgrades that can nearly match the upstart’s speedy internet service.
AT&T and Comcast have successfully delayed Google Fiber’s expansion around the country long enough to finish upgrades that can nearly match the upstart’s speedy internet service.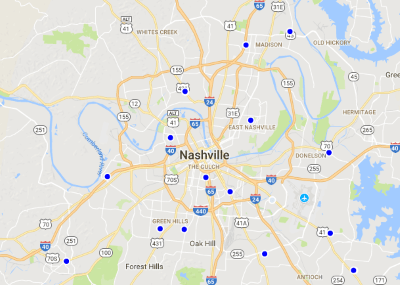

 Comcast announced this week it is expanding its $9.95 discount internet access program Internet Essentials to
Comcast announced this week it is expanding its $9.95 discount internet access program Internet Essentials to  Qualified Assistance Programs
Qualified Assistance Programs In the seven years of its existence, Comcast has only managed to enroll six million people in the program, a fraction of those that would otherwise qualify who live in Comcast service areas. Most critics blame Comcast’s onerous qualification requirements for the relatively low enrollment.
In the seven years of its existence, Comcast has only managed to enroll six million people in the program, a fraction of those that would otherwise qualify who live in Comcast service areas. Most critics blame Comcast’s onerous qualification requirements for the relatively low enrollment. Nearly half of all adults with an income below $30,000 don’t have home broadband service or a traditional computer, a 2017
Nearly half of all adults with an income below $30,000 don’t have home broadband service or a traditional computer, a 2017 Frustrated New Englanders that can’t get anywhere dealing with Comcast or Consolidated Communications’ customer service are getting fast fixes in New Hampshire by taking their complaints to the Consumer Protection and Antitrust Division of the attorney general’s office.
Frustrated New Englanders that can’t get anywhere dealing with Comcast or Consolidated Communications’ customer service are getting fast fixes in New Hampshire by taking their complaints to the Consumer Protection and Antitrust Division of the attorney general’s office.