Gone from Spectrum lineups across northern New England.
Many Spectrum cable television customers across the country have seen their broadcast TV lineups shrink as the company removes “duplicate” and “semi-local” stations, even as it hikes the cost of its Broadcast TV surcharge.
Southern Maine customers are the latest to be affected with the sudden removal of Boston’s ABC affiliate, WCVB-TV on June 5 — the last Boston area station on the television lineup.
“York (Maine) is part of the Portland TV market and we carry the designated in-market ABC affiliate — WMTW,” responded Andrew Russell, Spectrum’s director of communications for the northeast division. “We no longer carry the out-of-market ABC affiliate.”
Viewers trying to watch WCVB in southern Maine saw a screen stating “programming on this network is no longer available,” instead of local news and traffic information important for a number of southern Maine residents that commute down I-95 into the Boston area for work.
“I am fit to be tied,” York Beach resident Ken Morrison told the Bangor Daily News. “And I’m not alone. A lot of people are very upset about it.”
Subscribers in distant suburbs, exurban or rural areas between two major cities often had access (often for decades) to several stations in adjacent television markets. Each subscriber could choose the station serving the city that was most relevant in their lives. Prior to Spectrum and Time Warner Cable, cable systems in these areas were often locally owned and operated by smaller companies. These operators were responsive to the needs of their customers and distant over-the-air stations were often a part of the cable lineup from the 1970s forward. But as consolidation in cable industry continues, local lineups are now usually determined in a corporate office hundreds of miles away.
This Binghamton, N.Y. PBS station was thrown off the Spectrum lineup across several counties in the Southern Tier.
That could explain why Spectrum subscribers living in Tompkins and Cortland counties in New York suddenly lost WSKG-TV, the PBS affiliate from nearby Binghamton in favor of Syracuse-based WCNY-TV. Local residents do not consider themselves a part of Syracuse. Most consider themselves residents of the Southern Tier, which stretches along the New York-Pennsylvania border and includes Binghamton, Corning, Elmira, Hornell, Olean, Salamanca, Dunkirk, Jamestown, and Vestal. Residents will tell you they have more in common with their neighbors in northern Pennsylvania than Syracuse, but Spectrum apparently knew better and announced viewers in the two counties would now have to be satisfied watching a PBS station broadcasting to an audience at least 50 miles away.
Spectrum’s decision in this case does not appear to be a financial one.
“A public media organization like us gets no money from Charter to air our programming,” said WSKG’s management. “Our programming is provided to them for free, by law.”
WSKG believes what is actually behind Spectrum’s decision to change the lineup is the regionalization of their cable system head-ends, from which television programming is managed. Programming seen on Spectrum subscribers’ TV screens across much of the Southern Tier and part of the Finger Lakes region is now managed from Charter offices in Syracuse.
“In this case, because our tower is more than 70 miles from Syracuse’s head-end, where the signal originates, there’s a line of demarcation where they don’t have to carry our signal anymore,” said WSKG station president and chief executive, Greg Catlin. “In this case, that cut-off is Cortland and Tompkins County. They have every right to be doing what they’re doing. That doesn’t mean they have to do it.”
Subscribers were exceptionally unhappy to lose their Binghamton PBS station, and the station received a significant number of listener and viewer contributions from an area that is now cut off. The Southern Tier, like Pennsylvania to the south, is notorious for poor signals due to mountainous terrain, which limits television and FM radio reception. Verizon offers no competing television service in this part of New York, leaving residents with satellite television as the only possible alternative.

WPTZ in Plattsburgh is off Spectrum lineups in several parts of northern New York.
The first week of June was a significant date on the calendar for many residents in Spectrum’s northeastern service areas. In northern New York, Spectrum customers were notified they were losing WPTZ, the NBC affiliate in Plattsburgh, in favor of Syracuse’s NBC station WSTM-TV. That Syracuse station now produces news and current affairs programming for three Syracuse stations – WSTM itself, WTVH (CBS) and WSTQ (CW) under the “CNY Central” brand. But subscribers who lost WPTZ do not consider themselves a part of central New York and would more likely choose to visit Vermont than Syracuse.
In other parts of New England, Spectrum customers also lost WMUR-TV — the New Hampshire station with one of the best regarded news operations in northern New England, in favor of WVNY in Burlington, Vt. Newscasts on WVNY are produced by its sister station WFFF-TV. WMUR has a larger American audience than WVNY. In fact, this Vermont ABC affiliate has far more viewers in southern Québec and Montréal than it does in its own home market.
Back in Maine, the local congressional delegation is turning up the heat on Spectrum, so far to no avail. State Reps. Lydia Blume and Patricia Hymanson of York have written a letter to Spectrum demanding the company reinstate WCVB or reduce the cable television bills of affected customers to compensate. So far, Spectrum has done neither.
<
div>
Morrison told the Bangor newspaper Channel 5 “is the channel of the household. We watch it every day, multiple times a day,” he said. “Many people in the York area commute to Boston. The traffic reports on Channel 5 are essential.” WCVB was also the last Boston channel that could be accessed through Spectrum. Boston channels 4 and 7 have already been discontinued.

WMUR in Manchester, N.H. is gone for many New England Spectrum subscribers.
After contacting town officials, who hold the franchise agreement with Spectrum until it expires in 2022, Morrison learned a powerful lesson about deregulation. When a cable company lacks competition or regulation, it can do pretty much what it wants.
York town manager Steve Burns says his hands are tied, noting that Spectrum’s franchise agreement is written to automatically renew (for their convenience) unless the town wants to attempt to renegotiate.
“But negotiate how?” Burns asked. “Comcast is not going to come in and compete with Spectrum. They divvy up the territory. And there’s no one else.”
Spectrum has also made sure that Burns’ phone is among those that rings first when a customer has a complaint, noting Spectrum prints his name and number on each subscriber’s bill, listing him as the “franchise administrator” for the town.
“But it doesn’t mean anything,” Burns told the newspaper. “We have no authority. They decide the programming and the fees. I don’t think we’re important to them.”
So far, all Spectrum has been willing to do is mail out a channel request form to residents who complain, but there is scant evidence the cable company will restore the Boston station, because it has refused other similar requests from subscribers across the country.
For customers in the Berkshires in western Massachusetts, they know only too well how responsive Spectrum is to channel requests. When Spectrum took over Time Warner Cable, local subscribers lost access to several stations (most recently WCVB as well), forcing some to watch local news from stations either in Albany, N.Y., or Springfield, Mass. At the same time, customers were notified Spectrum was increasing its Broadcast TV surcharge, for fewer channels.
Spectrum did not offer any significant response to U.S. Sens. Ed Markey and Elizabeth Warren, or Congressman Richard Neal when they contacted Charter Communications to complain. In Maine, it is the same story for Sens. Angus King and Susan Collins, as well as Rep. Chellie Pingree.
 Charter Communications today launched Spectrum Mobile, a new no-contract mobile phone service for existing Spectrum internet customers offering two simplified plans, including a “pay per gigabyte” plan that will allow customers to get unlimited calling, texting and 1 GB of data for $14 a month.
Charter Communications today launched Spectrum Mobile, a new no-contract mobile phone service for existing Spectrum internet customers offering two simplified plans, including a “pay per gigabyte” plan that will allow customers to get unlimited calling, texting and 1 GB of data for $14 a month.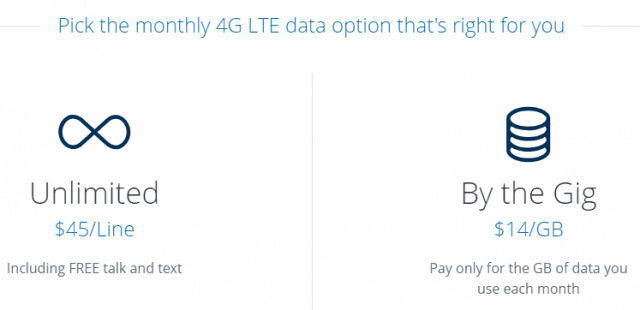


 Subscribe
Subscribe Two weeks ago, New York State’s telecommunications regulator gave Charter Communications 14 days to fully and unconditionally agree to the terms and condition of the 2016 Merger Order that granted the cable company permission to acquire Time Warner Cable. On the last day, hours before the deadline expired, Charter agreed, sort of.
Two weeks ago, New York State’s telecommunications regulator gave Charter Communications 14 days to fully and unconditionally agree to the terms and condition of the 2016 Merger Order that granted the cable company permission to acquire Time Warner Cable. On the last day, hours before the deadline expired, Charter agreed, sort of.
 New York’s top telecommunications regulator has called Charter Communications a purveyor of fake ads, deception, and broken promises and has again called into question how much longer the company should be allowed to do business in New York State.
New York’s top telecommunications regulator has called Charter Communications a purveyor of fake ads, deception, and broken promises and has again called into question how much longer the company should be allowed to do business in New York State.

 According to a PSC investigation and a Public Service Commission order, Spectrum missed its required December 16, 2017 build-out commitment to extend its network to pass additional residences and businesses by 12,245 passings. Spectrum also failed to cure, as required, its earlier failure by March 16, 2018. For these two failures, Spectrum was ordered by the Public Service Commission to forfeit $2 million. These failures came on top of
According to a PSC investigation and a Public Service Commission order, Spectrum missed its required December 16, 2017 build-out commitment to extend its network to pass additional residences and businesses by 12,245 passings. Spectrum also failed to cure, as required, its earlier failure by March 16, 2018. For these two failures, Spectrum was ordered by the Public Service Commission to forfeit $2 million. These failures came on top of