 In 2017, negotiations between the city of McAllen, Tex. and wireless companies over the cost of placing new wireless infrastructure neared agreement at $1,500 per network node, an amount not out of line with the kind of infrastructure fees being charged in other cities where utilities want to place their equipment in the public rights-of-way. But just before contracts were ready to sign, the wireless companies broke off negotiations with city officials and began lobbying for a new Texas state law that would set the terms and conditions for placing telecommunications infrastructure statewide regardless of the wishes of individual Texas towns and cities.
In 2017, negotiations between the city of McAllen, Tex. and wireless companies over the cost of placing new wireless infrastructure neared agreement at $1,500 per network node, an amount not out of line with the kind of infrastructure fees being charged in other cities where utilities want to place their equipment in the public rights-of-way. But just before contracts were ready to sign, the wireless companies broke off negotiations with city officials and began lobbying for a new Texas state law that would set the terms and conditions for placing telecommunications infrastructure statewide regardless of the wishes of individual Texas towns and cities.
SB 1004 was the kind of bill companies like AT&T love. Drafted from talking points supplied by the telecom industry and introduced by a friendly legislator — Republican State Sen. Kelly Hancock, (dubbed “THE WORST” by Texas Monthly magazine) — AT&T and Hancock partnered up to push the legislation through the state legislature, with the help of more than 100 lobbyists working with a budget of $7.8 million, according to a Texas Monitor analysis.
AT&T counts Texas as its corporate home, and company spends lavishly to have its way. It has been the largest lobbying force in the state by far for at least two decades, with 108 registered lobbyists. In second place is TXU Energy Retail, which registered just 29 lobbyists. AT&T offers politicians in the states where it provides local phone service a continuous fountain of campaign contributions. Since 2007, AT&T has spent more than $2.2 million on Texas politicians alone. AT&T donated to 175 of the 181 members of the Texas House and Senate, and its legislative achievements are impressive, winning passage of 14 of the 28 bills the company supported or wrote. Hancock counts AT&T among his top corporate donors, along with the former Time Warner Cable and Comcast.
SB 1004 will cost Texas communities a substantial amount of local control over wireless infrastructure, along with millions of dollars in pole attachment and oversight fees. Hancock, who has no background in telecommunications, arbitrarily set fee caps on wireless facilities at $20 a year for locating equipment on an existing pole and $250 a year if a company attaches equipment on something else. To observers, it isn’t just a bargain for the wireless industry, it could also means some towns and cities could be forced to spend public tax dollars to manage and monitor wireless company infrastructure should something goes awry.
McAllen is among 31 cities in Texas fighting to overturn AT&T’s state law. The city is upset because SB 1004 strips its authority to manage public rights-of-way. By bending over backwards to the wireless industry, companies can put 5G small cells and other equipment just about anywhere with little recourse. In fact, the Texas law mandates companies use pre-existing street signs, traffic garages, and street/traffic lighting as antenna locations wherever possible, which is good news for AT&T but could cause visual pollution and potential safety issues for residents. With below-market attachment fees topping out at just $250, four major national wireless companies can sprout antennas all over town, whether they create eyesores or not.
 Bennett Sandlin, executive director of the Texas Municipal League, called that an “unconstitutionally low amount of money.”
Bennett Sandlin, executive director of the Texas Municipal League, called that an “unconstitutionally low amount of money.”
“It’s mandatory that when private companies want to make a profit using public land that they pay a reasonable rental fee for it,” Sandlin told the Texas Monitor. “Just like if AT&T wanted to run these facilities through our backyard, we wouldn’t let them do it for free.”
Sandlin adds the wireless industry wants to be given special privileges under the guise of expanding internet access in return for getting cheap access to public rights-of-way, but they don’t want to be regulated like a public utility.
If the new law stands, it is estimated that Texas cities will lose up to $800 million a year in revenue from fees — money that will probably be made up by increasing taxes or other fees.
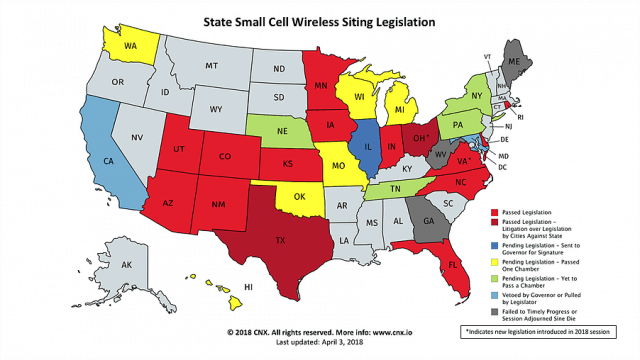
In Tennessee, the state has gone all out to hurry the passage of a similar law in hopes of convincing wireless companies to make the state one of the first targets for 5G expansion.
Sen. Bill Ketron (R-Murfreesboro), believes clearing a path for rapid 5G deployment will attract billions of dollars of new investment in the state.
“It’s going to transform the world as we currently know it. We’re expecting speeds anywhere from 30 to 50 percent faster as far as connectivity is concerned,” Ketron told his colleagues in the Tennessee legislature. “It opens up that bandwidth for all the data, everything that we’re doing from texting to telemedicine to even autonomous vehicles.”
House Bill 2279 and its companion SB 2504 are written almost word for word on the recommendations of AT&T and other wireless lobbyists. Like a Christmas tree decorated with ornaments, all of AT&T’s legislative priorities can be found in both bills, and not by accident. The phone company’s lobbyists have worked hand in hand with other internet providers, lawmakers, and local governments and co-ops to push the bill for rapid passage. After four months, it is nearing the governor’s signature.
The handful of critics, mostly Democrats, have been reduced to offering concern about the bill’s impact on local self-governance. Sen. Lee Harris (D-Shelby County) told colleagues, “I’m inclined to support this bill, but it does give me pause that we would intervene in these negotiations and set a price,” referring to the bill’s capped application fee of $100 per small cell installation, with a $35 annual renewal fee.
Ketron has frequently defended the bill’s cap on fees, which most observers claim are substantially lower than what wireless companies expected to pay, by claiming he wanted to prevent cities and towns from “cashing in on poles because that would be passed on to all the users through their rate fees, and I know my bill is already high enough.”
Sen. Ketron moving HB 2279 forward in the Tennessee legislature on April 11, 2018.
The potential revenue hit to municipalities would normally be enough to rally opposition, but because of AT&T’s lobbying efforts, most cities and counties in Tennessee have remained neutral on the bill, signaling a virtual guarantee it will become law. The company has worked hard to try to reassure communities the new law will be revenue neutral and be sensitive to the aesthetic needs of local communities. The bill promises that in the event a small cell damages or brings down a pole, the owner of the equipment will be responsible to fix the damage or provide an identical replacement light or pole at the company’s expense.
But based on stories from other communities that have gotten small cell technology for existing 4G LTE networks, problems remain. The biggest issue for residents is visual clutter on poles in their front yards. Some companies also install “lawn refrigerator” cabinets that house backup batteries or other equipment to keep small cells operational in the event of a power outage. Residents frequently complain about these unsightly metal boxes that can appear overnight in the public right-of-way, sometimes right in front of their home, with no warning.
Some town engineers also question the safety of some installations, particularly if multiple carriers seek to place equipment on the same poles. Some have expressed concern about what impact the extra equipment might have in a vehicle collision that brings a pole down onto another vehicle. There are also broader implications once a town surrenders authority over its public rights-of-way to state officials.
Ketron’s personal knowledge of 5G technology and his credibility to deliver on the promises and claims he has made to his colleagues is also open to question. During a brief floor session to consider House Bill 2279, Ketron frequently became tongue-twisted explaining the merits of 5G networks, their functionality, and what benefits they will offer rural Tennessee consumers.
In rambling introductory remarks, Ketron claimed, “the connectivity speed through that bandwidth what 5G brings us […] all are going to be communicating through all that bandwidth of that data.” He also promised a colleague in rural Tennessee that 5G service had a real potential to solve the state’s rural broadband problems, despite the fact the technology would be very costly to deploy in rural areas because of required fiber backhaul and the limited range of each small cell.
The Tennessee Electric Cooperative believes 5G deployment will likely stop with the suburbs, unlikely to expand into rural areas because of its limited range.
“Because of this, we don’t anticipate it will ever see widespread use outside of densely populated areas,” Trent Scott, spokesman for the organization told the Memphis Daily News. “The economics of deploying current 5G technology in sparsely populated areas are going to be a challenge.”
But the idea of AT&T and other wireless companies spending billions on new wireless infrastructure in Tennessee attracts political support for the short-term jobs for installers. The future of 5G technology and its use with Tennessee’s smart grid and intelligent transportation projects of the future may explain why the bill has attracted 40 co-sponsors.
But on the local level in communities like McAllen, there is also recognition wireless companies stand to earn tens of billions from the next generation of wireless technology, and they will be able to earn that revenue at a relatively cheap cost if communities surrender their ability to leverage their publicly owned assets like rights of way. McAllen officials hoped to negotiate a new network of public hotspots to help bring internet access to those who cannot afford traditional internet subscriptions. If AT&T agreed, the city was willing to steeply discount their fees. But no companies showed any interest in the idea. With enthusiastic state legislators willing to introduce legislation tailor-made for those companies, they didn’t have to.
The Tennessee legislature debated passage of the state’s 5G-related legislation for just 15 minutes before passing it 32-1. But did members truly understand it? (14:44)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Pierce’s alleged scheme fell apart when Quintillion began invoicing clients based on the fake contracts. At least one protested, claiming it did not use Quintillion’s network. A subsequent internal investigation allegedly founds dozens of phony contracts kept in Pierce’s Google Drive account, with at least 78 moved to the service’s trash bin 48 hours before investigators began searching Pierce’s computer. Prosecutors were able to recover the deleted documents with a search warrant presented to Google.
Pierce’s alleged scheme fell apart when Quintillion began invoicing clients based on the fake contracts. At least one protested, claiming it did not use Quintillion’s network. A subsequent internal investigation allegedly founds dozens of phony contracts kept in Pierce’s Google Drive account, with at least 78 moved to the service’s trash bin 48 hours before investigators began searching Pierce’s computer. Prosecutors were able to recover the deleted documents with a search warrant presented to Google. Charter Communications is taking the city of El Centro, Calif., to federal court for interfering in a dispute between Spectrum and a local TV station owner that has resulted in two stations being blacked out on the local cable system for nearly three months.
Charter Communications is taking the city of El Centro, Calif., to federal court for interfering in a dispute between Spectrum and a local TV station owner that has resulted in two stations being blacked out on the local cable system for nearly three months. “Northwest’s pulling its authorization for Charter to carry its broadcast signals is not a ‘service interruption’ within the meaning of the City Code provisions in question,” Charter argued in its lawsuit. “Even if it were, while El Centro demands that Charter ‘cure’ its alleged violations, the only means for Charter to do so is to finalize a retransmission agreement with Northwest. The City’s citations are thus intended to pressure Charter to accept Northwest’s unreasonable terms by imposing fines and intentionally damaging Charter’s reputation and harming its goodwill and relationships with its existing and prospective customers.”
“Northwest’s pulling its authorization for Charter to carry its broadcast signals is not a ‘service interruption’ within the meaning of the City Code provisions in question,” Charter argued in its lawsuit. “Even if it were, while El Centro demands that Charter ‘cure’ its alleged violations, the only means for Charter to do so is to finalize a retransmission agreement with Northwest. The City’s citations are thus intended to pressure Charter to accept Northwest’s unreasonable terms by imposing fines and intentionally damaging Charter’s reputation and harming its goodwill and relationships with its existing and prospective customers.” “Rather than negotiating in good faith like all other parties would do and what the law requires, Charter has taken a ‘take it or leave it’ approach,” added Brady. “In an effort this week to get this back on track, Northwest submitted a new proposal to Spectrum. Spectrum’s representative communicated that they really wanted to get this resolved, but would not counter Northwest’s proposal and would not respond at all in writing. Odd behavior for a company that claims to be negotiating in good faith. It appears that Charter would rather bully a small municipality than to engage in a good faith negotiation.”
“Rather than negotiating in good faith like all other parties would do and what the law requires, Charter has taken a ‘take it or leave it’ approach,” added Brady. “In an effort this week to get this back on track, Northwest submitted a new proposal to Spectrum. Spectrum’s representative communicated that they really wanted to get this resolved, but would not counter Northwest’s proposal and would not respond at all in writing. Odd behavior for a company that claims to be negotiating in good faith. It appears that Charter would rather bully a small municipality than to engage in a good faith negotiation.” “Despite the fact the fee is itemized and justified as a pass-through, Charter did not eliminate or reduce that fee, even though it was no longer incurring costs associated with carriage of … at least two network affiliates,” Crescent City officials told the FCC.
“Despite the fact the fee is itemized and justified as a pass-through, Charter did not eliminate or reduce that fee, even though it was no longer incurring costs associated with carriage of … at least two network affiliates,” Crescent City officials told the FCC.

 The loss was devastating to residents, especially at the nursing home.
The loss was devastating to residents, especially at the nursing home.
 Of the 64 properties he manages, Scally told Habitat fewer than a dozen have signed up for a bulk rate, and those deals were signed years ago.
Of the 64 properties he manages, Scally told Habitat fewer than a dozen have signed up for a bulk rate, and those deals were signed years ago.
 Spectrum ignores her complaints, she claims, transferring her from call center to call center in search of a solution. She finally took her complaint to the FCC, something she does not think should be required after paying the company $1,600 a month for cable television.
Spectrum ignores her complaints, she claims, transferring her from call center to call center in search of a solution. She finally took her complaint to the FCC, something she does not think should be required after paying the company $1,600 a month for cable television. Nathan Gray woke up one morning this month and received an alarming notification from Comcast, his internet provider, claiming he had exceeded his Comcast
Nathan Gray woke up one morning this month and received an alarming notification from Comcast, his internet provider, claiming he had exceeded his Comcast  “Today when I logged in, I had apparently used 196 GB yesterday,” Amaasing wrote. “196 GB in 24 hours? Seriously?”
“Today when I logged in, I had apparently used 196 GB yesterday,” Amaasing wrote. “196 GB in 24 hours? Seriously?”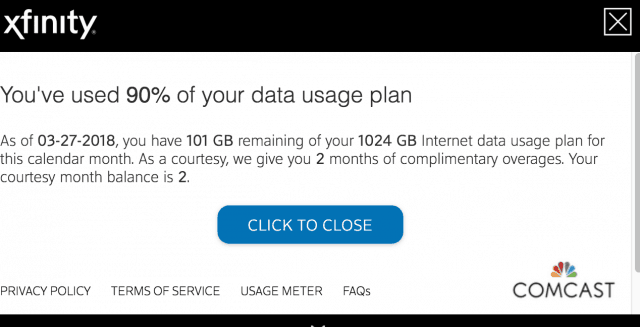 After “courtesy months” expire, you are on the hook for whatever excess usage Comcast determines you have consumed. Some Comcast customers assume the courtesy month counter resets each calendar year, but in fact it only resets after 12 consecutive months of staying within your allowance limit.
After “courtesy months” expire, you are on the hook for whatever excess usage Comcast determines you have consumed. Some Comcast customers assume the courtesy month counter resets each calendar year, but in fact it only resets after 12 consecutive months of staying within your allowance limit.