
The Unimax U683CL
An inexpensive $39 Chinese-made smartphone offered by a U.S. government-subsidized Lifeline mobile phone service provider is wide open to malware and trojan horse apps, leaving users exposed to privacy violations, adware, and auto-installed backdoor apps that might expose some to fraud.
Malwarebytes Labs, an online security company, issued a serious warning to the public about the Unimax U683CL smartphone’s compromised-from-the-box status, and criticized provider Assurance Wireless for selling the phone and ignoring repeated warnings sent to the company about the phone.
“Assurance Wireless by Virgin Mobile offers the UMX U683CL phone as their most budget conscious option. At only $35 [$39 as of Jan. 13, 2020] under the government-funded program, it’s an attractive offering,” Nathan Collier, a senior malware intelligence analyst at Malwarebytes Labs writes in a company blog. “However, what it comes installed with is appalling.”
Malwarebytes began getting complaints about the phone last fall, and secured one to investigate further. It quickly emerged the phone arrived with questionable software pre-installed:
The first questionable app found on the UMX U683CL poses as an updater named Wireless Update. Yes, it is capable of updating the mobile device. In fact, it’s the only way to update the mobile device’s operating system (OS). Conversely, it is also capable of auto-installing apps without user consent.
Thus, we detect this app as Android/PUP.Riskware.Autoins.Fota.fbcvd, a detection name that should sound familiar to Malwarebytes for Android customers. That’s because the app is actually a variant of Adups, a China-based company caught collecting user data, creating backdoors for mobile devices and, yes, developing auto-installers.
From the moment you log into the mobile device, Wireless Update starts auto-installing apps. To repeat: There is no user consent collected to do so, no buttons to click to accept the installs, it just installs apps on its own. While the apps it installs are initially clean and free of malware, it’s important to note that these apps are added to the device with zero notification or permission required from the user. This opens the potential for malware to unknowingly be installed in a future update to any of the apps added by Wireless Update at any time.
The second piece of unremovable malware is the UMX’s own “Settings” app, crucial to operating the phone. Researchers called this “heavily-obfuscated malware” that is detected as Android/Trojan.Dropper.Agent.UMX. This app quietly downloads and installs apps without the user’s permission, most recently including a variant of HiddenAds, which forces users to endure frequent advertising screens on their phone, even when not web browsing.
 The malware activates the moment a user powers on their phone for the first time. Most customers will simply be annoyed if ad-related apps automatically install, but with a security-compromised phone opening the door to more malware in the future, this “lowers the bar on bad behavior by app development companies,” according to Collier.
The malware activates the moment a user powers on their phone for the first time. Most customers will simply be annoyed if ad-related apps automatically install, but with a security-compromised phone opening the door to more malware in the future, this “lowers the bar on bad behavior by app development companies,” according to Collier.
“Budget should not dictate whether a user can remain safe on his or her mobile device. Shell out thousands for an iPhone, and escape pre-installed maliciousness. But use government-assisted funding to purchase a device and pay the price in malware? That’s not the type of malware-free existence we envision at Malwarebytes,” Collier said.
“We informed Assurance Wireless of our findings and asked them point blank why a U.S.-funded mobile carrier is selling a mobile device infected with pre-installed malware? After giving them adequate time to respond, we unfortunately never heard back,” Collier added.
![]() Spectrum Mobile customers enrolled in an unlimited data plan will get free access to Verizon’s millimeter wave 5G network, if they own a device that supports 5G service.
Spectrum Mobile customers enrolled in an unlimited data plan will get free access to Verizon’s millimeter wave 5G network, if they own a device that supports 5G service.


 Subscribe
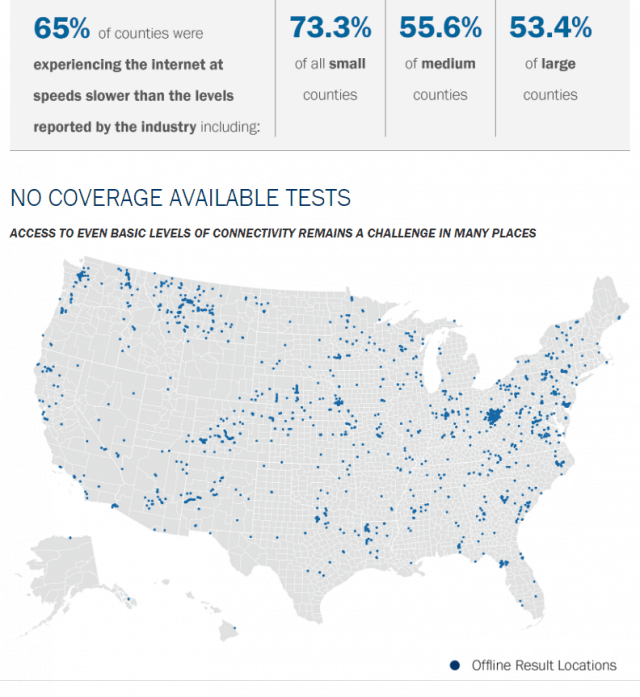
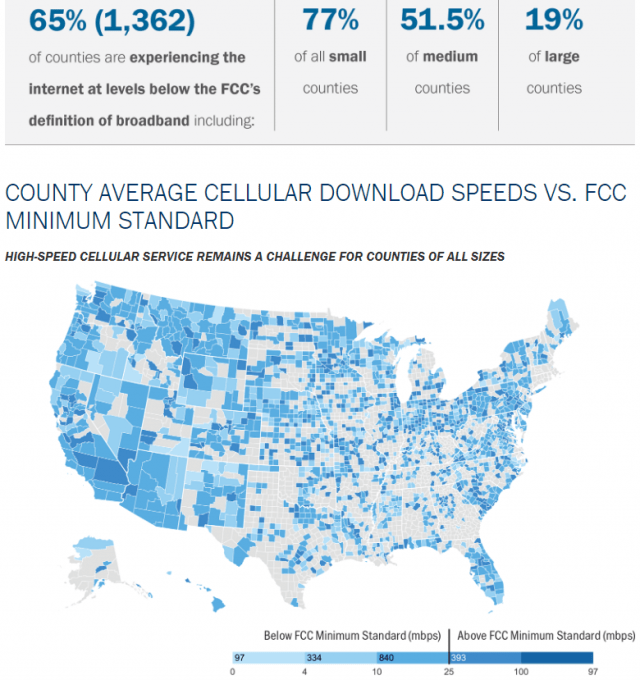
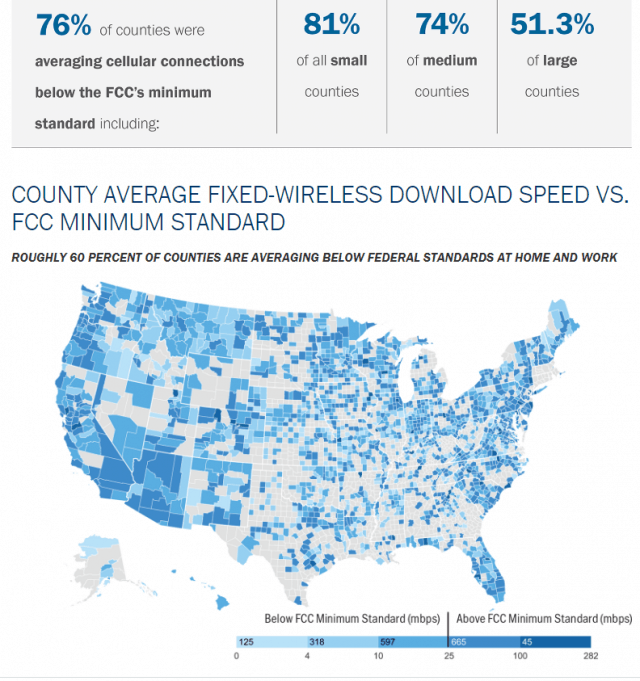
Subscribe Nearly two-thirds of counties in the United States have real world wireless download speeds below the Federal Communications Commission’s minimum to be considered broadband — 25 Mbps. In rural counties, the number is even higher: 77% cannot get reliable speed at or above 25 Mbps.
Nearly two-thirds of counties in the United States have real world wireless download speeds below the Federal Communications Commission’s minimum to be considered broadband — 25 Mbps. In rural counties, the number is even higher: 77% cannot get reliable speed at or above 25 Mbps.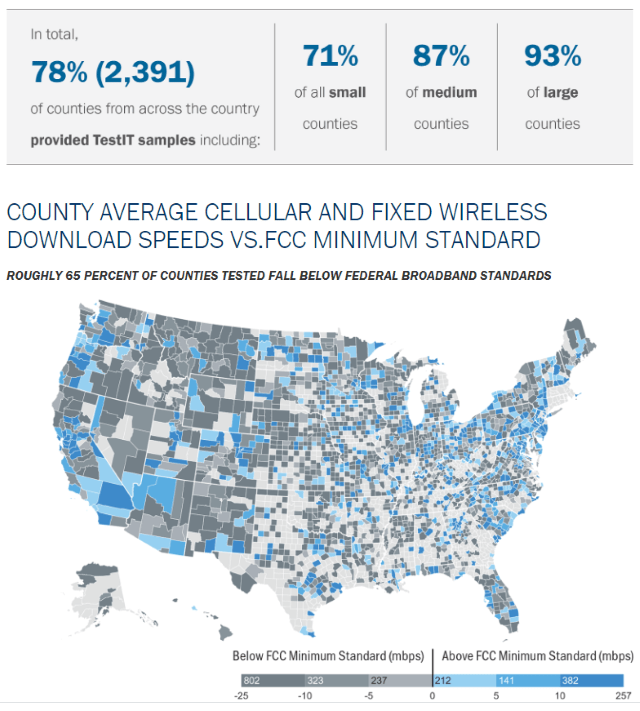

 The malware activates the moment a user powers on their phone for the first time. Most customers will simply be annoyed if ad-related apps automatically install, but with a security-compromised phone opening the door to more malware in the future, this “lowers the bar on bad behavior by app development companies,” according to Collier.
The malware activates the moment a user powers on their phone for the first time. Most customers will simply be annoyed if ad-related apps automatically install, but with a security-compromised phone opening the door to more malware in the future, this “lowers the bar on bad behavior by app development companies,” according to Collier.
 “It’s very much a mobility strategy, with a secondary product of Home [5G], rather than us changing our overarching mobility deployment to try to accelerate Home at the expense of the overall 130 million customer base,” Dunne explained.
“It’s very much a mobility strategy, with a secondary product of Home [5G], rather than us changing our overarching mobility deployment to try to accelerate Home at the expense of the overall 130 million customer base,” Dunne explained. More than 121,000 homes and businesses in 17 states will receive subsidized satellite internet service from Viasat, after the Federal Communications Commission
More than 121,000 homes and businesses in 17 states will receive subsidized satellite internet service from Viasat, after the Federal Communications Commission 