AT&T, Comcast, Verizon, Time Warner Cable and the cable industry’s chief lobbying group spent $42.8 million during the 2013-2014 election cycle to weigh in on issues including burying Net Neutrality, outlawing community broadband competition, winning tax breaks for themselves, and avoiding consumer protection regulations.
A Common Cause analysis of data from the Center for Responsive Politics and the Institute for Money in State Politics shows that the usual suspects poured money into political coffers on the state and federal level to influence lawmakers.
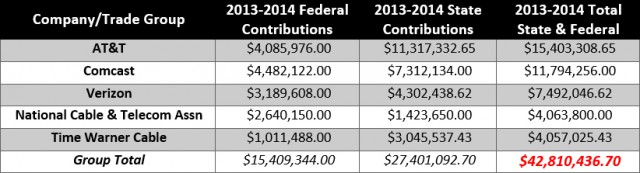
On the federal level, murky party committees received the largest individual checks: a total of $862,223 for House and Senate Republicans and $552,605 for Democrats. Individual members of Congress also received their own contributions, including Republican House Speaker John Boehner ($98,175 from Comcast) and Democratic Senator Mark Pryor ($88,650 from Comcast, TWC, and National Cable and Telecom. Assn.) Pryor will need to spend his contributions quickly. He was de-elected by Arkansas voters last Tuesday.
Net Neutrality is a major topic on the minds of the cable and telco companies, as is ongoing deregulation and decommissioning rural landline service, and pushback on revelations AT&T and Verizon were only too happy to turn over your phone records to the federal government.
In the states, the bigger the issues coming up in the legislature, the bigger the campaign checks. In Florida, AT&T is the state’s single largest source of political donations, giving $1.53 million to state lawmakers in the past year and another $660,000 to Gov. Rick Scott (R) and his appointed heads of state agencies. AT&T is lobbying for eliminating Florida’s telecommunications tax, win the right to place cell towers wherever they wish without much interference from local officials, and further deregulation. Most of AT&T’s money goes into the hands of the state’s Republicans.
In New York and California, Democrats got a major chunk of money from Comcast and Time Warner Cable — New York Governor Andrew Cuomo received $60,800 each from both Comcast and Time Warner Cable (totaling $121,600). California Governor Jerry Brown received $54,400 from Time Warner Cable and $27,200 from Comcast. Both states are reviewing the merger of the two companies this year. AT&T and Verizon are also major donors – AT&T wants to dismantle the rural telephone network in California and Verizon is trying to convince the New York legislature to approve its own rural landline replacement – Voice Link. It also wants reduced scrutiny of its landline performance in New York and more access to New York City buildings where it faces resistance from property owners who want compensation from Verizon to install FiOS.


 Subscribe
Subscribe T-Mobile has asked the Federal Communications Commission to investigate AT&T’s “artificially high roaming rates” charged when its customers travel outside of T-Mobile’s home service area.
T-Mobile has asked the Federal Communications Commission to investigate AT&T’s “artificially high roaming rates” charged when its customers travel outside of T-Mobile’s home service area. Because of AT&T’s artificially high roaming rates, T-Mobile wireless customers roaming in South Africa have a better user experience than customers roaming on AT&T’s network in South Dakota, argues T-Mobile. Their speed is twice as fast, and their data usage is unlimited.
Because of AT&T’s artificially high roaming rates, T-Mobile wireless customers roaming in South Africa have a better user experience than customers roaming on AT&T’s network in South Dakota, argues T-Mobile. Their speed is twice as fast, and their data usage is unlimited.





 Comcast: 88% of customers met or exceeded state and federal standards;
Comcast: 88% of customers met or exceeded state and federal standards;
 But some critics contend $664 million is insufficient to wire every building in Ireland for fiber service and suspect the government may try to backtrack and choose fiber to the cabinet or wireless service for the most isolated communities that could prove extremely expensive to reach with fiber.
But some critics contend $664 million is insufficient to wire every building in Ireland for fiber service and suspect the government may try to backtrack and choose fiber to the cabinet or wireless service for the most isolated communities that could prove extremely expensive to reach with fiber.