A bipartisan group of senators from some of America’s most rural and broadband-challenged states blasted the mapping skills of the Federal Communications Commission in a hearing Tuesday.
The senators were upset because the FCC’s Universal Service Fund will pay subsidies to extend wireless connectivity only in areas deemed to have inadequate or non-existent coverage. The FCC’s latest wireless coverage map is the determining factor whether communities get subsidies to expand service or not, and many in attendance at the Communications, Technology, Innovation, and the Internet subcommittee hearing quickly called it worthless.
Sen. Jerry Moran (R-Kan.) said the map’s “value is nil,” quickly followed by the Subcommittee chair Sen. Roger Wicker (R-Miss.) who added, “we might as well say it, Mr. Moran, that map is utterly worthless of giving us good information.”
“The simple answer is: it’s garbage in, garbage out,” said Steve Berry, CEO of the Competitive Carriers Association, which counts several small, rural cell phone companies as members.
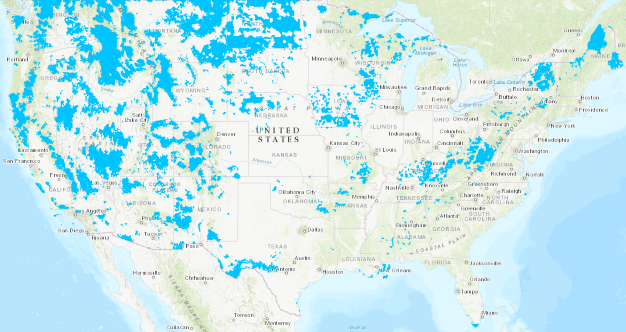
This FCC map shows (in blue) areas identified as eligible to receive wireless subsidies to expand service where little or none exists today. (click map to expand)
The latest version of the map was heralded by the FCC as a significant improvement over the 2012 map used during the first round of funding. But critics like Berry claimed the map still relies entirely on carrier-provided data, much of it based on network capacity, and there is an incentive for existing wireless carriers to overestimate coverage because it assures funds won’t be given to potential competitors to strengthen their cellular networks.
The FCC claimed it gave carriers new benchmarks to meet in its latest map, including a request to only identify an area as covered if it achieves 80% certainty of coverage at 4G LTE speeds of 5 Mbps or more. To identify underserved zones, the FCC asked carriers not to identify areas that passed the first test as served if cell towers in that zone exceeded 30% of capacity. But Berry noted the FCC did not include a signal strength component, which means a carrier could report a significant area as getting adequate coverage based on the capacity of their network in a strong reception zone, even if customers nearby reported ‘no bars’ of signal strength or coverage that dropped completely once indoors.
Sen. Wicker
Senators from Kansas, New Hampshire and Mississippi were astonished to see maps that claimed virtually 100% of all three states were fully covered with mobile broadband service. The senators rejected that assertion.
Sen. Maggie Hassan (D-N.H.) has devoted a section on her website to collecting reports from New Hampshire residents getting poor cell phone reception, and she has been a frequent critic of the FCC’s coverage maps which she has repeatedly called inaccurate.
In northern Mississippi, wireless coverage is so poor the Mississippi Public Service Commission launched an initiative to collect real-world data about reception through its “Zap the Gap” initiative. But the FCC’s latest map suggests the problem is solved in the most signal-challenged areas in the northern part of the state, with the exception of small pockets in the Holly Springs National Forest, the Enid Lake area, areas east of Coffeeville, parts of Belmont, and areas east of Smithville.
The four major national wireless carriers suggest there is no problem with wireless coverage in Mississippi either. AT&T claims to reach 98% of the state, Verizon Wireless 96.43%, T-Mobile 66.36%, and Sprint 30.92%. Regional carrier C Spire claims 4G LTE coverage that falls somewhere between T-Mobile and AT&T in reach.
Sen. Jon Tester (D-Mont.) told the subcommittee in his state, the FCC’s maps have little resemblance to reality, showing 4G LTE speeds in areas where no cellular reception exists at all.
“The FCC is wrong, they screwed up, we’re getting screwed because they screwed up, so how do we fix it?” Tester asked. “There has got to be a way to get the FCC’s attention on this issue. We’ve got to do better, folks, it’s not working.”

Mississippi’s program to report cellular coverage gaps.
Independent cell phone companies that specialize in serving areas the larger carriers ignore are hamstrung by the FCC and its maps, according to Mike Romano, senior vice president for policy for NTCA – The Rural Broadband Association — a trade group and lobbyist for smaller rural providers. Romano told the subcommittee if any cellular company reports coverage to even one household in a census block (which can cover a large geographic area in rural states), that entire block is ineligible for Connect America Fund subsidies.
The FCC, rural carriers complain, is relying on small wireless companies to serve as the map’s fact checkers and forces them to start a costly challenge procedure if they want to present evidence showing the map is wrong. Such proceedings are expensive and time-consuming, they argue. Even if successfully challenged, that does not win the companies a subsidy. It only opens the door to a competitive bidding process where challengers could face competing bids from larger companies that made no effort to challenge the map data.
A group of senators signed a joint letter to FCC Chairman Ajit Pai complaining about the accuracy issues surrounding the FCC’s wireless map:


 Subscribe
Subscribe The Chair of the New York State Public Service Commission announced today that the Commission is
The Chair of the New York State Public Service Commission announced today that the Commission is  In two instances, the staff found Charter was claiming new service expansion in buildings clearly already covered by the city’s existing franchise agreement.
In two instances, the staff found Charter was claiming new service expansion in buildings clearly already covered by the city’s existing franchise agreement.



 “I shouldn’t have been surprised to learn industry completely re-wrote proposed broadband legislation to their favor as a ‘substitute bill’ in legislative committee today,” Orr wrote on her Facebook page on Feb. 19. “The substitute bill is substantially different than the original bill. And it wasn’t posted online or anywhere for anyone except insiders to have access to. CenturyLink and Spectrum are bullies. It’s wrong, and they are hurting Cheyenne and other Wyoming communities from gaining affordable access.”
“I shouldn’t have been surprised to learn industry completely re-wrote proposed broadband legislation to their favor as a ‘substitute bill’ in legislative committee today,” Orr wrote on her Facebook page on Feb. 19. “The substitute bill is substantially different than the original bill. And it wasn’t posted online or anywhere for anyone except insiders to have access to. CenturyLink and Spectrum are bullies. It’s wrong, and they are hurting Cheyenne and other Wyoming communities from gaining affordable access.” Despite the massive amount of extra money from the Trump Administration’s corporate tax cuts generating huge revenue spikes for America’s telecom companies, Frontier Communications disappointed investors with today’s news it was
Despite the massive amount of extra money from the Trump Administration’s corporate tax cuts generating huge revenue spikes for America’s telecom companies, Frontier Communications disappointed investors with today’s news it was 