North America’s broadband rankings continue to take a beating at the expense of countries deploying fiber optic broadband. While the United States and Canada cope with aging landline technology and an uncompetitive marketplace that tells consumers they don’t need fiber-fast broadband speed, countries like Bulgaria, Lithuania and Estonia are lighting up 50-100Mbps networks that often charge lower prices than North Americans pay for 1-3Mbps DSL.
North America’s broadband rankings continue to take a beating at the expense of countries deploying fiber optic broadband. While the United States and Canada cope with aging landline technology and an uncompetitive marketplace that tells consumers they don’t need fiber-fast broadband speed, countries like Bulgaria, Lithuania and Estonia are lighting up 50-100Mbps networks that often charge lower prices than North Americans pay for 1-3Mbps DSL.
Ookla, a global leader in broadband testing and web-based network diagnostic applications, reports that the best performing broadband networks for speed, value, and performance are increasingly in Europe and Asia. While both the United States and Canada used to be among the world leaders in broadband infrastructure, that is no longer true.
Some examples:
- The United States now scores 31st in average download speed, Canada is 33rd;
- In upload speed, America now ranks 37th, Canada a woeful 69th;
- Ookla’s Household Quality Index, which ranks packet loss and general reliability of home connections found Canada scoring 27th place, the United States 38th;
- At a cost per megabit, neither the US or Canada offers very good value. The USA ranked 29th ($4.95 per megabit), Canada 33rd ($5.85 per megabit);
- Neither country does a great job delivering the speeds and service promised either. The USA ranked 25th, Canada 32nd.
Ookla found that while speeds are rising in North America, they are not increasing nearly as fast as in other, higher-ranked countries. Most of the speed gains in North America come from cable or limited fiber-broadband deployments like Verizon FiOS or community-owned fiber to the home networks. Wireline ADSL service, which represented a larger proportion of home Internet connections in 2008, continues to lose ground to faster options from cable companies, community-owned broadband, and phone company fiber upgrades. In eastern Europe, the Baltics, Russia and Ukraine, many of the dramatic boosts in broadband speed and quality come as a result of national fiber network upgrade projects.
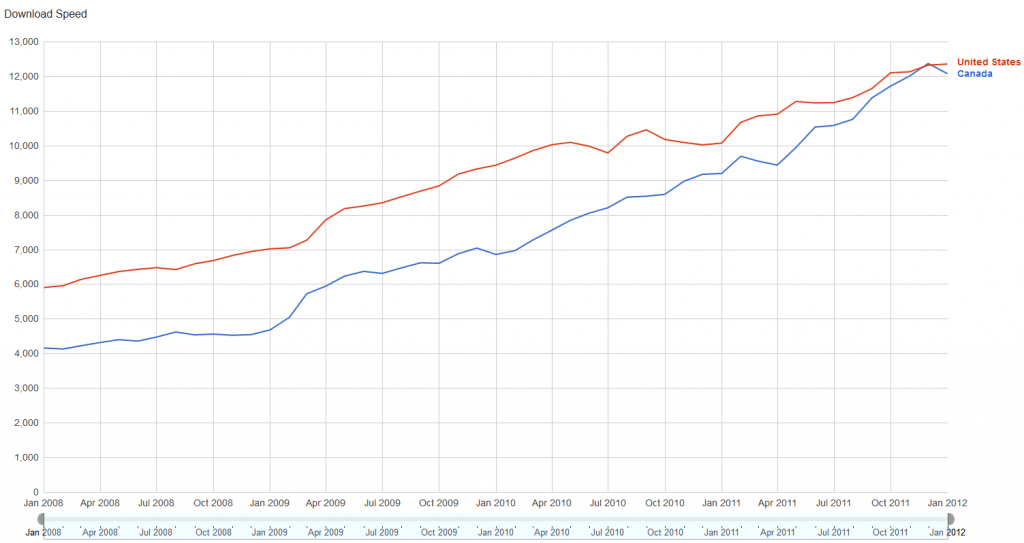
While speeds in North America are gradually increasing, both the U.S. and Canada are being outpaced by many countries in Europe and Asia.
While providers in the United States and Canada often dismiss fiber as too costly, Ookla found fiber-based networks delivering some of the world’s best values in broadband.
For example, on a cost-per-megabit basis, Bulgaria’s new fiber networks deliver the world’s cheapest Internet service, at an average of just $0.64 per megabit. The average broadband speeds in the country are now higher than 21/11Mbps.

Elion headquarters in Tallinn. Elion delivers fiber broadband to homes across Estonia.
Contrast that with average speeds in the United States (12.41/2.97Mbps) and Canada (11.95/1.70Mbps). Other top scoring countries for cost-per-megabit include:
-
Romania $0.97 USD
-
-
-
Republic of Moldova $1.41 USD
-
-
-
-
-
In terms of download speed, Estonia’s investment in a national fiber network is now paying dividends, with a dramatic increase in national average broadband speeds to 50/28Mbps. As new cities join Estonia’s fiber network, speeds take a dramatic upswing. Contrast average speeds in Saue (101.03Mbps), Viimsi (98.98Mbps), Tallinn (69.80Mbps), and Võru (65.58Mbps) with ADSL-rich Pärnu (12.55Mbps), Paide (12.40Mbps), Rapla (8.93Mbps), and Valga (7.71Mbps).
It is much the same story in other fiber-rich countries, where broadband speeds far exceed the averages in the United States and Canada:

Look what happens to Estonia's broadband speed rankings when it switched on its national fiber broadband network.
- Lithuania 31.65 Mbps
- South Korea 31.44 Mbps
- Latvia 25.42 Mbps
- Sweden 24.62 Mbps
- Romania 24.47 Mbps
- Netherlands 24.36 Mbps
- Singapore 22.94 Mbps
- Bulgaria 21.12 Mbps
- Iceland 20.53 Mbps
Despite all of the bad news, the cable industry’s trade publication Multichannel News tried to find victory in the jaws of defeat, noting things could be worse… if they ran traditional phone companies.
Cable operators delivered the fastest average broadband download speeds in 2011 — with major MSOs easily blasting by rival telco and satellite Internet services — according to data from independent testing firm Ookla.
For the full year, the six fastest residential Internet service providers in the U.S. based on average download speed were Comcast, Charter Communications, Cablevision Systems, Time Warner Cable and Insight Communications.
[…] Comcast and Charter delivered average download speeds of 17.19 Megabits per second, followed by Cablevision at 16.40 Mbps, Cox at 15.76 Mbps, TWC at 14.41 Mbps and Insight at 14.22 Mbps.
Verizon Communications fared better than its telco peers with an average download speed of 12.94 Mbps, thanks to FiOS Internet, its fiber-to-the-home service that provides up to 150 Mbps downstream. And overall, Verizon had the highest upstream speeds with an average of 7.41 Mbps. Still, the company’s legacy DSL services dragged down overall speeds.
Behind DSL were woefully slower speeds from the nation’s wireless ISPs (which include 3G broadband from large companies like Verizon Wireless and AT&T), and perennially last place satellite Internet.

Moffett
Despite repeated claims by providers that consumers don’t need fiber-fast broadband speeds, industry analyst Craig Moffett at Sanford Bernstein tells a different story:
“Technology adoption is creating a feedback loop that increasingly favors cable’s physical infrastructure,” Moffett wrote in a research note last month. “As more people are served by higher-speed connections, more and more applications are evolving to take advantage of them. Customers with lower-speed connections are increasingly being forced to upgrade to higher speed connections… or be left behind.”
The conclusion reached by Multichannel News columnist Todd Spangler:
“The relative broadband speeds of cable vs. telco isn’t merely an academic curiosity: Major providers are increasingly touting Internet performance in their marketing as they fight for consumers’ dollars.”
Unfortunately for the cable industry, although DOCSIS 3 upgrades have afforded dramatic increases in broadband download speeds, upload speeds lag behind. Fiber to the home networks are best positioned to achieve victory in the global broadband race. That is important not only because it delivers consumer dollars to the best provider in town, but fuels the further development of the digital, knowledge-based economy North America increasingly seeks to lead.



 Subscribe
Subscribe