
Rep. Rocky Miller (R-Lake Ozark)
A Missouri state representative with a track record of supporting AT&T and other telecommunications companies has introduced a bill that would effectively prohibit community broadband competition in a bid to protect incumbent phone and cable companies.
Rep. Rocky Miller’s (R-Lake Ozark) House Bill 437 would strictly prohibit the construction of public broadband networks in any part of Missouri served by a private provider, regardless of the quality of service available or its cost, without a referendum that includes a mandated question observers consider slanted in favor of existing providers.
HB437 would banish community broadband networks as early as September unless services were already up and running. The bill would effectively stop any public broadband network intending to compete against an existing phone or cable company within the boundaries of a city, town, or village offering any level of broadband service. It would also require communities to schedule a referendum on any project budgeted above $100,000, and includes ballot language that implies public broadband projects would duplicate existing services, even if a private provider offers substantially slower broadband at a considerably higher price. (Emphasis below is ours):
“Shall [Anytown] offer [broadband], despite such service being currently offered within Anytown by x private businesses at an estimated cost of (insert cost estimate) to Anytown over the following five-year period?”
Miller’s proposal would also require voters to approve a specific and detailed “revenue stream” for public broadband projects and if the referendum fails to garner majority support, would prohibit the idea from coming up for a second vote until after two years have passed, allowing cable and phone companies to plan future countermeasures.
 The proposed bill also carefully protects existing providers from pressure to upgrade their networks.
The proposed bill also carefully protects existing providers from pressure to upgrade their networks.
Miller’s bill defines “substantially similar” in a way that would treat DSL service as functionally equivalent to gigabit broadband as both could be “used for the same purpose as the good or service it is being compared to, irrespective of how the good or service is delivered.”
In other words, if you can reach Rep. Miller’s campaign website on a CenturyLink 1.5Mbps DSL connection and over a co-op gigabit fiber to the home connection, that means they are functionally equivalent in the eyes of Miller’s bill. Residents voting in a referendum would be asked if it is worthwhile constructing fiber to the home service when CenturyLink is offering substantially similar DSL.
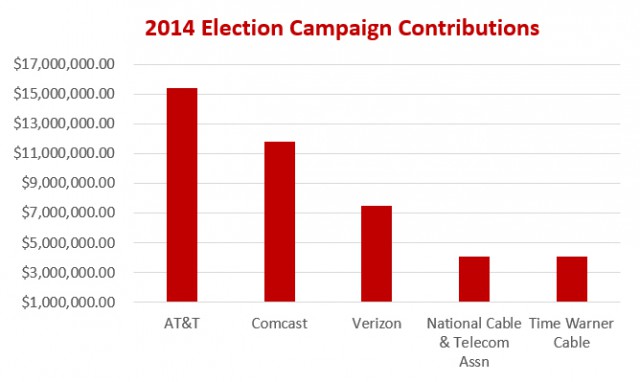
Among the telecom companies that had no trouble connecting to Rep. Miller to hand him campaign contributions: AT&T, CenturyLink, Comcast, and Charter Communications
The Coalition for Local Internet Choice was unhappy to see yet another state bill introduced designed to limit competition and take away the right of local communities to plan their own broadband future.
“The state of Missouri is the latest legislature to attempt to erect barriers to the deployment of broadband networks that are critical to the future of its local economies and the nation, via House Bill 437,” said a statement released by the group. “High-bandwidth communications networks are the electricity of the 21st century and no community should be stymied or hampered in its efforts to deploy new future-proof communications infrastructure for its citizens – either by itself or with willing private partners.”
 The group urged the Missouri legislature to reject the bill.
The group urged the Missouri legislature to reject the bill.
In 2013, Miller hit the ground running in his freshman year to achieve his campaign pledge of “getting the government out of the way of economic development.” In the Missouri state legislature, Miller strongly supported AT&T’s other state legislative priority: deregulation of cell tower placement. Miller traveled around Missouri promoting HB650, an AT&T inspired bill that would strip away local oversight powers of cell sites.
The issue became a hot topic, particularly in rural and scenic areas of Missouri, where local officials complained the bill would allow haphazard placement of cell towers within their communities.
“[The] bill inhibits a city’s ability to regulate cell towers as we have in the past,” Osage Beach city attorney Ed Rucker said. “The process we have in place has worked, and has worked well.”
Had HB650 become law, Osage Beach residents would today be surrounded by six new cell towers around the city, with little say in where they ended up. The bill Miller supported would have also eliminated a requirement that providers repair, replace, or remove damaged or abandoned cell towers, potentially leaving local taxpayers to pick up the tab.
Miller claimed the legislation would allow expansion of wireless broadband across rural Missouri and remove objectionable fees. HB650 would limit municipal fees to $500 for co-locating an antenna on a pre-existing tower and $1,500 for an application to build a new tower. Local communities complained those limits were below their costs to research the impact and placement of cell towers.
“That cost is an inhibitor to broadband,” Miller countered. “It’s beginning to look like the fees are an impediment to the expansion of broadband.”
Miller did not mention AT&T’s interest in cell tower expansion is also connected to its plan to retire rural landline service in favor of its wireless network, saving the company billions while earning billions more in new revenue from selling wireless landline replacement service over its more costly wireless network. The cell tower bill was eventually caught up in a legal dispute after a court ruled the broader bill that included the cell tower deregulation language was unconstitutional on a procedural matter.


 Subscribe
Subscribe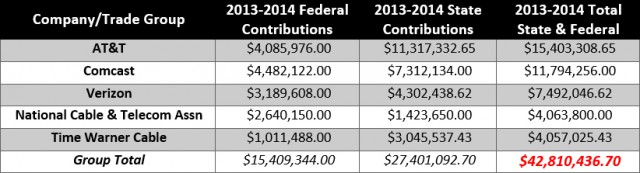


 “Those who advocated the Telecommunications Act of 1996 promised more competition and diversity, but the opposite happened,” said Common Cause president Chellie Pingree back in 1995. “Citizens, excluded from the process when the Act was negotiated in Congress, must have a seat at the table as Congress proposes to revisit this law.”
“Those who advocated the Telecommunications Act of 1996 promised more competition and diversity, but the opposite happened,” said Common Cause president Chellie Pingree back in 1995. “Citizens, excluded from the process when the Act was negotiated in Congress, must have a seat at the table as Congress proposes to revisit this law.”

 Mbps for average households can have a material impact on the economy,” he writes. “A 6Mbps connection could easily support several home users simultaneously shopping on multiple e-commerce sites, downloading iTunes, streaming Spotify, and so on. Do Americans really need gigabit to the home?”
Mbps for average households can have a material impact on the economy,” he writes. “A 6Mbps connection could easily support several home users simultaneously shopping on multiple e-commerce sites, downloading iTunes, streaming Spotify, and so on. Do Americans really need gigabit to the home?” Any digital economy business dependent on fast Internet can see the economics, and often relocate.
Any digital economy business dependent on fast Internet can see the economics, and often relocate.